Abstract
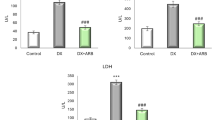
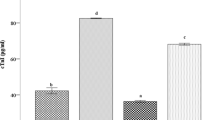
Irinotecan (CPT-11), commonly used in the treatment of many cancer types, may have several side effects that limit the use of CPT-11 in specific tissues such as the heart. In the current study, positive effects of curcumin (CRC) was determined in terms of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties against heart damage, caused by CPT-11, in rats. Rats were divided randomly into four equal groups (Control, CPT-11, CRC, and CPT-11 + CRC). CPT-11 10 mg/kg/day was administered intraperitoneally and CRC 100 mg/kg−1 was given orally. Blood and tissue samples were collected from all groups at day 30 for the detection of oxidative stress, histological changes, and cytokine levels. Results showed that CPT-11 caused dramatic changes in heart tissue for oxidative stress parameters (TBARS, SOD, CAT, GSH, and GPx levels), histological tissue damage, and cytokine levels (TNF and IL-4). CRC therapy reversed the elevated oxidative stress, histological tissue damages, and immunological changes and protected cardiac tissue against CPT-11 toxicity when given together with CPT-11.
In conclusion, CPT-11 caused adverse effects on cytokine levels, histological alterations, and oxidative stress in rats. However, CRC treatment eliminated these toxic effects with its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Thus, these results suggest that CRC may play a protective role against CPT-11 toxicity in heart tissue of rats.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 673–677
Alvarenga EM, Souza LK, Araújo TS, Nogueira KM, Sousa FB, Araújo AR et al (2016) Carvacrol reduces irinotecan-induced intestinal mucositis through inhibition of inflammation and oxidative damage via TRPA1 receptor activation. Chem Biol Interact 260:129–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.11.009
Avci H, Epikmen ET, Ipek E, Tunca R, Birincioglu SS, Akşit H et al (2017) Protective effects of silymarin and curcumin on cyclophosphamide-induced cardiotoxicity. Exp Toxicol Pathol 69(5):317–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2017.02.002
Chen TH, Yang YC, Wang JC, Wang JJ (2013) Curcumin treatment protects against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury-induced cardiac dysfunction and myocardial injury. Transplant Proc 45(10):3546–3549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.09.006
Ciftci O, Tanyildizi S, Godekmerdan A (2010) Protective effect of curcumin on immune system and body weight gain on rats intoxicated with 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 32(1):99–104. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923970903164318
Ciftci O, Ozdemir I, Cakir O, Demir S (2011a) The determination of oxidative damage in heart tissue of rats caused by ruthenium(II) and gold(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes. Toxicol Ind Health 27(8):735–741. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233710395993
Ciftci O, Ozdemir I, Tanyildizi S, Yildiz S, Oguzturk H (2011b) Antioxidative effects of curcumin, β-myrcene and 1,8-cineole against 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced oxidative stress in rats liver. Toxicol Ind Health 27(5):447–453. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233710388452
Ciftci O, Beytur A, Vardi N, Ozdemir I (2012) Evaluation of reproductive toxicity in male rats treated with novel synthesized ruthenium(II) and gold(I)-NHC complexes. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 38(1):40–46. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639045.2011.589853
El Kamouni S, El Kebbaj R, Andreoletti P, El Ktaibi A, Rharrassi I, Essamadi A, El Kebbaj MS, Mandard S, Latruffe N, Vamecq J, Nasser B, Cherkaoui-Malki M (2017) Protective effect of argan and olive oils against LPS-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in mice livers. Int J Mol Sci 18(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102181
Forsgård RA, Korpela R, Holma R, Lindén J, Frias R, Spillmann T, Österlund P (2016) Intestinal permeability to iohexol as an in vivo marker of chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal toxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78(4):863–874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3150-3
Hu ZP, Yang XX, Chan SY, Xu AL, Duan W, Zhu YZ et al (2006) St. John’s wort attenuates irinotecan-induced diarrhea via down-regulation of intestinal pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibition of intestinal epithelial apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 216(2):225–237
Jaiswal SK, Gupta VK, Siddiqi NJ, Sharma B (2017) Curcumin mediated attenuation of carbofuran induced toxicity in the heart of Wistar rats. Cell Mol Biol 63(6):12–17. https://doi.org/10.14715/cmb/2017.63.6.3
Jin M, Park SY, Shen Q, Lai Y, Ou X, Mao Z (2017) Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of curcumin on Pam3CSK4-stimulated microglial cells. Int J Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2017.3217
Khatri A, Gaber MW, Brundage RC, Naimark MD, Hanna SK, Stewart CF (2011) Effect of radiation on the penetration of irinotecan in rat cerebrospinal fluid. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68(3):721–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1542-3
Lam W, Jiang Z, Guan F, Hu R, Liu SH, Chu E et al (2014) The number of intestinal bacteria is not critical for the enhancement of antitumor activity and reduction of intestinal toxicity of irinotecan by the Chinese herbal medicine. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:490. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-490
Li X, Liu X (2005) Effect of curcumin on immune function of mice. J Huazhong Uniiv Sci Technol Med Sci 25:137–140
Li X, Cao T, Ma S, Jing Z, Bi Y, Zhou J et al (2017) Curcumin ameliorates cardiac dysfunction induced by mechanical trauma. Eur J Pharmacol 814:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.07.048
Liu YQ, Li WQ, Morris-Natschke SL, Qian K, Yang L, Zhu GX et al (2015) Perspectives on biologically active camptothecin derivatives. Med Res Rev 35(4):753–789. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21342
Liu H, Wang C, Qiao Z, Xu Y (2017) Protective effect of curcumin against myocardium injury in ischemia reperfusion rats. Pharm Biol 55(1):1144–1148. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2016.121474
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Osawa T (2007) Nephroprotective and hepatoprotective effects of curcuminoids. Adv Exp Med Biol 595:407–423
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Parthasarathy N, Manickam R (2011) Effect of kaempferol on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine induced colorectal carcinoma in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 654:1:75–79
Rtibi K, Selmi S, Grami D, Sebai H, Amri M, Marzouki L (2017) Irinotecan chemotherapy-induced intestinal oxidative stress: underlying causes of disturbed mucosal water and electrolyte transport. Pathophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathophys.2017.07.002
Sadzuka Y, Hirota S (1997) Effect of CPT-11 on lipid peroxide level in mouse tissues. Jpn J Cancer Res 88(5):512–516
Saral S, Ozcelik E, Cetin A, Saral O, Basak N, Aydın M, Ciftci O (2016) Protective role of Diospyros lotus on cisplatin-induced changes in sperm characteristics, testicular damage and oxidative stress in rats. Andrologia 48(3):308–317. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12448 Epub 2015 Jul 14
Satouchi M, Kotani Y, Shibata T, Ando M, Nakagawa K, Yamamoto N et al (2014) Phase III study comparing amrubicin plus cisplatin with irinotecan plus cisplatin in the treatment of extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 32(12):1262–1268
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Sharma RK, Cwiklinski K, Aalinkeel R, Reynolds JL, Sykes DE, Quaye E, Oh J, Mahajan SD, Schwartz SA (2017) Immunomodulatory activities of curcumin-stabilized silver nanoparticles: efficacy as an antiretroviral therapeutic. Immunol Investig 46(8):833–846. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820139.2017.1371908
Sood PK, Nahar U, Nehru B (2011) Curcumin attenuates aluminum-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in rat brain. Neurotox Res 20(4):351–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-011-9249-8 Epub 2011 Jun 9
Subrata KB (2016) Does the interdependence between oxidative stress and inflammation explain the antioxidant paradox Hindawi Publishing Corporation Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, Article ID 5698931, 9 pages. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5698931
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li YA (1988) Simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Van Cutsem E, Lenz HJ, Kohne CH, Heinemann V, Tejpar S, Melezínek I et al (2015) Fluorouracil,leucovorin, and irinotecan plus cetuximab treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 33(7):692–700
Vrdoljak AL, Berend S, Zeljezić D, Piljac-Zegarac J, Plestina S, Kuca K et al (2009) Irinotecan side effects relieved by the use of HI-6 oxime: in vivo experimental approach. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 105(6):401–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2009.00460.x
Yagi K (1988) Simple assay for the level of total lipid peroxides in serum or plasma. Methods Mol Biol 108:101–106
Zhang L, Man S, Qiu H, Liu Z, Zhang M, Ma L (2016) Curcumin-cyclodextrin complexes enhanced the anti-cancer effects of curcumin. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 48:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was carried out in accordance with ethical standards in all aspects.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciftci, O., Turkmen, N.B. & Taslıdere, A. Curcumin protects heart tissue against irinotecan-induced damage in terms of cytokine level alterations, oxidative stress, and histological damage in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 391, 783–791 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1495-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1495-3