Abstract
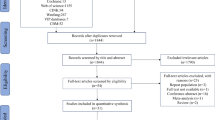
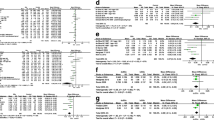
This systematic review aims to assess the occurrence and risks of osteopenia and osteoporosis in patientswith Wilson's disease (WD). A literature search was conducted utilizing EMBASE and MEDLINE frominception through April 2017. Studies assessing the occurrence or risk of osteopenia and/or osteoporosis inWD patients were included. Effect estimates from the individual study were extracted and combined usingrandom-effect, generic inverse variance method of DerSimonian and Laird. Of 754 studies, four studies with283 WD patients met the eligibility criteria and were included in the data analysis. The pooled prevalencerates of osteopenia and osteoporosis in WD patients were 36.5% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 14.8%-65.7%) and 27.7% (95%CI: 8.6%-60.9%), respectively. When meta-analysis was limited only to adults, the estimated prevalence rates of osteopenia, osteoporosis, and vertebral fracture were 50.0% (95%CI: 42.0%-58.0%), 17.6% (95%CI: 6.7%-38.6%) and 8.01% (95%CI: 4.05%-15.2%), respectively. Meta-regressionshowed significant impacts of age (negative correlation; P=0.002) and male status (positive correlation;P < 0.001) on the prevalence of osteoporosis. The data on risks of osteopenia and osteoporosis in WDpatients were limited. We suggests that there are potential associations of WD with osteopenia and/orosteoporosis. Also, young age and male status are correlated with the higher prevalence of osteoporosis inWD patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandmann O, Weiss KH, Kaler SG (2015) Wilson’s disease and other neurological copper disorders. Lancet Neurol 14:103–113
Coffey AJ, Durkie M, Hague S et al (2013) A genetic study of Wilson’s disease in the United Kingdom. Brain 136:1476–1487
Quemeneur AS, Trocello JM, Ea HK, Woimant F, Liote F (2011) Miscellaneous non-inflammatory musculoskeletal conditions. Musculoskeletal conditions associated with Wilson’s disease. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 25:627–636
Aggarwal A, Aggarwal N, Nagral A, Jankharia G, Bhatt M (2009) A novel global assessment scale for Wilson’s disease (GAS for WD). Mov Disord 24:509–518
Yu H, Xie JJ, Chen YC, Dong QY, Dong Y, Ni W, Wu ZY (2017) Clinical features and outcome in patients with osseomuscular type of Wilson’s disease. BMC Neurol 17:34
Jeremiah MP, Unwin BK, Greenawald MH, Casiano VE (2015) Diagnosis and management of osteoporosis. Am Fam Physician 92:261–268
Ebeling PR (2008) Clinical practice. Osteoporosis in men. N Engl J Med 358:1474–1482
Cetinkaya A, Ozen H, Yuce A, Saltik-Temizel IN, Demir H, Gurakan F (2014) Bone mineralization in children with Wilson’s disease. Indian J Gastroenterol 33:427–431
Hegedus D, Ferencz V, Lakatos PL, Meszaros S, Lakatos P, Horvath C, Szalay F (2002) Decreased bone density, elevated serum osteoprotegerin, and beta-cross-laps in Wilson disease. J Bone Miner Res 17:1961–1967
Selimoglu MA, Ertekin V, Doneray H, Yildirim M (2008) Bone mineral density of children with Wilson disease: efficacy of penicillamine and zinc therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol 42:194–198
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097
Lewiecki EM, Watts NB, McClung MR, Petak SM, Bachrach LK, Shepherd JA, Downs RW Jr, International Society for Clinical D (2004) Official positions of the international society for clinical densitometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3651–3655
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25:603–605
DerSimonian R, Kacker R (2007) Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp Clin Trials 28:105–114
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Kelley GA, Kelley KS (2012) Statistical models for meta-analysis: a brief tutorial. World J Methodol 2:27–32
Easterbrook PJ, Berlin JA, Gopalan R, Matthews DR (1991) Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 337:867–872
Quemeneur AS, Trocello JM, Ea HK, Ostertag A, Leyendecker A, Duclos-Vallee JC, de Vernejoul MC, Woimant F, Liote F (2014) Bone status and fractures in 85 adults with Wilson’s disease. Osteoporos Int 25:2573–2580
Weiss KH, Van de Moortele M, Gotthardt DN et al (2015) Bone demineralisation in a large cohort of Wilson disease patients. J Inherit Metab Dis 38:949–956
Higgins JP, Green S (2011) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. Available from www.cochranehandbook.orgorg.
Finby N, Bearn AG (1958) Roentgenographic abnormalities of the skeletal system in Wilson’s disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Am J Roentgenol Radium Therapy, Nucl Med 79:603–611
Shin JJ, Lee JP, Rah JH (2015) Fracture in a young male patient leading to the diagnosis of Wilson’s disease: a case report. J Bone Metab 22:33–37
Nakchbandi IA (2014) Osteoporosis and fractures in liver disease: relevance, pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. World J Gastroenterol 20:9427–9438
Xie YZ, Zhang XZ, XH X, Zhang ZX, Feng YK (1985) Radiologic study of 42 cases of Wilson disease. Skelet Radiol 13:114–119
Subrahmanyam DK, Vadivelan M, Giridharan S, Balamurugan N (2014) Wilson’s disease—a rare cause of renal tubular acidosis with metabolic bone disease. Indian J Nephrol 24:171–174
Litwin T, Gromadzka G, Czlonkowska A (2012) Gender differences in Wilson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 312:31–35
Huang X, Xu Y, Partridge NC (2013) Dancing with sex hormones, could iron contribute to the gender difference in osteoporosis? Bone 55:458–460
Kim BJ, Ahn SH, Bae SJ, Kim EH, Lee SH, Kim HK, Choe JW, Koh JM, Kim GS (2012) Iron overload accelerates bone loss in healthy postmenopausal women and middle-aged men: a 3-year retrospective longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res 27:2279–2290
Jeney V (2017) Clinical impact and cellular mechanisms of iron overload-associated bone loss. Front Pharmacol 8:77
Hafkemeyer P, Schupp M, Storch M, Gerok W, Haussinger D (1994) Excessive iron storage in a patient with Wilson’s disease. Clin Investig 72:134–136
Walshe JM, Cox DW (1998) Effect of treatment of Wilson’s disease on natural history of haemochromatosis. Lancet 352:112–113
Shiono Y, Wakusawa S, Hayashi H, Takikawa T, Yano M, Okada T, Mabuchi H, Kono S, Miyajima H (2001) Iron accumulation in the liver of male patients with Wilson’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 96:3147–3151
Pfeiffenberger J, Gotthardt DN, Herrmann T, Seessle J, Merle U, Schirmacher P, Stremmel W, Weiss KH (2012) Iron metabolism and the role of HFE gene polymorphisms in Wilson disease. Liver Int 32:165–170
Aksoy M, Camli N, Dincol K, Erdem S, Akgun T (1972) Osseous changes in Wilson’s disease. A radiologic study of nine patients. Radiology 102:505–509
Ferenci P, Czlonkowska A, Merle U, Ferenc S, Gromadzka G, Yurdaydin C, Vogel W, Bruha R, Schmidt HT, Stremmel W (2007) Late-onset Wilson’s disease. Gastroenterology 132:1294–1298
Gafni RI, Baron J (2004) Overdiagnosis of osteoporosis in children due to misinterpretation of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). J Pediatr 144:253–257
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to Marian MacMaster and Joan Yanicke, our lovely librarians at the Medical Library, Metrowest Medical Center, for helping us retrieve all the relevant articles.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
PROSPERO registration number for this systematic review is 2017:CRD42017072769
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chenbhanich, J., Thongprayoon, C., Atsawarungruangkit, A. et al. Osteoporosis and bone mineral density in patients with Wilson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 29, 315–322 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-4295-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-4295-6