Abstract
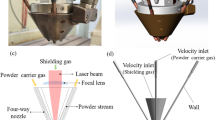
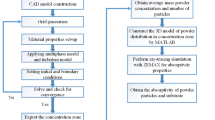
Pre-mixed powder is frequently used powder supply to fabricate functional gradient material by laser metal deposition (LMD). Argon gas flow blows the powder mixture following feeding pipe to melt pool in the LMD process. The powder mixture easily separates since the ingredient particles have different accelerations which are caused by different densities and sizes under the dynamic interaction with argon gas flow. This study investigated the argon gas flow rate’s effect on pre-mixed powder separation using modeling methodology. A CFD-DEM model, which gave consideration to both particle-particle collision and particle-argon gas flow interaction, was employed to simulate the pre-mixed powder flow in the feeding pipe. Three argon gas flow rates 6, 7, and 8 m/s were selected, analyzed, and compared based on their effects on powder mixture separations. Pre-mixed Cu and 4047 Al powders with equal volume percentages (50 to 50%) were investigated during their transportation process under three argon gas flow rates. All particles’ dynamic flow behaviors and the powder distributions were simulated and observed. The volume percentage of each kind of powder was plotted by quantifying the distribution of different particles after exiting the nozzle. It can be found that the intersection point of both powder volume percentages appeared increasingly earlier along with the increasing argon gas flow rate. To prove the correctness of the simulation results, the CFD-DEM model in this study was then validated by an experiment done by authors before. The results from this study are valuable contributions to the research of functionally graded material fabrication with pre-mixed powder through LMD process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li W, Zhang J, Zhang X, Liou F (2017) Effect of optimizing particle size on directed energy deposition of functionally graded material with blown pre-mixed multi-powder. Manufacturing Letters 13:39–43
Li W, Karnati S, Zhang Y, Liou F (2018) Investigating and eliminating powder separation in pre-mixed powder supply for laser metal deposition process. J Mater Process Technol 254:294–301
Li W, Chen X, Yan L, Zhang J, Zhang X, Liou F (2017) Additive manufacturing of a new Fe-Cr-Ni alloy with gradually changing compositions with elemental powder mixes and thermodynamic calculation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol
Li W, Yan L, Karnati S, Liou F, Newkirk J, Taminger KMB, Seufzer WJ (2017) Ti-Fe intermetallics analysis and control in joining titanium alloy and stainless steel by laser metal deposition. J Mater Process Technol 242:39–48
Carroll BE, Otis RA, Borgonia JP, Suh J-O, Dillon RP, Shapiro AA, Hofmann DC, Liu Z-K, Beese AM (2016) Functionally graded material of 304L stainless steel and inconel 625 fabricated by directed energy deposition: characterization and thermodynamic modeling. Acta Mater 108:46–54
Li W, Liou F, Newkirk J, Taminger KMB, Seufzer WJ (2017) Investigation on Ti6Al4V-V-Cr-Fe-SS316 multi-layers metallic structure fabricated by laser 3D printing. Sci Rep 7:7977
Li W, Karnati S, Kriewall C, Liou F, Newkirk J, Taminger KMB, Seufzer WJ, (2017) Fabrication and characterization of a functionally graded material from Ti-6Al-4 V to SS316 by laser metal deposition. Addit Manuf 14:95–104
Zhu H, Zhou Z, Yang R, Yu A (2008) Discrete particle simulation of particulate systems: a review of major applications and findings. Chem Eng Sci 63(23):5728–5770
Li W, Yan L, Chen X, Zhang J, Zhang X, Liou F (2018) Directed energy depositing a new Fe-Cr-Ni alloy with gradually changing composition with elemental powder mixes and particle size’effect in fabrication process. J Mater Process Technol 255:96–104
Zhao J, Shan T (2013) Coupled CFD–DEM simulation of fluid–particle interaction in geomechanics. Powder Technol 239:248–258
Parteli EJ, Pöschel T (2016) Particle-based simulation of powder application in additive manufacturing. Powder Technol 288:96–102
Haeri S, Wang Y, Ghita O, Sun J (2017) Discrete element simulation and experimental study of powder spreading process in additive manufacturing. Powder Technol 306:45–54
Guide, A. F. U 2011 Release 14.0, ANSYS fluent user manual. Inc., November
Parteli EJ. Using LIGGGHTS for performing DEM simulations of particles of complex shapes with the multisphere method," Proc. In: DEM6-6th International Conference on Discrete Element Methods and Related Techniques, Golden USA
Kloss C, Goniva C, Hager A, Amberger S, Pirker S (2012) Models, algorithms and validation for open source DEM and CFD–DEM. Prog Comput Fluid Dyn Int J 12(2–3):140–152
Zekovic S, Dwivedi R, Kovacevic R (2007) Numerical simulation and experimental investigation of gas–powder flow from radially symmetrical nozzles in laser-based direct metal deposition. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 47(1):112–123
Thompson SM, Bian L, Shamsaei N, Yadollahi A (2015) An overview of direct laser deposition for additive manufacturing; Part I: transport phenomena, modeling and diagnostics. Addit Manuf 8:36–62
Wen S, Shin Y, Murthy J, Sojka P (2009) Modeling of coaxial powder flow for the laser direct deposition process. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52(25):5867–5877
Lia W, Zhanga J, Karnatia S, Zhanga Y, Lioua F, Newkirkb J, Tamingerc K, Seufzerc W. Modeling and experimental investigation of pre-mixed multi-powder flow in fabricating functional gradient material by laser metal deposition process
Morsi S, Alexander A (1972) An investigation of particle trajectories in two-phase flow systems. J Fluid Mech 55(02):193–208
Pan H, Sparks T, Thakar YD, Liou F (2006) The investigation of gravity-driven metal powder flow in coaxial nozzle for laser-aided direct metal deposition process. J Manuf Sci Eng 128(2):541–553
Serag-Eldin M, Spalding D (1979) Computations of three-dimensional gas-turbine combustion chamber flows. J Eng Power 101(3):326–336
Launder BE, Spalding DB 1972 Lectures in mathematical models of turbulence
Deen N, Annaland MVS, Van der Hoef M, Kuipers J (2007) Review of discrete particle modeling of fluidized beds. Chem Eng Sci 62(1):28–44
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided for this study by the NASA EP-SCoR Grant number NNX13AM99A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Zhang, X. & Liou, F. Modeling analysis of argon gas flow rate’s effect on pre-mixed powder separation in laser metal deposition process and experimental validation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96, 4321–4331 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1909-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-1909-x