Abstract
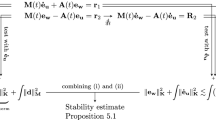
Stability and convergence of full discretizations of various surface evolution equations are studied in this paper. The proposed discretization combines a higher-order evolving-surface finite element method for space discretization with higher-order linearly implicit backward difference formulae for time discretization. The stability of the full discretization is studied in the matrix–vector formulation of the numerical method. The geometry of the problem enters into the bounds of the consistency errors, but does not enter into the proof of stability. Numerical examples illustrate the convergence behaviour of the full discretization.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akrivis, G., Lubich, C.: Fully implicit, linearly implicit and implicit–explicit backward difference formulae for quasi-linear parabolic equations. Numer. Math. 131(4), 713–735 (2015)
Akrivis, G., Li, B., Lubich, C.: Combining maximal regularity and energy estimates for time discretizations of quasilinear parabolic equations. Math. Comput. 86(306), 1527–1552 (2017)
Barrett, J.W., Deckelnick, K., Styles, V.: Numerical analysis for a system coupling curve evolution to reaction diffusion on the curve. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 55(2), 1080–1100 (2017)
Dahlquist, G.: G-stability is equivalent to A-stability. BIT 18, 384–401 (1978)
Demlow, A.: Higher-order finite element methods and pointwise error estimates for elliptic problems on surfaces. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(2), 805–807 (2009)
Dziuk, G.: Finite elements for the Beltrami operator on arbitrary surfaces. In: Partial Differential Equations and Calculus of Variations. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 1357, pp. 142–155. Springer, Berlin (1988)
Dziuk, G., Elliott, C.M.: Finite elements on evolving surfaces. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 27(2), 262–292 (2007)
Dziuk, G., Elliott, C.M.: Fully discrete evolving surface finite element method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(5), 2677–2694 (2012)
Dziuk, G., Elliott, C.M.: \(L^2\)-estimates for the evolving surface finite element method. Math. Comput. 82(281), 1–24 (2013)
Dziuk, G., Lubich, C., Mansour, D.E.: Runge-Kutta time discretization of parabolic differential equations on evolving surfaces. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 32(2), 394–416 (2012)
Gautschi, W.: Numerical Analysis, 1st edn. Birkauser, Boston (1997)
Hairer, E., Wanner, G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations II: Stiff and Differetial-Algebraic Problems, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1996)
Kovács, B.: High-order evolving surface finite element method for parabolic problems on evolving surfaces. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 38(1), 430–459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1093/imanum/drx013
Kovács, B., Li, B., Lubich, C., Power Guerra, C.A.: Convergence of finite elements on an evolving surface driven by diffusion on the surface. Numer. Math. 137(3), 643–689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-017-0888-4
Kovács, B., Power Guerra, C.A.: Error analysis for full discretizations of quasilinear parabolic problems on evolving surfaces. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 32(4), 1200–1231 (2016)
Lubich, C., Mansour, D.E., Venkataraman, C.: Backward difference time discretization of parabolic differential equations on evolving surfaces. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 33(4), 1365–1385 (2013)
Nevanlinna, O., Odeh, F.: Multiplier techniques for linear multistep methods. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 3(4), 377–423 (1981)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, SFB 1173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kovács, B., Lubich, C. Linearly implicit full discretization of surface evolution. Numer. Math. 140, 121–152 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-018-0962-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-018-0962-6