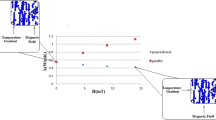
Abstract.
Magnetorheological (MR) fluids are a class of smart materials whose rheological properties may be rapidly modified by the application of a magnetic field. These materials typically consist of micron-sized ferrous particles dispersed in a fluid. In the present paper, we consider the full system of equations as well as the Clausius-Duhem inequality for moving isotropic MR fluids in an electro-magnetic field. We present the material constitutive relations for a non-Newtonian incompressible MR fluid. To illustrate the validity of the constitutive relations, the flow of a MR fluid between two parallel fixed plates under the influence of a constant magnetic field perpendicular to the flow direction is considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkovsky, B.M., Medvedev, V.F., Krakov, M.S.: Magnetic Fluids - Engineering Applications. Oxford: Oxford University Press 1993
Berkovsky, B.M.: Magnetic Fluids and Application Handbook. New York: Begell House 1996
Blums, E., Cebers, A., Maiorov. M.M.: Magnetic Fluids. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter 1997
Brigadnov, I.A.: Mathematical correctness and numerical methods for solution of the plasticity initial-boundary value problems. Mech. Solids 4, 62-74 (1996)
Brown, W.F.: Magnetoelastic Interactions. Springer, Berlin 1966
Carlson, J.D., Catanzarite, D.M., St. Clair, K.A.: Commercial magnetorheological fluid devices. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 10, 2857-2865 (1996)
Carlson, J.D., Jolly, M.R.: MR fluid, foam and elastomer devices. Mechatronics 10, 555-569 (2000)
Drozdov, A.D.: Finite Elasticity and Viscoelasticity: A Course in the Nonlinear Mechanics of Solids. Singapure: World Scientific 1996
Dyke, S.J., Spencer, B.F. Jr., Sain, M.K., Carslon, J.D.: Modeling and Control of Magnetorheological Dampers for Seimic Response Reduction. Smart Mat. Struct. 5, 565-575 (1996)
Eringen, A.C.: Mechanics of Continua. New York: Wiley 1980
Eringen, A.C., Maugin, G.: Electrodynamics of Continua, Vol. I and II. New York: Springer 1989
Felt, D.W., Hagenbüchle, M., Liu, J.: Rheology of a magnetorheological fluid. J. Intelligent Mater. Syst. Struct. 7, 589-593 (1996)
Hutter, K., van de Ven, A.A.F.:Field Matter Interactions in Thermoelastic Solids. Lecture Notes in Physics, vol. 88, Springer, Berlin 1978
Jackson, J.D.: Klassische Elektrodynamik. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter (1983)
Jolly, M.R., Carlson, J.D., Muñoz, B.C.: A model of the behaviour of magnetorheological materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 5, 607-614 (1996)
Jolly, M.R., Bender, J.W., Carlson, J.D.: Properties and application of commercial magnetorheological fluids. SPIE 5th Annual Int. Symp. on Smart Structures and Materials, San Diego, CA 1998
Jolly, M.R., Bender, J.W., Mathers, R.T.: Indirect measurements of microstructure development in magnetorheological fluids. Int. J. Modern Phys. B 13, 2036-2043 (1999)
Kordonsky, W.: Magnetorheological effects as a base of new devices and technologies. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 122, 395-398 (1993)
Kovetz, A.: Electromagnetic Theory. New York, Oxford: University Press 2000
Lazareva, T.G., Kabisheva, I.V., Prodan, S.A.: Homogeneous magnetorheological materials. J. Intelligent Mater. Syst. Struct. 9, 655-661 (1998)
Lurie, A.I.: Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity. Amsterdam: North-Holland 1990
Minkowski, H.: Die Grundgleichungen für die elektromagnetischen Vorgänge in bewegten Körpern. Göttinger Nach., 53-111 (1908)
Mohebi, M., Jamashi, N., Flores, G.A., Jing Liu: Numerical study of the role of magnetic field ramping rate on the structure formation in magnetorheological fluids, Int. J. Modern Phys. 13, 2060-2067 (1999)
Nakato, M., Yamamoto, H.: Dynamic viscoelasticity of a magnetorheological fluid in oscillatory slit flow. Int. J. Modern Phys. 13, 2068-2076 (1999)
Nečas, J., Ŝilhavý, M.: Viscous Multipolar Fluids. Quart. Appl. Math. 49, 247-265 (1991)
Pao, Y.H.: Electromagnetic Forces in Deformable Continua. In: Nevat-Nasser, S. (ed.): Mechanics Today. Vol. 4. Pergamon Press, 1978, pp. 209-306
Rabinow, J.: The magnetic fluid clutch. AIEE Trans. 67, 1308-1315 (1948)
Rajagopal, K.R., Yalamanchili, R.C., Wineman, A.S.: Modeling electro-rheological materials through mixture theory. Int. J. Engng. Sci. 32(3), 481-500 (1994)
Rajagopal, K.R., R\(\mathring{\textrm u}\)žička, M.: Mathematical modeling of electrorheological materials. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 13, 59-78 (2001)
Rajagopal, K.R., Tao, L.: Modeling of the microwave drying process of aqueous dielectrics. Z. angev. Math. Phys. 53, 923-948 (2002)
Rosensweig, R.E.: Ferrohydrodynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1985
Spencer, A.J.M.: Theory of Invariants. In: Eringen, A.c. (ed.): Continuum Physics Vol. 1. New York: Academic Press 1971
Truesdell, C., Toupin, R.: The Classical Field Theories. In: Flügge, W. (ed.): Handbuch der Physik, Vol. III/1. New York: Springer 1960
Truesdell, C.: Rational Thermodynamics. New York: Springer (1984)
Truesdell, C.: First Course in Rational Continuum Mechanics, Vol. I. New York: Academic Press 1991
Truesdell, C., Noll, W.: The Non-Linear Field Theories of Mechanics, 2nd edn. Berlin: Springer 1992
Weiss, K.D., Carlson, J.D., Nixon, D.A.: Viscoelastic properties of magneto- and electrorheological fluids. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. & Struct. 5, 772-775 (1994)
Wineman, A.S., Rajagopal, K.R.: On constitutive equations for electrorheological materials. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 7, 1-22 (1995)
Winslow, W.M.: Induced vibration of suspensions. J. Appl. Phys. 20, 1137-1140 (1949)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K.R. Rajagopal
Received: 14 July 2003, Accepted: 18 May 2004, Published online: 22 February 2005
Correspondence to: A. Dorfmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brigadnov, I.A., Dorfmann, A. Mathematical modeling of magnetorheological fluids. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 17, 29–42 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-004-0185-1
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-004-0185-1