Abstract
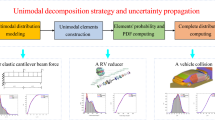
In practical engineering applications, random variables may follow multimodal distributions with multiple modes in the probability density functions, such as the structural fatigue stress of a steel bridge carrying both highway and railway traffic and the vibratory load of a blade subject to stochastic dynamic excitations, etc. Traditional uncertainty propagation methods are mainly used to treat random variables with only unimodal probability density functions, which, therefore, tend to result in large computational errors when multimodal probability density functions are involved. In this paper, an uncertainty propagation method is developed for problems in which multimodal probability density functions are involved. Firstly, the multimodal probability density functions of input random variables are established using the Gaussian mixture model. Secondly, the uncertainties of the input random variables are propagated to the response function through an integration of the sparse grid numerical method and maximum entropy method. Finally, the convergence mechanism is developed to improve the uncertainty propagation accuracy step by step. Two numerical examples and one engineering application are studied to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirinia G, Kamranzad B, Mafi S (2017) Wind and wave energy potential in southern Caspian Sea using uncertainty analysis. Energy 120:332–345
Augusti G, Baratta A, Casciati F (1984) Probabilistic methods in structural engineering. Chapman and Hall
Balakrishnan S, Wainwright MJ, Yu B (2017) Statistical guarantees for the EM algorithm: from population to sample-based analysis. Ann Stat 45(1):77–120
Ballaben JS, Sampaio R, Rosales MB (2017) Uncertainty quantification in the dynamics of a guyed mast subjected to wind load. Eng Struct 132:456–470
Ban Z, Liu J, Cao L (2018) Superpixel segmentation using Gaussian mixture model. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(8):4105–4117
Brietung K (1984) Asymptotic approximations for multinormal integral. J Eng Mech 110(3):357–366
Bucher CG (1988) Adaptive sampling-an iterative fast Monte Carlo procedure. Struct Saf 5(2):119–126
Dempster A, Laird N, Rubin D (1977) Maximum likelihood estimation from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc B 39:1–38
Doltsinis I, Kang Z (2004) Robust design of structures using optimization methods. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(23–26):2221–2237
Du X, Chen W (2002) Sequential optimization and reliability assessment method for efficient probabilistic design. J Mech Des 126(2):871–880
Echard B, Gayton N, Lemaire M (2011) AK-MCS: an active learning reliability method combining kriging and Monte Carlo simulation. Struct Saf 33:145–154
Figueiredo MAT, Jian AK (2002) Unsupervised learning of finite mixture models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24(3):381–396
Gerstner T, Griebel M (1998) Dimension integration using sparse grids. Numerical Algorithms 18(3–4):209–232
Haider SW, Harichandran RS, Dwaikat MB (2009) Closed-form solutions for bimodal axle load spectra and relative pavement damage estimation. J Transp Eng 135(12):974–983
He J, Gao S, Gong J (2014) A sparse grid stochastic collocation method for structural reliability analysis. Struct Saf 51:29–34
He J, Guan X, Jha R (2016) Improve the accuracy of asymptotic approximation in reliability problems involving multimodal distributions. IEEE Trans Reliab 65(4):1724–1736
Hu Z, Du X (2017) A mean value reliability method for bimodal distributions, in: Proceedings of the ASME 2017 International Design Engineering Technical Conference & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Paper DETC 2017–67279
Jaynes ET (1957) Information theory and statistical mechanics. Phys Rev 106(4):620
Keshavarzzadeh V, Fernandez F, Tortorelli DA (2017) Topology optimization under uncertainty via non-intrusive polynomial chaos expansion. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 318:120–147
Keshtegar B, Chakraborty S (2018) A hybrid self-adaptive conjugate first order reliability method for robust structural reliability analysis. Appl Math Model 53:319–332
Khan FA, Khelifi F, Tahir MA, Bouridane A (2019) Dissimilarity Gaussian mixture models for efficient offline handwritten text-independent identification using SIFT and RootSIFT descriptors. IEEE T Inf Foren Sec 14(2):289–303
Lee SH, Chen W (2009) A comparative study of uncertainty propagation methods for black-box-type problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37(3):239–253
Lee SH, Kwak BM (2006) Response surface augmented moment method for efficient reliability analysis. Struct Saf 28:261–272
Lima RS, Kucuk A, Berndt CC (2002) Bimodal distribution of mechanical properties on plasma sprayed nanostructured partially stabilized zirconia. Materials Science & Engineering A 327(2):224–232
Low BK, Tang WH (2007) Efficient spreadsheet algorithm for first-order reliability method. J Eng Mech 133(12):1378–1387
MaiTre OPL, Knio OM, Najm HN, Ghanem RG (2004) Uncertainty propagation using wiener–Haar expansions. J Comput Phys 197(1):28–57
Melchers RE (1999) Structural reliability analsyis and prediction. John Willy & Sons
Moens E, Araújo NA, Vicsek T, Herrmann HJ (2014) Shock waves on complex networks. Sci Rep 4:4949
Mori Y, Kato T (2003) Multinormal integrals by importance sampling for series system reliability. Struct Saf 25(4):363–378
Ni YQ, Ye XW, Ko JM (2010) Monitoring-based fatigue reliability assessment of steel bridges: analytical model and application. J Struct Eng 136(12):1563–1573
Ni YQ, Ye XW, Ko JM (2011) Modeling of stress spectrum using long-term monitoring data and finite mixture distributions. J Eng Mech 138(2):175–183
Pan Q, Dias D (2017) An efficient reliability method combining adaptive support vector machine and Monte Carlo simulation. Struct Saf 67:85–95
Papadrakakis M, Stefanou G, Papadopoulos V (2010) Computational methods in stochastic dynamics. Springer
Pranesh S, Ghosh D (2018) A FETI-DP based parallel hybrid stochastic finite element method for large stochastic systems. Comput Struct 195:64–73
Rackwitz R, Flessler B (1978) Structural reliability under combined random load sequences. Comput Struct 9(5):489–494
Rasmussen CE (2000) The infinite Gaussian mixture model. Adv Neural Inf Proces Syst 12(11):554–560
Redner RA, Walker HF (1984) Mixture densities, maximum likelihood and the EM algorithm. SIAM Rev:195–239
Schuöllera GI, Jensen HA (2008) Computational methods in optimization considering uncertainties-an overview. Computer Methods in Applied Mechinics and Engineering 198(1):2–13
Shi Y, Lu Z, Chen S, Xu L (2018) A reliability analysis method based on analytical expressions of the first four moments of the surrogate model of the performance function. Mech Syst Signal Process 111:47–67
Smolyak SA (1963) Quadrature and interpolation formulas for tensor products of certain classes of functions. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 4:240–243
Stefanou G (2009) The stochastic finite element method: past, present and future. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198(9–12):1031–1051
Timm DH, Tisdale SM, Turochy RE (2005) Axle load spectra characterization by mixed distribution modelling. J Transp Eng 131(2):83–88
Xia B, Lü H, Yu D, Jiang C (2015) Reliability-based design optimization of structural systems under hybrid pobabilistic and interval model. Comput Struct 160:126–134
Xiong F, Greene S, Chen W, Xiong Y, Yang S (2010) A new sparse grid based method for uncertianty propagation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(3):335–349
Xiu D, Hesthaven J (2005) High order collocation method for differential equations with random inputs. SIAM J Sci Comput 27(3):1118–1139
Xu J, Dang C, Kong F (2017) Efficient reliability analysis of structures with the rotational quasi-symmetric point- and the maximum entropy methods. Mech Syst Signal Process 95:58–76
Youn BD, Choi KK, Yang RJ, Gu L (2004) Reliability-based design optimization for crashworthiness of vehicle side impact. Struct Multidiscip Optim 26(3–4):272–283
Zellner A, Highfield RA (1988) Calculation of maximum entropy distributions and approximation of marginalposterior distributions. J Econ 37:195–209
Zhang J, Du X (2010) A second-order reliability method with first-order efficiency. J Mech Des 132(10):1006–1014
Zhang X, He J, Takezawa A, Kang Z (2018) Robust topology optimization of phononic crystals with random field uncertainty. Int J Numer Methods Eng 115(5):1154–1173
Zhang Z, Jiang C, Han X, Ruan XX (2019) A high-precision probabilistic uncertainty propagation method for problems involving multimodal distributions. Mech Syst Signal Pr, accepted
Zhao YG, Ono T (2001) Moment methods for structural reliability. Struct Saf 23(1):47–75
Zivkovic Z (2004) Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on pattern recognition
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51805157, Grant No. 51725502 and Grant No. 51490662), Hunan Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2019JJ40015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Byeng D Youn
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(RAR 6 kb)
Appendix
Appendix
Deduction of the ith non-standard central moment \( {m}_i^{\prime } \):
where
Therefore, \( {m}_i^{\prime } \) is rewritten as:
According to the rules of integral operation:
\( {B}_i^{j+1}=\left(\begin{array}{c}i\\ {}j\end{array}\right) \) is the binomial coefficient. Let j = j + 1, then, we obtain:
where \( {B}_i^j=\left(\begin{array}{c}i\\ {}j-1\end{array}\right) \).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Wang, J., Jiang, C. et al. A new uncertainty propagation method considering multimodal probability density functions. Struct Multidisc Optim 60, 1983–1999 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02301-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02301-y