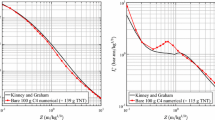
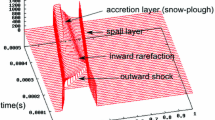
Abstract
Heterogeneous explosives contain a mixture of standard explosive material and reactive metal particles. The inclusion of metal particles alters the energy density and energy release timescales involved in the blast event. Available experimental evidence indicates that metal particles may be damaged or fragmented during heterogeneous blast, altering the distribution of particle sizes from their initial state. This paper discusses adaptation and application of fragmentation theory and physical models for particle damage during condensed matter detonation, aerodynamic breakup of molten particles, and particle impact fragmentation with nearby structures. The shock compression and impact fragmentation models are based on the energy methods for dynamic fragmentation by Grady and Kipp, while aerodynamic breakup is treated according to Weber number stability criteria for droplets. These particle fragmentation models are validated against fundamental test cases from the literature. The models are then applied to heterogeneous blast scenarios including free field and wall reflection in a semi-confined urban street. Comparison with experimental records of pressure shows good agreement despite challenges inherent in the complexity of heterogeneous blast measurement and multiphase simulation.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, F., Frost, D.L., Thibault, P.A., Murray, S.B.: Explosive dispersal of solid particles. Shock Waves 10, 431–443 (2001)
Zhang, F., Thibault, P.A., Link, R.A.: Shock interaction with solid particles in condensed matter and related momentum transfer. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 459, 705–726 (2003)
Ripley, R.C., Zhang, F., Lien, F.-S.: Acceleration and heating of metal particles in condensed matter detonation. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 468(2142), 1564–1590 (2012)
Zhang, F., Yoshinaka, A., Anderson, J., Ripley, R.: Confined heterogeneous blast. In: 19th International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Calgary (2006)
Frost, D.L., Zhang, F.: The nature of heterogeneous blast explosives. In: 19th International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Calgary (2006)
Yoshinaka, A., Zhang, F., Wilson, W.: Effect of shock compression on aluminum particles in condensed media. In: 15th APS Topical Meeting on Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, Kohala Coast (2007)
Kim, K., Wilson, W., Peiris, S., Needham, C., Watry, C., Ortley, D., Zhang, F.: Effects of particle damage during detonation of thermobarics on subsequent reactions. In: 21st International Colloquium on the Dynamics of Explosions and Reactive Systems, Poitiers (2007)
Ogura, T., Okada, K., Abe, T., Wakabayashi, K., Ishikawa, K., Kuroda, E., Matsumura, T., Nakayama, Y., Yoshida, M.: Pyrometry study on fireballs generated upon the explosion of TNT. In: 34th International Annual Conference of ICT—Energetic Materials: Reactions of Propellants, Explosives and Pyrotechnics, vol. 18, pp. 1–12 (2003)
Goroshin, S., Frost, D.L., Levine, J., Yoshinaka, A., Zhang, F.: Optical pyrometry of fireballs of metalized explosives. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 31(3), 169–181 (2006)
Frost, D.L., Goroshin, S., Janidlo, S., Pryszlak, J., Levine, J., Zhang, F.: Fragmentation of reactive metal particles during impact with a plate. In: 13th APS Topical Meeting on Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, Portland (2003)
Frost, D.L., Cairns, M., Goroshin, S., Leadbetter, J., Ripley, R.C., Zhang, F.: Reflected heterogeneous blast. In: 20th International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Oslo (2008)
Leadbetter, J., Ripley, R.C., Zhang, F.: Explosive dispersal of metal particles in urban street structures. In: International Symposium on the Effects of Munitions with Structures 12.1, Orlando (2007)
Leadbetter, J., Ripley, R.C., Zhang, F.: Fragmentation of metal particles in urban street explosions. In: 20th International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Oslo (2008)
Ripley, R.C., Cloney, C., Donahue, L., Frost, D.L., Zhang, F.: Enhanced loading due to reflected heterogeneous blast. In: 21st International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Jerusalem (2010)
Ripley, R.C., Zhang, F.: Effect of aerodynamic breakup on combustion of aluminum particles from heterogeneous explosives. In: 23rd International Colloquium on the Dynamics of Explosions and Reactive Systems, Irvine (2011)
Grady, D.E.: The spall strength of condensed matter. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 36(3), 353–384 (1988)
Yew, C.H., Grady, D.E., Lawrence, R.J.: A simple model for debris clouds produced by hypervelocity particle impact. Int. J. Impact Eng 14, 851–862 (1993)
Davison, L., Grady, D.E., Shahinpoor, M.: High Pressure Shock Compression of Solids II: Dynamic Fracture and Fragmentation. Springer, New York (1996)
Grady, D.E., Kipp, M.E.: Fragmentation properties of metals. Int. J. Impact Eng. 20(1–5), 293–308 (1997)
Kolev, N.I.: Acceleration induced droplet and bubble fragmentation. In: Multiphase Flow Dynamics 2, 3rd edn, pp 207–248. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Gelfand, B.E.: Droplet breakup phenomena in flows with velocity lag. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 22(3), 201–265 (1996)
Pilch, M., Erdman, C.A.: Use of breakup time data and velocity history data to predict the maximum size of stable fragments for acceleration-induced breakup of a liquid drop. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 13(6), 741–757 (1987)
Gale, W.F., Totemeier, T.C.: Smithells Metals Reference Book, 8th edn. Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2004)
Hatch, J.E.: Aluminum: Properties and Physical Metallurgy, 2nd edn. ASM International, Materials Park (1984)
Caveny, L.H., Gany, A.: Breakup of Al\(_{2}\)O\(_{3}\) agglomerates in accelerating flowfields. AIAA J. 17(12), 1368–1371 (1979)
Zhang, F., Wilson, W.H.: Reaction of fragments from cased explosive charges. In: 20th International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Oslo (2008)
Champagne, V.K., Helfritch, D.J., Trexler, M.D.: Some material characteristics of cold sprayed structures. Res. Lett. Mater. Sci. (2007). doi:10.1155/2007/27347
Christman, D.R., Isbell, W.M., Babcock, S.G., McMillan, A.R., Green, S.J.: Measurements of Dynamic Properties of Materials Volume III: 6061-T6 Aluminum, Tech. Rep. DNA Report DASA 2501-3, AD735966 (1971)
Grady, D.E., Kipp, M.E.: Impact failure and fragmentation properties of metals. Tech. Rep. SAND98-0387, Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, USA (1998)
Dykhuizen, R.C., Smith, M.F., Gilmore, D.L., Neiser, R.A., Jiang, X., Sampath, S.: Impact of high velocity cold spray particles. Tech. Rep. SAND98-2682J, Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, USA (1998)
Kipp, M.E., Grady, D.E., Swegle, J.W.: Experimental and numerical studies of high-velocity impact fragmentation. Tech. Rep. SAND93-0773, Sandia National Laboratories,Albuquerque, USA (1993)
Fauchais, P., Vardelle, A., Vardelle, M., Fukumoto, M.: Knowledge concerning splat formation: an invited review. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 13(3), 337–360 (2004)
Johnson, K.L.: Contact Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1985)
Ripley, R.C., Zhang, F., Leadbetter, J.: Acceleration, heating, and reaction of aluminum particles in condensed explosive dispersal. In: 20th International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Oslo (2008)
Needham, C.: Update on the status of numerical modeling of non-ideal explosives. In: 19th International Symposium on Military Aspects of Blast and Shock, Calgary (2006)
Donahue, L., Zhang, F., Ripley, R.C.: Numerical models for afterburning of TNT detonation products in air. Shock Waves 23(6), 559–573 (2013). doi:10.1007/s00193-013-0467-2
Zhang, F., Gerrard, K., Ripley, R.C.: Reaction mechanism of aluminum-particle-air detonation. J. Propuls. Power 25(4), 845–858 (2009)
Smirnov, N.: Combustion and detonation in multi-phase media: initiation of detonation in dispersed-film systems behind a shock wave. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 31(4), 779–793 (1988)
Lees, J., Williamson, B.H.J.: Combined very high pressure/high temperature calibration of the tetrahedral anvil apparatus, fusion curves of zinc, aluminum, germanium and silicon to 60 kilobars. Nature 208, 278–279 (1965)
Moriarty, J.A., Young, D.A., Ross, M.: Theoretical study of the aluminum melting curve to very high pressure. Phys. Rev. B 30(2), 578–588 (1984)
Gonor, A.L.: High-pressure vaporization and boiling of condensed material: a generalized Clausius–Clapeyron equation. In: 12th APS Topical Meeting on Shock Compression of Condensed Matter, Atlanta (2001)
Van Steenkiste, T.H., Smith, J.R., Teets, R.E.: Aluminum coatings via kinetic spray with relatively large power particles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 154, 237–252 (2002)
Janidlo, S.: High velocity impact and fragmentation of reactive metallic particles. Master’s thesis, McGill University, Canada (2004)
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly appreciate the contributions of J. Leadbetter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by L. Bauwens.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ripley, R.C., Donahue, L. & Zhang, F. Fragmentation of metal particles during heterogeneous explosion. Shock Waves 25, 151–167 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-015-0552-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-015-0552-9