Abstract
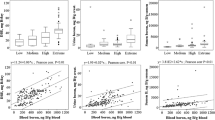
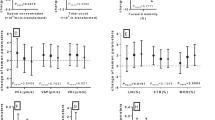
Boron-associated shifts in sex ratios at birth were suggested earlier and attributed to a decrease in Y- vs. X-bearing sperm cells. As the matter is pivotal in the discussion of reproductive toxicity of boron/borates, re-investigation in a highly borate-exposed population was required. In the present study, 304 male workers in Bandirma and Bigadic (Turkey) with different degrees of occupational and environmental exposure to boron were investigated. Boron was quantified in blood, urine and semen, and the persons were allocated to exposure groups along B blood levels. In the highest (“extreme”) exposure group (n = 69), calculated mean daily boron exposures, semen boron and blood boron concentrations were 44.91 ± 18.32 mg B/day, 1643.23 ± 965.44 ng B/g semen and 553.83 ± 149.52 ng B/g blood, respectively. Overall, an association between boron exposure and Y:X sperm ratios in semen was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). Also, the mean Y:X sperm ratios in semen samples of workers allocated to the different exposure groups were statistically not different in pairwise comparisons (p > 0.05). Additionally, a boron-associated shift in sex ratio at birth towards female offspring was not visible. In essence, the present results do not support an association between boron exposure and decreased Y:X sperm ratio in males, even under extreme boron exposure conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basaran N, Duydu Y, Bolt HM (2012) Reproductive toxicity in boron exposed workers in Bandirma, Turkey. J Trace Elem Med Biol 26(2–3):165–167
Bolt HM, Basaran N, Duydu Y (2012) Human environmental and occupational exposures to boric acid: reconciliation with experimental reproductive toxicity data. J Toxicol Environ Health A 75(8–10):508–514
Bolt HM, Duydu Y, Basaran N, Golka K (2017) Boron and its compounds: current biological research activities. Arch Toxicol 91:2719–2722
Chang LB, Robbins AW, Wei F, Xun L, Wu G, Li N, Elashoff DA (2006) Boron workers in China, exploring work and lifestyle factors related to boron exposure. AAOHN J 54(19):435–443
Conover WJ (1999) Practical nonparametric statistics, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Ustundag A, Aydin S, Undeger U et al (2011) Reproductive toxicity parameters and biological monitoring in occupationally and environmentally boron-exposed persons in Bandirma, Turkey. Arch Toxicol 85(6):589–600
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Ustundag A, Aydin S, Undeger et al (2012a) Assessment of DNA integrity (COMET assay) in sperm cells of boron exposed workers. Arch Toxicol 86(1):27–35
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Bolt HM (2012b) Exposure assessment of boron in Bandirma boric acid production plant. J Trace Elem Med Biol 26(2–3):161–164
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Bolt HM (2015) Risk assessment of borates in occupational settings. In: Kabay N, Bryjak M, Hilal N, eds. Boron separation processes, 1st Edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 65–105
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Ustundag A, Aydin S, Undeger U et al (2016) Is boric acid toxic to reproduction in humans? Assessment of the animal reproductive toxicity data and epidemiological study results. Curr Drug Deliv 13(3):324–329
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Aydın S, Ustundag A, Yalcin CO, Goktas HG, Bacanli M, Aydos K, Atabekoglu CS, Golka K, Ickstadt K, Schwerdtle T, Werner M, Meyer S, Bolt HM (2018a) Evaluation of FSH, LH, testosterone levels and semen parameters in male workers under extreme boron exposure conditions. Arch Toxicol 92(10):3051–3059
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Aydin S, Ustundag A, Yalcin CO, Goktas HG, Bacanli M, Aydos K, Atabekoglu CS, Golka K, Ickstadt K, Schwerdtle T, Werner M, Meyer S, Bolt HM (2018b) Birth weight of newborns and pregnancy outcomes of environmentally boron- exposed females in Turkey. Arch Toxicol 92(8):2475–2485
EU Drinking Water Directive, Council Directive 98/83/EC, of 3 November 1998, on the quality of water intended for human consumption. Off J Eur Comm L 330/32. https://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:1998:330:0032:0054:EN:PDF. Accessed 29 Nov 2018
Fort DJ, Fort TD, Mathis MB, Ball RW (2016) Boric acid is reproductively toxic to adult Xenopus laevis, but not endocrine active. Toxicol Sci 154(1):16–26
Gomez I, Marshall T, Tsai P, Shao YS, Guo YL (2002) Number of boys born to men exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls. Lancet 300(13):143–144
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Korkmaz M, Sayli U, Sayli BS, Bakirdere S, Titretir S, Ataman OY, Keskin S (2007) Estimation of human daily boron exposure in a boron-rich area. Br J Nutr 98:571–575
Korkmaz M, Yenigun M, Bakirdere S, Ataman OY, Keskin S, Muezzinoglu T, Lekili M (2011) Effects of chronic boron exposure on semen profile. Biol Trace Elem Res 143(2):738–750
Mocarelli P, Gerthoux PM, Ferrari E, Patterson DG Jr, Kieszak SM, Brambilla P, Vincoli N, Signorini S, Tramacere P, Carreri V, Sampson EJ, Turner WE, Needham LL (2000) Paternal concentration of dioxin and sex ratio of offspring. Lancet 355:1858–1863
Moore JA, An Expert Scientific Committee (1997) An assessment of boric acid and borax using the IEHR evaluative process for assessing human developmental and reproductive toxicity of agents. Reprod Toxicol 11(1):123–160
Moorman WJ, Ahlers HW, Chapin RE, Daston GP, Foster PMD, Kavlock RJ, Morawetz JS, Schnorr TM, Schrader SM (2000) Prioritization of NTP reproductive toxicants for field studies. Reprod Toxicol 14:293–301
Price CJ, Strong PL, Marr MC, Myers CB, Murray FJ (1996) Developmental toxicity NOAEL and postnatal recovery in rats fed boric acid during gestation. Fundam Appl Toxicol 32:179–193
R Core Team (2017) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex:32008R1272. Accessed 29 Nov 2018
Robbins WA, Wei F, Elashoff DA, Wu G, Xun L, Jia J (2008) Y:X sperm ratio in boron-exposed men. J Androl 29(1):115–121
Robbins WA, Xun L, Jia J, Kennedy N, Elashoff DA, Ping L (2010) Chronic boron exposure and human semen parameters. Reprod Toxicol 29:184–190
Sayli BS (1998) An assessment of fertility in boron-exposed Turkish subpopulations, 2. evidence that boron has no effect on human reproduction. Biol Trace Elem Res 66(1–3):409–422
Sayli BS (2003) Low frequency of fertility among workers in a borate processing facility. Biol Trace Elem Res 93(1–3):19–28
Scialli AR, Bonde JP, Brüske-Hohlfeld I, Culver BD, Li Y, Sullivan FM (2010) An overview of male reproductive studies of boron with an emphasis on studies of highly exposed Chinese workers. Reprod Toxicol 29:10–24
Tiido T, Rignell-Hydbom A, Jönsson B, Giwercman YL, Rylander L, Hagmar L, Giwercman A (2005) Exposure to persistent organochlorine pollutants associates with human sperm Y:X chromosome ratio. Hum Reprod 20:1903–1909
Tiido T, Rignell-Hydbom A, Jönsson Bo AG, Giwercman YL, Pedersen HS, Wojtyniak B, Ludwicki JK, Lesovoy V, Zvyezday V, Spano M, Manicardi GC, Bizzaro D, Bonefeld-Jorgensen Eva C, Toft G, Bonde JP, Rylander L, Hagmar L, Giwercman A (2006) Impact of PCB and p,p-DDE contaminants on human sperm Y:X chromosome ratio: Studies in three European populations and the Inuit population in Greenland. Environ Health Perspect 114(5):718–724
Weir RJ, Fisher RS (1972) Toxicology studies on borax and boric acid. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 23:351–364
WHO (2010) World Health Organization laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen, Fifth Edition. http://www.who.int/reproductivehealth/ publications/infertility/9789241547789$4en/. Accessed 29 Nov 2018
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality, fourth edition, 2011. WHO Press, World Health Organization, 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/drinking-water-quality-guidelines-4-including-1st-addendum/en/. Accessed 19 Mar 2018
Whorton D, Haas J, Trent L (1994) Reproductive effects of inorganic borates on male employees: Birth rate assessment. Environ Health Perspect 102(7):129–131
Xing X, Wu G, Wei F, Liu P, Wei H, Whang C, Xu J, Xun L, Jia J, Kennedy N, Elashoff D, Robbins W (2008) Biomarkers of environmental and workplace boron exposure. J Occup Environ Hyg 5:141–147
Yazbeck C, Kloppmann W, Cottier R, Sahuquillo J, Debotte G, Huel G (2005) Health impact evaluation of boron in drinking water: a geographical risk assessment in Northern France. Environ Geochem Health 27:419–427
Acknowledgements
The semen samples used in this study were sampled within the scope of the “Boron Project I” (2008–2010) and the “Boron Project II” (2014–2017). The “Boron Project I” was funded by Eti Mine Works General Management and BOREN (2008-G0207). The “Boron Project II” was funded by Eti Mine Works General Management (2014–2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The project was funded by Eti Mine. Eti Mine had no influence on the conduct of the study and has not influenced the results and interpretation. Thus, the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duydu, Y., Başaran, N., Yalçın, C.Ö. et al. Boron-exposed male workers in Turkey: no change in sperm Y:X chromosome ratio and in offspring’s sex ratio. Arch Toxicol 93, 743–751 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02391-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02391-z