Abstract
Purpose
To examine implant migration and articular behavior of primary total knee arthroplasty (TKA) at 10 years after index surgery and correlate to implant alignment.
Methods
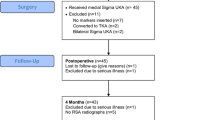
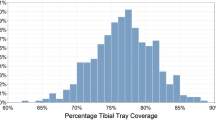
Thirty-five patients underwent a cemented posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty with a surgical objective of neutral alignment and were enrolled in a long-term radiostereometric analysis (RSA) study. At 10 years after surgery, patients were analyzed for implant migration using RSA as well as radiographic assessment of articular behavior at four positions of knee flexion. Implant position and alignment was measured on full-length radiographs. Patient demographics and reported outcomes were also collected.
Results
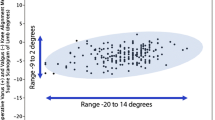
No difference between patient demographics or patient-reported outcomes were found. When categorized into neutral and varus groupings, no difference in migration was present. If alignment was considered as a continuous variable, there was no correlation between overall leg alignment and migration, however, migration increased with an increasing varus tibial alignment. Although contact location did not differ between neutral and varus groups through a range of motion, condylar liftoff was much more common in the varus group, of which all were lateral liftoff.
Conclusions
Increased tibial varus results in increased implant migration. Overall varus limb alignment is correlated with isolated lateral compartment liftoff, and liftoff occurs more commonly than in neutral aligned knees. The increased migration and liftoff raise concerns about the longevity of malaligned total knee replacements. If a goal of overall varus limb alignment is desired for TKA, the tibia should remain neutral.
Level of evidence
Level III.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, Victor J (2012) The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:45–53
Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB, Faris PM, Keating EM, Redelman R, Faris GW, Davis KE. (2004) Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 19:26–34
Bourne RB, Chesworth BM, Davis AM, Mahomed NN, Charron KD (2010) Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: who is satisfied and who is not? Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:57–63
Cooke TD, Sled EA, Scudamore RA (2007) Frontal plane knee alignment: a call for standardized measurement. J Rheumatol 34:1796–1801
de Vries LM, van der Weegen W, Pilot P, Stolarczyk PA, Sijbesma T, Hoffman EL (2014) The predictive value of radiostereometric analysis for stem survival in total hip arthroplasty. A systematic review. Hip Int 24:215–222
Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Kim RH, Sharma A (2010) Gap balancing versus measured resection technique for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:102–107
Fleming BC, Peura GD, Abate JA, Beynnon BD (2001) Accuracy and repeatability of Roentgen stereophotogrammetric analysis (RSA) for measuring knee laxity in longitudinal studies. J Biomech 34:1355–1359
Hamai S, Miura H, Okazaki K, Shimoto T, Higaki H, Iwamoto Y (2014) No influence of coronal laxity and alignment on lift-off after well-balanced and aligned total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:1799–1804
Insall JN, Scuderi GR, Komistek RD, Math K, Dennis DA, Anderson DT (2002) Correlation between condylar lift-off and femoral component alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 403:143–152
Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Lau E, Bozic KJ (2014) Impact of the economic downturn on total joint replacement demand in the United States: updated projections to 2021. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96:624–630
Liau JJ, Cheng CK, Huang CH, Lo WH (2002) The effect of malalignment on stresses in polyethylene component of total knee prostheses–a finite element analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 17:140–146
Lombardi AV Jr, Berend KR, Ng VY (2011) Neutral mechanical alignment: a requirement for successful TKA: affirms. Orthopedics 34:e504-506
Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Harimaya K, Matsunobu T, Iwamoto Y (1999) Changes in knee alignment after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 14:566–570
Morgan SS, Bonshahi A, Pradhan N, Gregory A, Gambhir A, Porter ML (2008) The influence of postoperative coronal alignment on revision surgery in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 32:639–642
Mu S, Moro-Oka T, Johal P, Hamai S, Freeman MA, Banks SA (2011) Comparison of static and dynamic knee kinematics during squatting. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 26:106–108
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ (2010) Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92:2143–2149
Perillo-Marcone A, Barrett DS, Taylor M (2000) The importance of tibial alignment: finite element analysis of tibial malalignment. J Arthroplasty 15:1020–1027
Pijls BG, Valstar ER, Nouta KA, Plevier JW, Fiocco M, Middeldorp S, Nelissen RG (2012) Early migration of tibial components is associated with late revision: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 21,000 knee arthroplasties. Acta Orthop 83:614–624
Prins AH, Kaptein BL, Banks SA, Stoel BC, Nelissen RG, Valstar ER (2014) Detecting condylar contact loss using single-plane fluoroscopy: a comparison with in vivo force data and in vitro bi-plane data. J Biomech 47:1682–1688
Riviere C, Iranpour F, Auvinet E, Howell S, Pascal A, Cobb J, SebastienParratte. (2017) alignment options for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res
Saevarsson SK, Romeo CI, Anglin C (2013) Are static and dynamic kinematics comparable after total knee arthroplasty? J Biomech 46:1169–1175
Teeter MG, Thoren J, Yuan X, McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Lanting BA, Naudie DD (2016) Migration of a cemented fixed-bearing, polished titanium tibial baseplate (Genesis II) at ten years : a radiostereometric analysis. Bone Joint J 98B:616–621
Thienpont E, Cornu O, Bellemans J, Victor J (2015) Current opinions about coronal plane alignment in total knee arthroplasty: A survey article. Acta Orthop Belg 81:471–477
Valstar ER, Nelissen RG, Reiber JH, Rozing PM (2002) The use of Roentgen stereophotogrammetry to study micromotion of orthopaedic implants. ISPRS J Photogramm 56:376–389
Vandekerckhove PJ, Lanting B, Bellemans J, Victor J, MacDonald S (2016) The current role of coronal plane alignment in total knee arthroplasty in a preoperative varus aligned population: an evidence based review. Acta Orthop Belg 82:129–142
Vandekerckhove PJ, Teeter MG, Naudie DD, Howard JL, MacDonald SJ, Lanting BA (2015) The impact of wear and lift-off on coronal plane alignment in TKA and implications to future constrained revision: a retrieval study. J Arthroplasty 30:2017–2020
Vandekerckhove PT, Matlovich N, Teeter MG, MacDonald SJ, Howard JL, Lanting BA (2017) The relationship between constitutional alignment and varus osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25:2873–2879
Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Claes S, Bellemans J (2013) Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2325–2330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MGT participated in the design of the study, conducted the statistical analysis, and co-wrote the initial manuscript draft. DDN, RWM, DWH, and SJM conceived of the initial migration study and collected the data. XY collected patient images and analyzed the data. BAL participated in the design of the study, collected the alignment data, and co-wrote the initial manuscript draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
One of the authors (DDN) is a paid consultant to Microport, Smith & Nephew, and Zimmer Biomet, and receives royalties from Smith & Nephew. One of the authors (RWM) is a paid consultant to Smith & Nephew. One of the authors (SJM) is a paid consultant to DePuy. One of the authors (BAL) is a paid consultant to DePuy, Smith & Nephew, and Stryker.
Funding
Smith & Nephew provided research funds in support of the study, but were not involved in study design or data analysis.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the institution.
Informed consent
Patients were informed, and they contented to conduct the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teeter, M.G., Naudie, D.D., McCalden, R.W. et al. Varus tibial alignment is associated with greater tibial baseplate migration at 10 years following total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26, 1610–1617 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4765-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4765-6