Abstract
Purpose
Intramedullary rods are widely used to align the distal femoral cut in total knee arthroplasty. We hypothesised that both coronal (varus/valgus) and sagittal (extension/flexion) cutting plane are affected by rotational changes of intramedullary femoral alignment guides.
Methods
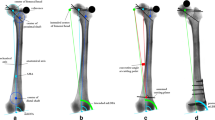
Distal femoral cuts using intramedullary alignment rods were simulated by means of a computer-aided engineering software in 4°, 6°, 8°, 10°, and 12° of valgus in relation to the femoral anatomical axis and 4° extension, neutral, as well as 4°, 8°, and 12° of flexion in relation to the femoral mechanical axis. This reflects the different angles between anatomical and mechanical axis in coronal and sagittal planes. To assess the influence of rotation of the alignment guide on the effective distal femoral cutting plane, all combinations were simulated with the rod gradually aligned from 40° of external to 40° of internal rotation.
Results
Rotational changes of the distal femoral alignment guides affect both the coronal and sagittal cutting planes. When alignment rods are intruded neutrally with regards to sagittal alignment, external rotation causes flexion, while internal rotation causes extension of the sagittal cutting plane. Simultaneously the coronal effect (valgus) decreases resulting in an increased varus of the cutting plane. However, when alignment rods are intruded in extension or flexion partly contradictory effects are observed. Generally the effect increases with the degree of valgus preset, rotation and flexion.
Conclusion
As incorrect rotation of intramedullary alignment guides for distal femoral cuts causes significant cutting errors, exact rotational alignment is crucial. Coronal cutting errors in the distal femoral plane might result in overall leg malalignment, asymmetric extension gaps and subsequent sagittal cutting errors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cinotti G, Sessa P, Rocca AD, Ripani FR, Giannicola G (2013) Effects of tibial torsion on distal alignment of extramedullary instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 84:275–279
Elloy MA, Manning MP, Johnson R (1992) Accuracy of intramedullary alignment in total knee replacement. J Biomed Eng 14:363–370
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 24:39–43
Gromov K, Korchi M, Thomsen MG, Husted H, Troelsen A (2014) What is the optimal alignment of the tibial and femoral components in knee arthroplasty? Acta Orthop 85:480–487
Harding IJ, Crawford RW, Mclardy-Smith P, Murray DW (1999) The importance of femoral intramedullary entry point in knee arthroplasty. Knee 6:207–210
Huang NF, Dowsey MM, Ee E, Stoney JD, Babazadeh S, Choong PF (2012) Coronal alignment correlates with outcome after total knee arthroplasty: five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty 27:1737–1741
Jiang CC, Insall JN (1989) Effect of rotation on the axial alignment of the femur. Pitfalls in the use of femoral intramedullary guides in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:50–56
Keshmiri A, Springorum HR, Baier C, Zeman F, Grifka J, Maderbacher G (2016) Changes in sagittal component alignment alters patellar kinematics in TKA: an in vitro study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24:823–829. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4004-6
Ma B, Long W, Rudan JF, Ellis RE (2006) Three-dimensional analysis of alignment error in using femoral intramedullary guides in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 21:271–278
Maderbacher G, Baier C, Benditz A, Wagner F, Greimel F, Grifka J, Keshmiri A (2017) Presence of rotational errors in long leg radiographs after total knee arthroplasty and impact on measured lower limb and component alignment. Int Orthop 41:1553–1560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3408-3
Maderbacher G, Keshmiri A, Schaumburger J, Zeman F, Birkenbach AM, Craiovan B, Grifka J, Baier C (2017) What is the optimal valgus pre-set for intramedullary femoral alignment rods in total knee arthroplasty? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:3480–3487
Maderbacher G, Schaumburger J, Baier C, Zeman F, Springorum HR, Birkenbach AM, Grifka J, Keshmiri A (2016) Appropriate sagittal femoral component alignment cannot be ensured by intramedullary alignment rods. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24:2453–2460
Mihalko WM, Boyle J, Clark LD, Krackow KA (2005) The variability of intramedullary alignment of the femoral component during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20:25–28
Mizu-uchi H, Matsuda S, Miura H, Hikagi H, Okazaki K, Iwamoto Y (2006) The effect of ankle rotation on cutting of the tibia in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 88:2632–2636
Nuño-Siebrecht N, Tanzer M, Bobyn JD (2000) Potential errors in axial alignment using intramedullary instrumentation for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 15:228–230
Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM (1993) Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 8:419–426
Reed SC, Gollish J (1997) The accuracy of femoral intramedullary guides in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 12:677–682
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Tan H, Wang Y, Long T, Nie B, Mao Z, Yue B (2018) How to accurately determine the distal femoral valgus cut angle in the valgus knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3778-1. [Epub ahead of print]
Teter KE, Bregman D, Colwell CW Jr (1995) The efficacy of intramedullary femoral alignment in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 321:117–121
Tsukeoka T, Tsuneizumi Y, Lee TH (2013) The effect of rotational fixation error of the tibial cutting guide and the distance between the guide and the bone on the tibial osteotomy in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 28:1094–1098
Tsukeoka T, Tsuneizumi Y, Lee TH (2013) The effect of the posterior slope of the tibial plateau osteotomy with a rotational error on tibial component malalignment in total knee Replacement. Bone Joint J 95-B:1201–1203
Victor J (2009) Rotational alignment of the distal femur: a literature review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 95:365–372
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG (1994) Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–43
Yehyawi TM, Callaghan JJ, Pedersen DR, O’Rourke MR, Liu SS (2007) Variances in sagittal femoral shaft bowing in patients undergoing TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 464:99–104
Funding
No financial contributions were received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
As a three-dimensional computer simulation of cutting block alignment was performed, an approval of the local ethical committee was not necessary and a statistical analysis cannot be provided.
Informed consent
For this type of formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maderbacher, G., Matussek, J., Keshmiri, A. et al. Rotation of intramedullary alignment rods affects distal femoral cutting plane in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26, 3311–3316 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-4875-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-4875-9