Abstract
Purposes
A fixed severe valgus knee is a surgical challenge. A safe post-operative Hip-Knee-Ankle angle (HKA) range of 180° ± 4 was recommended, but recent studies mentioned equal results from outliers of this range. Nevertheless, no distinction was made between varus and valgus knees, as well as over-corrected or under-corrected knees. Did post-operative nonaligned total knee replacements (TKR) from fixed severe valgus knees behave differently from the properly aligned population? Did over-corrected knees behave differently from under-corrected knees?
Methods
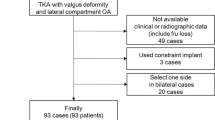
Through a multi-center retrospective cohort study, we provided 557 knees of at least 10° of minimal pre-operative valgus; in this population 75 presented a post-operative Hip-Knee-Ankle angle (HKA) outside of the 180° ± 4 range; 23 of them had at least 5° of varus; 52 of them had at least 5° of valgus. Median pre-operative HKA of the entire cohort was 194° (range 190–198). Median follow-up was 8 years (range 5–11); Knee Society Score (KSS) results, HKA, Femoral and Tibial Mechanical Angles (FMA, TMA) and complication rates were obtained. The outlier group (HKA ≤ 175 or ≥ 185) was compared to the control group (HKA 180 ± 4); over-corrected (HKA ≤ 175) and under-corrected (HKA ≥ 185) sub-groups were individually tested against the control group.
Results
The outlier group had a lower Final Knee Score than the aligned group (p = 0.023). In the over-corrected sub-group, median post-operative FMA was 88° (SD 4°) and median TMA was 87° (SD 4°). The complication rate was higher (p = 0.019). Knee (p = 0.018), Function (p = 0.034) and Final Knee Scores (p = 0.03) were statistically lower than in the control group. In the under-corrected sub-group, mean post-operative FMA was 93° (SD 2°) and mean TMA was 91° (SD 2°). The complication rate was lower (p = 0.019) and there was no difference with the control group concerning KSS.
Conclusions
In case of pre-operative fixed severe valgus knee, one should avoid over-correcting HKA angle and especially the TMA. Over-correction of a severe preoperative valgus in a post-operative varus was prejudicial for TKA survival. Keeping a severe valgus knee in low valgus to avoid using a more constrained implant and/or ligament releases will not decrease the 5–10 year implant survival and functional scores.
Level of evidence
Level IV—Case series.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brilhault J, Lautman S, Favard L, Burdin P (2002) Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy lateral release in total knee arthroplasty for a fixed valgus deformity. Bone Joint J 84:1131–1137
Charnley J (1972) The long-term results of low-friction arthroplasty of the hip performed as a primary intervention. Bone Joint J 54:61–76
Clarke HD, Fuchs R, Scuderi GR, Scott WN, Insall JN (2005) Clinical results in valgus total knee arthroplasty with the “Pie Crust” technique of lateral soft tissue releases. J Arthroplasty 20:1010–1014
Devane PA, Horne JG, Martin K, Coldham G, Krause B (1997) Three-dimensional polyethylene wear of a press-fit titanium prosthesis: factors influencing generation of polyethylene debris. J Arthroplasty 12:256–266
D’Lima DD, Chen PC, Colwell CW (2001) Polyethylene contact stresses, articular congruity, and knee alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:232–238
Eckhoff DG, Bach JM, Spitzer VM, Reinig KD, Bagur MM, Baldini TH, Flannery NM (2005) Three-dimensional mechanics, kinematics, and morphology of the knee viewed in virtual reality. J Bone Joint Surg 87:71–80
Gallo J, Goodman SB, Konttinen YT, Wimmer MA, Holinka M (2013) Osteolysis around total knee arthroplasty: a review of pathogenetic mechanisms. Acta Biomater 9:8046–8058
Hadi M, Barlow T, Ahmed I, Dunbar M, McCulloch P, Griffin D (2016) Does malalignment affect patient reported outcomes following total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of the literature. SpringerPlus 5:1201
Huang T-W, Chuang P-Y, Lee C-Y, Lin S-J, Huang K-C, Shen S-H, Tsai Y-H, Lee MS, Hsu RW-W (2016) Total knee arthroplasty in patients with Ranawat type-II valgus arthritic knee with a marked coronal femoral bowing deformity: comparison between computer-assisted surgery and intra-articular resection. J Orthop Surg 11:88
Insall J, Ranawat CS, Scott WN, Walker P (1976) Total condylar knee replacment: preliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res 120:149–154
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Keblish PA (1991) The lateral approach to the valgus knee. Surgical technique and analysis of 53 cases with over two-year follow-up evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 271:52–62
Kim Y-H, Park J-W, Kim J-S, Park S-D (2014) The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment of knee prosthesis. Int Orthop 38:379–385
Krackow KA, Jones MM, Teeny SM, Hungerford DS (1991) Primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with fixed valgus deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res 273:9–18
Lombardi AV, Berend KR, Ng VY (2011) Neutral mechanical alignment: a requirement for successful TKA: affirms. Orthopedics 34:504–506
Magnussen RA, Weppe F, Demey G, Servien E, Lustig S (2011) Residual varus alignment does not compromise results of TKAs in patients with preoperative varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:3443–3450
Martin JR, Beahrs TR, Stuhlman CR, Trousdale RT (2016) Complex primary total knee arthroplasty: long-term outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg 98:1459–1470
Miyasaka KC, Ranawat CS, Mullaji A (1997) 10- to 20-year followup of total knee arthroplasty for valgus deformities. Clin Orthop Relat Res 345:29–37
Mont MA, Mahoney OM (2010) Commentary on an Article by Sebastien Parratte, MD., PhD et al.: “Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements”. J Bone Joint Surg 92-A:e16(1)–e16(2)
Nikolopoulos D, Michos I, Safos G, Safos P (2015) Current surgical strategies for total arthroplasty in valgus knee. World J Orthop 6:469
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ (2010) Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg 92:2143–2149
Peters CL, Jimenez C, Erickson J, Anderson MB, Pelt CE (2013) Lessons learned from selective soft-tissue release for gap balancing in primary total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 1216 consecutive total knee arthroplasties: AAOS exhibit selection. J Bone Joint Surg 95:e152-1
Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, Rasquinha VJ, Rossi R, Babhulkar S (2005) Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg 87:271–284
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Davis P, Farris A, Malinzak RA, Berend ME, Meding JB (2013) Preoperative malalignment increases risk of failure after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 95:126–131
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Meding JB, Pierson JL, Berend ME, Malinzak RA (2011) The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg 93:1588–1596
Rodriguez JA, Bas MA, Orishimo KF, Robinson J, Nicholas SJ (2016) Differential effect of total knee arthroplasty on valgus and varus knee biomechanics during Gait. J Arthroplasty 31:248–253
Schmalzried TP, Szuszczewicz ES, Northfield MR, Akizuki KH, Frankel RE, Belcher G, Amstutz HC (1998) Quantitative assessment of walking activity after total hip or knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg 80:54–59
Shan L, Shan B, Suzuki A, Nouh F, Saxena A (2015) Intermediate and long-term quality of life after total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg 97:156–168
Smith CR, Vignos MF, Lenhart RL, Kaiser J, Thelen DG (2016) The influence of component alignment and ligament properties on tibiofemoral contact forces in total knee replacement. J Biomech Eng 138:021017
Stucinskas J, Robertsson O, Sirka A, Lebedev A, Wingstrand H, Tarasevicius S (2015) Moderate varus/valgus malalignment after total knee arthroplasty has little effect on knee function or muscle strength. Acta Orthop 86:728–733
Werner FW, Ayers DC, Maletsky LP, Rullkoetter PJ (2005) The effect of valgus/varus malalignment on load distribution in total knee replacements. J Biomech 38:349–355
Whiteside LA (1993) Correction of ligament and bone defects in total arthroplasty of the severely valgus knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 288:234–245
Funding
No funding was necessary for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
French Orthopedic Society SOFCOT does not require an ethical approval statement for inhouse studies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyer, B., Pailhé, R., Ramdane, N. et al. Under-corrected knees do not fail more than aligned knees at 8 years in fixed severe valgus total knee replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26, 3386–3394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-4906-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-4906-6