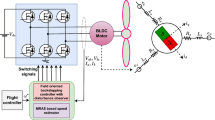
Abstract
Variable-speed wind energy conversion systems based on permanent-magnet synchronous generators (PMSGs) are typically controlled using the field-oriented control (FOC) principles. Therefore, accurate information of the rotor speed and position are essential to perform the required reference frame transformations. These signals can be obtained by mechanical sensors (e.g., position encoders or speed transducers) or via estimation schemes. This paper proposes a sensorless FOC strategy for direct-driven PMSGs in variable-speed wind turbines. A synchronously rotating reference frame phase-locked loop (PLL) that utilizes a model-based back elector-motive force (back-EMF) estimation is employed to estimate the rotor speed and position of the PMSG. The proposed sensorless FOC strategy is experimentally implemented, and its performance is investigated for all operation conditions and under parameter variations of the PMSG.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liserre M, Cardenas R, Molinas M, Rodriguez J (2011) Overview of multi-MW wind turbines and wind parks. IEEE Trans. Ind Electron 58(4):1081–1095
Jeong HG, Lee KB (2014) A control scheme to fulfill the grid-code under various fault conditions in the grid-connected wind turbines. Electr Eng J 96(2):199–210
Abdelrahem M, Kennel R (2016) Fault-ride through strategy for permanent-magnet synchronous generators in variable-speed wind turbines. Energies 9(12):1–15
Abdel-Salam M, Ahmed A, Abdel-Sater M (2011) Harmonic mitigation, maximum power point tracking and dynamic performance of variable speed grid connected wind turbine. J Electr Power Compon Syst 39(2):176–190
Zhang Z, Hackl C, Abdelrahem M, Kennel R (2016) Voltage sensorless direct model predictive control of 3L-NPC back-to-back power converter PMSG wind turbine systems with fast dynamics. In: Proceedings of power and energy student summit (PESS 2016)
Zhao Y, Wei C, Zhang Z, Qiao W (2013) A review on position/speed sensorless control for permanent-magnet synchronous machine-based wind energy conversion systems. IEEE J Emerg Sel Topics Power Electron 1(4):203–216
Benadja M, Chandra A (2015) Adaptive sensorless control of PMSGs-based offshore wind farm and VSC-HVdc stations. IEEE J Emerg Sel Topics Power Electron 3(4):918–931
Abdelrahem M, Hackl C, Kennel R (2017) Simplified model predictive current control without mechanical sensors for variable-speed wind energy conversion systems. Electr Eng J 99(1):367–377
Abdelrahem M, Hackl C, Zhang Z, Kennel R (2016) Sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous generators in variable-speed wind turbine systems. In: Proceedings of power and energy student summit (PESS 2016), Aachen, Germany, 19–20 January 2016
Rigatos G, Siano P, Zervos N (2014) Sensorless control of distributed power generators with the derivative-free nonlinear Kalman filter. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(11):6369–6382
Yan J, Lin H, Feng Y, Guo X, Huang Y, Zhu ZQ (2013) Improved sliding mode model reference adaptive system speed observer for fuzzy control of direct-drive permanent magnet synchronous generator wind power generation system. IET Renew Power Gener 7(1):28–35
Abdelrahem M, Hackl C, Kennel R (2016) Model predictive control of permanent magnet synchronous generators in variable-speed wind turbine systems. In: Proceedings of power and energy student summit (PESS 2016), Aachen, Germany, 19–20 January 2016
Liu W, Chen L, Ou J, Cheng S (2011) Simulation of PMSG wind turbine system with sensor-less control technology based on model reference adaptive system. In: International conference on electrical machines and systems, Beijing, 2011, pp. 1–3
Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Qiao W, Qu L (2014) A space-vector-modulated sensorless direct-torque control for direct-drive PMSG wind turbines. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 50(4):2331–2341 July-Aug. 2014
Koch G, Gabbi T, Henz G, Vieira RP, Pinheiro H (2015) Sensorless technique applied to PMSG of WECS using sliding mode observer. In: IEEE 13th Brazilian power electronics conference and 1st southern power electronics conference (COBEP/SPEC), Fortaleza, 2015, pp. 1–6
Huang K, Zheng L, Huang S, Xiao L, Li W (2011) Sensorless control for direct-drive PMSG wind turbines based on sliding mode observer. In: International conference on electrical machines and systems, Beijing, pp. 1–5
Hui Li, Shi KL, McLaren PG (2005) Neural-network-based sensorless maximum wind energy capture with compensated power coefficient. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 41(6):1548–1556
Singh M, Chandra A (2011) Application of adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system for sensorless control of PMSG-based wind turbine with nonlinear-load-compensation capabilities. IEEE Trans Power Electron 26(1):165–175
Golestan S, Guerrero JM, Vasquez JC (2017) Three-phase PLLs: a review of recent advances. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(3):1894–1907
Comanescu M, Xu L (2006) An improved flux observer based on PLL frequency estimator for sensorless vector control of induction motors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 53(1):50–56
Preindl M, Schaltz E (2011) Sensorless model predictive direct current control using novel second-order PLL observer for PMSM drive systems. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(9):4087–4095
Tong L et al (2014) An SRF-PLL-based sensorless vector control using the predictive deadbeat algorithm for the direct-driven permanent magnet synchronous generator. IEEE Trans Power Electron 29(6):2837–2849
Fan S, Wang P, Wen C (2010) A new sensorless control strategy used in direct-drive PMSG wind power system. In: 2nd international symposium on power electronics for distributed generation systems. China, Hefei, pp 611–615
Dirscherl C, Hackl C, Schechner K (2015) Modellierung und Regelung von modernen Windkraftanlagen: Eine Einführung” (Chapter 24). In: Schröder D (ed) Elektrische Antriebe - Regelung von Antriebssystemen. Springer, New York, pp 1540–1614
Hackl C, Kamper M, Kullick J, Mitchel J (2016) Current control of reluctance synchronous machines with online adjustment of the controller parameters. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics (ISIE 2016), Santa Clara, USA, p. 153–160,
Shi T, Wang Z, Xia C (2015) Speed measurement error suppression for PMSM control system using self-adaption Kalman observer. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 62(5):2753–2763
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelrahem, M., Hackl, C.M. & Kennel, R. Implementation and experimental investigation of a sensorless field-oriented control scheme for permanent-magnet synchronous generators. Electr Eng 100, 849–856 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0554-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-017-0554-y