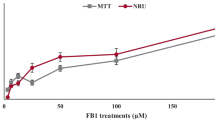
Abstract
FB1 is a common contaminant of cereal grains that affects human and animal health. It has become increasingly evident that epigenetic changes are implicated in FB1 toxicity. N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant post-transcriptional RNA modification, is influenced by fluctuations in redox status. Since oxidative stress is a characteristic of FB1 exposure, we determined if there is cross-talk between oxidative stress and m6A in FB1-exposed HepG2 cells. Briefly, HepG2 cells were treated with FB1 (0, 5, 50, 100, 200 µM; 24 h) and ROS, LDH and m6A levels were quantified. qPCR was used to determine the expression of m6A modulators, Nrf2, Keap1 and miR-27b, while western blotting was used to quantify Keap1 and Nrf2 protein expression. Methylation status of Keap1 and Nrf2 promoters was assessed and RNA immunoprecipitation quantified m6A-Keap1 and m6A-Nrf2 levels. FB1 induced accumulation of intracellular ROS (p ≤ 0.001) and LDH leakage (p ≤ 0.001). Elevated m6A levels (p ≤ 0.05) were accompanied by an increase in m6A “writers” [METLL3 (p ≤ 0.01) and METLL14 (p ≤ 0.01)], and “readers” [YTHDF1 (p ≤ 0.01), YTHDF2 (p ≤ 0.01), YTHDF3 (p ≤ 0.001) and YTHDC2 (p ≤ 0.01)] and a decrease in m6A “erasers” [ALKBH5 (p ≤ 0.001) and FTO (p ≤ 0.001)]. Hypermethylation and hypomethylation occurred at Keap1 (p ≤ 0.001) and Nrf2 (p ≤ 0.001) promoters, respectively. MiR-27b was reduced (p ≤ 0.001); however, m6A-Keap1 (p ≤ 0.05) and m6A-Nrf2 (p ≤ 0.01) levels were upregulated. This resulted in the ultimate decrease in Keap1 (p ≤ 0.001) and increase in Nrf2 (p ≤ 0.001) expression. Our findings reveal that m6A RNA methylation can be modified by exposure to FB1, and a cross-talk between m6A and redox regulators does occur.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All datasets generated in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam J-W, Bartel DP (2015) Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 4:e05005. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005
Alizadeh AM et al (2012) Fumonisin B1 contamination of cereals and risk of esophageal cancer in a high risk area in northeastern Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prevent 13:2625–2628
Arumugam T, Pillay Y, Ghazi T, Nagiah S, Abdul NS, Chuturgoon AA (2019) Fumonisin B(1)-induced oxidative stress triggers Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Mycotoxin Res 35:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-018-0335-0
Arumugam T, Ghazi T, Chuturgoon A (2020) Fumonisin B 1 epigenetically regulates PTEN expression and modulates DNA damage checkpoint regulation in HepG2 liver cells. Toxins 12:2–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100625
Barbano R et al (2013) Aberrant Keap1 methylation in breast cancer and association with clinicopathological features. Epigenetics 8:105–112
Cantara WA et al (2010) The RNA modification database, RNAMDB: 2011 update. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D195–D201
Chuturgoon A, Phulukdaree A, Moodley D (2014a) Fumonisin B1 induces global DNA hypomethylation in HepG2 cells—an alternative mechanism of action. Toxicology 315:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2013.11.004
Chuturgoon AA, Phulukdaree A, Moodley D (2014b) Fumonisin B1 modulates expression of human cytochrome P450 1b1 in human hepatoma (Hepg2) cells by repressing Mir-27b. Toxicol Lett 227:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.02.026
Demirel G, Alpertunga B, Ozden S (2015) Role of fumonisin B1 on DNA methylation changes in rat kidney and liver cells. Pharm Biol 53:1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.976714
Desrosiers R, Friderici K, Rottman F (1974) Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 71:3971–3975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.71.10.3971
Domijan A-M (2012) Fumonisin B1: a neurotoxic mycotoxin/fumonizin B1: Neurotoksični mikotoksin. Arch Ind Hyg Toxicol 63:531–544
Dominissini D et al (2012) Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 485:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11112
Eades G, Yang M, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Q (2011) miR-200a regulates Nrf2 activation by targeting Keap1 mRNA in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 286:40725–40733. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.275495
Fabrizio FP, Sparaneo A, Trombetta D, Muscarella LA (2018) Epigenetic versus genetic deregulation of the KEAP1/NRF2 axis in solid tumors: focus on methylation and noncoding RNAs. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:2492063. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2492063
Gelderblom W, Abel S, Smuts CM, Marnewick J, Marasas W, Lemmer ER, Ramljak D (2001) Fumonisin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis: mechanisms related to cancer initiation and promotion. Environ Health Perspect 109:291–300
Ghazi T, Nagiah S, Chuturgoon AA (2020a) Fusaric acid decreases p53 expression by altering promoter methylation and m6A RNA methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Epigenetics. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2020.1788324
Ghazi T, Nagiah S, Dhani S, Chuturgoon AA (2020b) Fusaric acid-induced epigenetic modulation of hepatic H3K9me3 triggers apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Epigenomics 12:955–972. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi-2019-0284
Han M et al (2020) Abnormality of m6A mRNA methylation is involved in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 14:98–98. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00098
Huang T, Gao Q, Feng T, Zheng Y, Guo J, Zeng W (2019) FTO knockout causes chromosome instability and G2/M arrest in mouse GC-1 cells. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00732
Idahor K (2010) Global distribution of Fumonisin B 1—a review. Acta SATECH 3:25–32
Jia G et al (2011) N6-Methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 7:885–887. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.687
Kamle M, Mahato D, Devi S, Lee K, Kang SG, Kumar P (2019) Fumonisins: impact on agriculture food, and human health and their management strategies. Toxins 11:238. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11060328
Kang KA et al (2014) Epigenetic modification of Nrf2 in 5-fluorouracil-resistant colon cancer cells: involvement of TET-dependent DNA demethylation. Cell Death Dis 5:e1183–e1183. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.149
Kennedy EM et al (2016) Posttranscriptional m6A editing of HIV-1 mRNAs enhances viral gene expression. Cell Host Microbe 19:675–685
Kobayashi A, Kang M-I, Watai Y, Tong KI, Shibata T, Uchida K, Yamamoto M (2006) Oxidative and electrophilic stresses activate Nrf2 through inhibition of ubiquitination activity of Keap1. Mol Cell Biol 26:221–229
Kouadio JH, Dano SD, Moukha S, Mobio TA, Creppy EE (2007) Effects of combinations of Fusarium mycotoxins on the inhibition of macromolecular synthesis, malondialdehyde levels, DNA methylation and fragmentation, and viability in Caco-2 cells. Toxicon 49:306–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.029
Lan Q, Liu PY, Haase J, Bell JL, Hüttelmaier S, Liu T (2019) The critical role of RNA m6A methylation in cancer. Cancer Res 79:1285–1292
Li Q, Li X, Tang H, Jiang B, Dou Y, Gorospe M, Wang W (2017) NSUN2-mediated m5C methylation and METTL3/METTL14-mediated m6A methylation cooperatively enhance p21 translation. J Cell Biochem 118:2587–2598
Liu X, Fan L, Yin S, Chen H, Hu H (2019) Molecular mechanisms of fumonisin B1-induced toxicities and its applications in the mechanism-based interventions. Toxicon 167:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.06.009
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR (2012) Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell 149:1635–1646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.003
Mobio TA et al (2000) Epigenetic properties of fumonisin B(1): cell cycle arrest and DNA base modification in C6 glioma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 164:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1006/taap.2000.8893
Müller S, Dekant W, Mally A (2012) Fumonisin B1 and the kidney: modes of action for renal tumor formation by fumonisin B1 in rodents. Food Chem Toxicol 50:3833–3846
Pan T (2013) N6-methyl-adenosine modification in messenger and long non-coding RNA. Trends Biochem Sci 38:204–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2012.12.006
Paramasivam A, Priyadharsini JV, Raghunandhakumar S (2020) Implications of m6A modification in autoimmune disorders. Cell Mol Immunol 17:550–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0307-0
Riley RT, Merrill AH (2019) Ceramide synthase inhibition by fumonisins: a perfect storm of perturbed sphingolipid metabolism, signaling, and disease. J Lipid Res 60:1183–1189
Roundtree IA, Evans ME, Pan T, He C (2017) Dynamic RNA modifications in gene expression regulation. Cell 169:1187–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.045
Schwartz S et al (2014) Perturbation of m6A writers reveals two distinct classes of mRNA methylation at internal and 5′ sites. Cell Rep 8:284–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.048
Shen F et al (2015) Decreased N(6)-methyladenosine in peripheral blood RNA from diabetic patients is associated with FTO expression rather than ALKBH5. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:E148-154. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-1893
Singh MP, Kang SC (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy activation attenuates fumonisin B1 induced hepatotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem Toxicol 110:371–382
Szabó A et al (2018) Dose and exposure time-dependent renal and hepatic effects of intraperitoneally administered fumonisin B1 in rats. Toxins 10:465
Tsuchiya Y, Nakajima M, Takagi S, Taniya T, Yokoi T (2006) MicroRNA regulates the expression of human cytochrome P450 1B1. Cancer Res 66:9090–9098. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-06-1403
Vickers KC et al (2013) MicroRNA-27b is a regulatory hub in lipid metabolism and is altered in dyslipidemia. Hepatology 57:533–542. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.25846
Wang X et al (2014) N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 505:117–120
Wang X et al (2015) N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 161:1388–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.014
Wang X et al (2016) Structural basis of N6-adenosine methylation by the METTL3–METTL14 complex. Nature 534:575–578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18298
Wang J, Ishfaq M, Xu L, Xia C, Chen C, Li J (2019) METTL3/m6A/miRNA-873–5p attenuated oxidative stress and apoptosis in colistin-induced kidney injury by modulating Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00517
Wu S, Lu H, Bai Y (2019) Nrf2 in cancers: a double-edged sword. Cancer Med 8:2252–2267. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2101
Wu J, Gan Z, Zhuo R, Zhang L, Wang T, Zhong X (2020) Resveratrol attenuates aflatoxin B(1)-induced ROS formation and increase of m(6)A RNA methylation. Animals (Basel) 10:677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040677
Xu W, Li F, Liu Z, Xu Z, Sun B, Cao J, Liu Y (2017) MicroRNA-27b inhibition promotes Nrf2/ARE pathway activation and alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury. Oncotarget 8:70669–70684. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19974
Xu K, Sun Y, Sheng B, Zheng Y, Wu X, Xu K (2019) Role of identified RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in liver. Anal Biochem 578:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.05.005
Yue Y, Liu J, He C (2015) RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev 29:1343–1355. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.262766.115
Zaccara S, Ries RJ, Jaffrey SR (2019) Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:608–624. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0168-5
Zhao T, Li X, Sun D, Zhang Z (2019) Oxidative stress: one potential factor for arsenite-induced increase of N6-methyladenosine in human keratinocytes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 69:95–103
Zhao T-X et al (2020a) Increased m6A RNA modification is related to the inhibition of the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response in di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced prepubertal testicular injury. Environ Pollut 259:113911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113911
Zhao Z, Meng J, Su R, Zhang J, Chen J, Ma X, Xia Q (2020b) Epitranscriptomics in liver disease: basic concepts and therapeutic potential. J Hepatol 73:664–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2020.04.009
Zheng G et al (2013) ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell 49:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.015
Zhengchang W, Chao X, Haifei W, Song G, Shenglong W, Wenbin B (2020). Res Square. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-73169/v1
Zhou Y, Zeng P, Li YH, Zhang Z, Cui Q (2016) SRAMP: prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based on sequence-derived features. Nucleic Acids Res 44:e91. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw104
Funding
The authors acknowledge the National Research Foundation (NRF-Grant No. 120820) of South Africa and College of Health Science (University of KwaZulu-Natal) for funding this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TA, TG, and AC conceptualised and designed the study. TA conducted all laboratory experiments, analysed the data and wrote the manuscript. TG and AC revised the manuscript. All authors have read the manuscript prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
Ethic was received from the University of KwaZulu-Natal’s Biomedical Research Ethics Committee. Ethics No. BE322/19.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, T., Ghazi, T. & Chuturgoon, A.A. Fumonisin B1 alters global m6A RNA methylation and epigenetically regulates Keap1-Nrf2 signaling in human hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Arch Toxicol 95, 1367–1378 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-02986-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-02986-5