Abstract
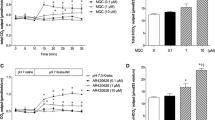
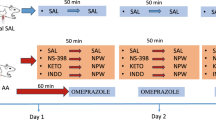
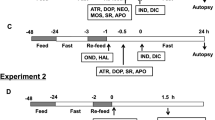
YF476 differs from the proton pump inhibitor (PPI) esomeprazole in mode of action by antagonizing the type 2 receptor of cholecystokinin/gastrin (CCK-2R). YF476 protection against diclofenac-induced gastric ulcers was compared to esomeprazole and correlated with plasma levels of hormones related to gastric pH (gastrin, ghrelin, and somatostatin), gastric gene expression of these hormones, their receptors, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). YF476 or esomeprazole pretreatments were followed by diclofenac. Four hours later, gastric tissue was excised and analyzed for ulcer index. An intragastrically implanted Bravo capsule measured pH for 5 days during YF476 plus pentagastrin treatment. Changes in gene expression were assayed for gastrin, ghrelin, and somatostatin; their receptors; and iNOS. YF476 acutely (within 4 h) protected against diclofenac-induced gastric ulcers equivalent to esomeprazole. Gastric pH recorded during 5 days in the presence of pentagastrin was 1.83 (±0.06). YF476 raised pH to 3.67 (±0.09) and plasma ghrelin, gastrin, and somatostatin increased. YF476 increased gene expression of somatostatin receptor and gastrin, while ghrelin receptor decreased; transcripts coding ghrelin, somatostatin, and CCK-2R remained unchanged. In the presence of diclofenac, esomeprazole increased expression of all these transcripts and that of iNOS, while YF476 yielded only decreased CCK-2R and increased iNOS transcripts. YF476 is a potential new preventative treatment for patients at risk of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced ulceration. Gastric gene expressions of ghrelin, gastrin, and somatostatin and their receptors differ between esomeprazole and YF476. Despite these differences and different modes of action to raise gastric pH, both drugs acutely increase iNOS, suggesting iNOS expression parallels pH.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCK-2R:
-
Type 2 receptor of cholecystokinin/gastrin
- CckbR:
-
Rat gene coding type 2 receptor of cholecystokinin
- CV:
-
Intraassay coefficient of variation
- ECL:
-
Enterochromaffin-like (cell)
- Gast :
-
Rat gastrin gene
- Ghrl :
-
Rat ghrelin gene
- GhsR:
-
Rat ghrelin receptor
- H2RA:
-
Histamine H2 receptor antagonist
- HPRT1:
-
Gene coding hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (i.e., expressed protein possessing enzymatic activity)
- NOS2:
-
Gene coding iNOS
- IV:
-
Intravenous
- NSAID:
-
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug
- PPI:
-
Proton pump inhibitor
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase reaction
- SstR2:
-
Rat gene coding type 2 receptor of somatostatin
- Sst:
-
Rat somatostatin gene
- SC:
-
Subcutaneous
- YF476:
-
(R)-1-[2,3-Dihydro-2-oxo-1-pivaloylmethyl-5-(2-pyri-dyl)-1H-1,4-benzo-diazepin-3-yl]-3-(3-methylaminophenyl)urea
References
Alioth C, Blum RA, D’Andrea DT et al (1993) Application of dual radiotelemetric technique in studying drug–drug interaction between diclofenac sodium and ranitidine HCl in volunteers. Pharm Res 10:1688–1692
Barrett TD, Lagaud G, Wagaman P et al (2012) The cholecystokinin CCK2 receptor antagonist, JNJ-26070109, inhibits gastric acid secretion and prevents omeprazole-induced acid rebound in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 166:1684–1693
Bennett A, Misiewicz JJ, Waller SL (1967) Analysis of the motor effects of gastrin and pentagastrin on the human alimentary tract in vitro. Gut 8:470–474
Boyce M, David O, Darwin K, Mitchell T, Johnston A, Warrington S (2012) Single oral doses of netazepide (YF476), a gastrin receptor antagonist, cause dose-dependent, sustained increases in gastric pH compared with placebo and ranitidine in healthy subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 36:181–189
Boyce M, Warrington S, Johnston A, Harris A (2000) Effect on gastric pH of single doses of YF476, a new gastrin antagonist, compared with ranitidine and placebo. Br J Clin Pharmacol 49:493P–494P
Boyce M, Warrington S, Nentwich H, Norris V, Hull R, Black J (2004) Effect of repeated doses ofYF476, a gastrin antagonist, on pentagastrin-induced changes in volume, hydrogen content and pH of gastric aspirate in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 57:684P
Chen D, Friis-Hansen L, Håkanson R, Zhao C-M (2005) Genetic dissection of the signaling pathways that control gastric acid secretion. Inflammopharmacol 13:201–207
Chen D, Zhao C-M, Norlén P et al (2000) Effect of CCK-2 receptor blockade on rat stomach ECL cells. Cell Tissue Res 299:81–95
Cui G, Takaishi S, Ai W et al (2006) Gastrin-induced apoptosis contributes to carcinogenesis in the stomach. Lab Invest 86:1037–1051
Cui G, Waldum HL (2007) Physiological and clinical significance of enterochromaffin-like cell activation in the regulation of gastric acid secretion. World J Gastroenterol 28:493–496
Dimaline R, Varro A (2007) Attack and defence in the gastric epithelium—a delicate balance. Exp Physiol 92:591–601
Ding X-Q, Lindström E, Håkanson R (1997) Evaluation of three novel cholecystokinin-B/gastrin receptor antagonists: a study of their effects on rat stomach enterochromaffin-like cell activity. Pharmacol Toxicol 81:232–237
Frazzoni M, Manno M, De Micheli E, Savarino V (2006) Intra-oesophageal acid suppression in complicated gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: esomeprazole versus lansoprazole. Dig Liver Dis 38:85–90
Håkanson R, Chen D, Andersson K et al (1994) The biology and physiology of the ECL cell. Yale J Biol Med 67:123–134
Jansson EA, Petersson J, Reinders C et al (2007) Protection from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-induced gastric ulcers by dietary nitrate. Free Radic Biol Med 15:510–518
Kapuscinski M, Shulkes A (1995) Secretory and biosynthetic responses of gastrin and somatostatin to acute changes in gastric acidity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 10:405–412
Kitano M, Norlén P, Ding XQ, Nakamura S, Håkanson R (2000) Long-lasting cholecystokinin(2) receptor blockade after a single subcutaneous injection of YF476 or YM022. Br J Pharmacol 130:699–705
Koh TJ, Chen D (2000) Gastrin as a growth factor in the gastrointestinal tract. Regul Pept 93:37–44
Leontiadis GI, Sreedharan A, Dorward S et al (2007) Systematic reviews of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Health Technol Assess 11:1–164
Levin F, Edholm T, Ehrström M, Wallin B, Schmidt PT, Kirchgessner AM et al (2005) Effect of peripherally administered ghrelin on gastric emptying and acid secretion in the rat. Regul Pept 131:59–65
Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Gladwin MT (2008) The nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:156–167
Martinsen TC, Kawase S, Håkanson R et al (2003) Spontaneous ECL cell carcinomas in cotton rats: natural course and prevention by a gastrin receptor antagonist. Carcinogenesis 24:1887–1896
McColl KE, Gillen D (2009) Evidence that proton-pump inhibitor therapy induces the symptoms it is used to treat. Gastroenterology 137:20–22
Nishida A, Kobayashi-Uchida A, Akuzawa S et al (1995) Gastrin receptor antagonist YM022 prevents hypersecretion after long term acid suppression. Am J Physiol 269:G699–G705
Nwokolo C, Smith J, Sawyerr A, Pounder R (1991) Rebound intragastric hyperacidity after abrupt withdrawal of histamine H2 receptor blockade. Gut 32:1455–1460
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L (2002) Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 30:e36
Reimer C, Søndergaard B, Hilsted L, Bytzer P (2009) Proton-pump inhibitor therapy induces acid-related symptoms in healthy volunteers after withdrawal of therapy. Gastroenterology 137:80–87
Rudholm T, Hellström PM, Theodorsson E, Campbell CA, McLean PG, Näslund E (2008) Bravo capsule system optimizes intragastric pH monitoring over prolonged time: effects of ghrelin on gastric acid and hormone secretion in the rat. World J Gastroenterol 28:6180–6187
Schubert ML (2008) Gastric secretion. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24:659–664
Semple G, Ryder H, Rooker D et al (1997) (3R)-N-(1-(tert-butylcarbonylmethyl)-2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-5-(2-pyridyl)-1H-1,4-benzodiazepin-3-yl)-N′-(3-(methylamino)phenyl)urea (YF476): a potent and orally active gastrin/CCK-B antagonist. J Med Chem 31:40:331–341
Shu Z, Jung M, Beger HG et al (1997) pH-dependent changes of nitric oxide, peroxynitrite, and reactive oxygen species in hepatocellular damage. Am J Physiol 273:G1118–G1126
Takemoto Y, Yuki H, Nishida A et al (1998) Effects of YF476, a potent and selective gastrin/CCK-B receptor antagonist, on gastric acid secretion in beagle dogs with gastric fistula. Arzneim Forsch 48:403–407
Takeuchi K, Kato S, Konaka A, Sugawa Y (1999) Luminal calcium in regulation of nitric oxide release and acid secretion in rat stomachs after damage. Dig Dis Sci 44:515–522
Takeuchi Y, Kitano S, Bandoh T, Matsumoto T, Baatar D, Kai S (2003) Acceleration of gastric ulcer healing by omeprazole in portal hypertensive rats. Is its action mediated by gastrin release and the stimulation of epithelial proliferation? Eur Surg Res 35:75–80
Takinami Y, Yuki H, Nishida A et al (1997) YF476 is a new potent and selective gastrin/cholecystokinin-B receptor antagonist in vitro and in vivo. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 11:113–120
Tatemichi M, Ogura T, Sakurazawa N, Nagata H, Sugita M, Esumi H (2003) Inducible nitric oxide synthase activity induced by sodium chloride solution prolongs luminal pH elevation in rat and mouse stomachs. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18:1039–1046
Tari A, Kamiyasu T, Yonei Y et al (1997) Role of gastrin/CCK-B receptor in the regulation of gastric acid secretion in rat. Dig Dis Sci 42:1901–1907
Vo PA, Lad B, Tomlinson JA, Francis S, Ahluwalia A (2005) Autoregulatory role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide (NO) on lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular inducible NO synthase expression and function. J Biol Chem 280:7236–7243
Wilder-Smith C, Halter F, Ernst T et al (1990) Loss of acid suppression during dosing with H2-receptor antagonists. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 4(Suppl 1):15–27
Yakabi K, Ro S, Onouhi T et al (2006) Histamine mediates the stimulatory action of ghrelin on acid secretion in rat stomach. Dig Dis Sci 51:1313–1321
Yakabi K, Kawashima J, Kato S (2008) Ghrelin and gastric acid secretion. World J Gastroenterol 7:6334–6338
Yoshizumi M, Perella MA, Burnett JC, Lee ME (1993) Tumor necrosis factor downregulates an endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA by shortening its half-life. Circ Res 73:205–209
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by GlaxoSmithKline and supported by Karolinska Institutet and Uppsala University. D-L Webb gratefully acknowledges grants from Bengt Ihres Foundation and Socialstyrelsen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dominic-Luc Webb and Tobias Rudholm-Feldreich contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Webb, DL., Rudholm-Feldreich, T., Gillberg, L. et al. The type 2 CCK/gastrin receptor antagonist YF476 acutely prevents NSAID-induced gastric ulceration while increasing iNOS expression. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 386, 41–49 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0812-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0812-5