Abstract
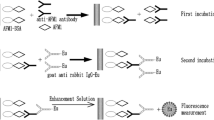
Using indirect competitive time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay (TRFIA), a rapid, highly selective and extremely sensitive method has been established for the determination of ochratoxin A (OA). Tests can be performed in a 96-well microplate using the toxin-specific polyclonal antibodies, obtained from rabbits immunized with ochratoxin A-keyhole limpet’s hemocyanin (OA–KLH). In indirect TRFIA format, ochratoxin A-bovine serum albumin conjugate (OA–BSA) is coated onto the microtitre plate and incubated with standard toxin (samples) and anti-OA antibody. A goat anti-rabbit IgG Eu3+ conjugate is used to enable the detection. The suitability of the assay for quantification of OA is also studied and samples are determined by OA-TRFIA using autoDELFIA1235 system. The results show that the polyclonal antibodies can be used at a dilution exceeding 1:8,000 and the OA detection limit is 0.02 μg/l for indirect competitive TRFIA formats. The 80, 50, and 20% inhibition binding effect dose (ED80, ED50, ED20) of OA were 0.195, 1.018, and 5.314 μg/l, respectively. The assay ranges from 0.02 to 400 μg/l. The cross reactivity with ochratoxin B is 5.6% and antibodies do not react with aflatoxin B1, phenylalanine and BSA. The within-run and between-run CVs of the OA-TRFIA are 2.6 and 5.2%, respectively. The mean recoveries from the OA-free cereals spiked with 1–200 μg of OA/kg of cereals sample were 95.8%. Both OA-TRFIA and OA-ELISA tests are applied for the quantitative measurement of OA in the same cereals, and the coefficient of correlation is 0.912. The results show that the novel TRFIA method can be applied to detect the OA contamination in cereals. It provides very high sensitivity and optimal range and will be useful to screen OA contamination easily, simply, and economically when the number of samples is large.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barna-Vetro I, Solti L, Teren J, Gyongyosi A, Szabo E, Wolfing A (1996) Sensitive ELISA test for the determination of ochratoxin A. J Agric Food Chem 44:4071–4074
Baxter ED (2001) The fate of ochratoxin A during malting and brewing. J Am Soc Brew Chem 59:98–100
Gyongyosi-Horvath A, Barna-Vetro I, Solti L (1996) A new monoclonal antibody detecting ochratoxin A at the picogram level. Lett Appl Microbiol 22:103–105
Hemmila I, Dakubu S, Mukkala VM (1984) Europium as a label in time-resolved immunofluorometric assays. Anal Biochem 137:335–338
Hohler D (1998) Ochratoxin A in food and feed: occurrence, legislation and mode of action. Z Ernaehrungswiss 37:2–12
Huang B, Xiao HL, Zhu LG, Tan C, Cai GM, Jin J (2001) Time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay of α-fetoprotein. Asian J Nucl Med 1:40–42
Kovacs F, Vanyi A (1994) Molds-mycotoxins-food contamination-human health aspects. Food Ind 12:362 – 365
Olsson J, Borjesson T, Lundstedt T, Schnurer J (2002) Detection and quantification of ochratoxin A and deoxynivalenol in barley grains by GC–MS and electronic nose. Int J Food Microbiol 72:203–214
Osborne BG (1979) Reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography determination of ochratoxin A in flour and bakery products. J Sci Food Agric 30:1065–1070
Scott PM, Kanhere SR (1995) Determination of ochratoxin A in beer. Food Addit Contam 12:591–598
Scott PM, Kanhere SR, Lawrence GA, Daley EF, Farber JM (1995) Fermentation of wort containing added ochratoxin A and fumonisins B1 and B2. Food Addit Contam 12:31–40
Thirumala Devi K, Mayo MA, Delfosse P, Reddy G, Reddy SV, Reddy DVR (2000) Production of polyclonal antibodies for ochratoxin A and its detection in chilies by ELISA. J Agric Food Chem 48:5079–5082
Visconti A, Pascale M, Centonze G (2000) Determination of ochratoxin A in domestic and imported beers in Italy by immunoaffinity clean-up and liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 888:321–326
Wang ML, Wang JM, Wang HZ (1998) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of ochratoxin corn. J Shandong Agric Univ 29:384–386
Weddeling K, Bassler HMS, Doerk H, Baron G (1994) Orientational experiments on the applicability of enzymic immunological methods for the detection of deoxynivalenol, ochratoxin A and zearalenone in brewing barley, malt and beer. Monatsschr Brauwiss 47:94–98
Acknowledgments
The Ministry of Science and Technology of China financially supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, B., Tao, W., Shi, J. et al. Determination of ochratoxin A by polyclonal antibodies based sensitive time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Arch Toxicol 80, 481–485 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0112-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0112-2