Abstract
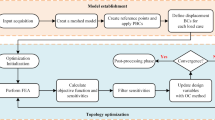
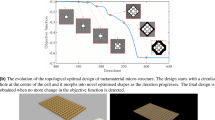
A novel design concept for buckling-induced mechanical metamaterials for energy absorption is presented. The force-displacement curves of the mechanical metamaterials are analyzed according to the curves of their unit cells, and the energy-absorbing characteristics of mechanical metamaterials are evaluated. Two topology optimization models are proposed. One maximizes the buckling-induced dissipated energy to facilitate the design of metamaterials with high energy absorption and low elastic strain energy. The other maximizes the dissipated energy with a constraint that the mechanical metamaterials should be self-recoverable. An energy interpolation scheme is employed to avoid numerical instabilities in the geometric nonlinear finite element analysis. A two-phase algorithm is proposed to find the optimized result from a uniform initial guess, and sensitivity analysis is performed. The optimized design has a larger amount of buckling-induced dissipated energy than the previously proposed structural prototypes. Moreover, the self-recoverable mechanical metamaterial is successfully designed by topology optimization.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bochenek B, Tajs-Zielińska K (2015) Minimal compliance topologies for maximal buckling load of columns. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51(5):1149–1157
Bruns TE, Sigmund O (2004) Toward the topology design of mechanisms that exhibit snap-through behavior. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(36):3973–4000
Bruns TE, Sigmund O, Tortorelli DA (2002) Numerical methods for the topology optimization of structures that exhibit snap-through. Int J Numer Methods Eng 55(10):1215–1237
Bruyneel M, Duysinx P, Fleury C (2002) A family of mma approximations for structural optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 24(4):263–276
Che K, Yuan C, Wu J, Qi HJ, Meaud J (2017) Three-dimensional-printed multistable mechanical metamaterials with a deterministic deformation sequence. J Appl Mech 84(1):011004
Correa DM, Klatt T, Cortes S, Haberman M, Kovar D, Seepersad C (2015) Negative stiffness honeycombs for recoverable shock isolation. Rapid Prototyp J 21(2):193–200
Costas M, Díaz J, Romera L, Hernández S (2014) A multi-objective surrogate-based optimization of the crashworthiness of a hybrid impact absorber. Int J Mech Sci 88:46–54
Deepak SR, Dinesh M, Sahu DK, Ananthasuresh GK (2009) A comparative study of the formulations and benchmark problems for the topology optimization of compliant mechanisms. J Mech Robot 1(1):011003
Dunning PD, Ovtchinnikov E, Scott J, Alicia Kim H (2016) Level-set topology optimization with many linear buckling constraints using an efficient and robust eigensolver. Int J Numer Methods Eng 107:1029–1053
Evans AG, He MY, Deshpande VS, Hutchinson JW, Jacobsen AJ, Carter WB (2010) Concepts for enhanced energy absorption using hollow micro-lattices. Int J Impact Eng 37(9):947–959
Fang J, Sun G, Na Q, Kim NH, Li Q (2016) On design optimization for structural crashworthiness and its state of the art. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:1–29
Findeisen C, Hohe J, Kadic M, Gumbsch P (2017) Characteristics of mechanical metamaterials based on buckling elements. J Mech Phys Solids 102:151–164
Forsberg J, Nilsson L (2007) Topology optimization in crashworthiness design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(1):1–12
Frenzel T, Findeisen C, Kadic M, Gumbsch P, Wegener M (2016) Tailored buckling microlattices as reusable light-weight shock absorbers. Adv Mater 28(28):5865–5870
Gao X, Ma H (2015) Topology optimization of continuum structures under buckling constraints. Comput Struct 157:142–152
Gatt R, Mizzi L, Azzopardi JI, Azzopardi KM, Attard D, Casha A, Briffa J, Grima JN (2015) Hierarchical auxetic mechanical metamaterials. Sci Rep 5:8395
Haghpanah B, Salari-Sharif L, Pourrajab P, Hopkins J, Valdevit L (2016) Multistable shape-reconfigurable architected materials. Adv Mater 28(36):7915–7920
He G, Huang X, Hu W, Li G (2016) Topology optimization of periodic structures using beso based on unstructured design points. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(2):271–275
Hu N, Burgueño R (2015) Buckling-induced smart applications: recent advances and trends. Smart Mater Struct 24(6):063001
James KA, Waisman H (2016) Layout design of a bi-stable cardiovascular stent using topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 305:869–890
Kawamoto A (2009) Stabilization of geometrically nonlinear topology optimization by the levenberg–marquardt method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37(4):429–433
Kiani M, Motoyama K, Rais-Rohani M, Shiozaki H (2014) Joint stiffness analysis and optimization as a mechanism for improving the structural design and performance of a vehicle. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part D Journal of Automobile Engineering 228(6):689–700
Kim JJ, Jang IG (2016) Image resolution enhancement for healthy weight-bearing bones based on topology optimization. J Biomech 49(13):3035–3040
Lahuerta RD, Simões ET, Campello EMB, Pimenta PM, Silva ECN (2013) Towards the stabilization of the low density elements in topology optimization with large deformation. Comput Mech 52(4):779–797
Lee H-A, Park G-J (2012) Topology optimization for structures with nonlinear behavior using the equivalent static loads method. J Mech Des 134(3):031004
Lee J-H, Wang L, Kooi S, Boyce MC, Thomas EL (2010) Enhanced energy dissipation in periodic epoxy nanoframes. Nano Lett 10(7):2592–2597
Lee J-H, Singer JP, Thomas EL (2012) Micro-/nanostructured mechanical metamaterials. Adv Mater 24(36):4782–4810
Li L, Zhang G, Khandelwal K (2017) Topology optimization of energy absorbing structures with maximum damage constraint. Int J Numer Methods Eng 112:737–775
Lindgaard E, Dahl J (2013) On compliance and buckling objective functions in topology optimization of snap-through problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47(3):409–421
Liu M, Zhang X, Fatikow S (2017) Design and analysis of a multi-notched flexure hinge for compliant mechanisms. Precis Eng 48:292–304
Luo Q, Tong L (2015) Structural topology optimization for maximum linear buckling loads by using a moving iso-surface threshold method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52(1):71–90
Luo Q, Tong L (2016) An algorithm for eradicating the effects of void elements on structural topology optimization for nonlinear compliance. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(4):695–714
Mayer RR, Kikuchi N, Scott RA (1996) Application of topological optimization techniques to structural crashworthiness. Int J Numer Methods Eng 39(8):1383–1403
Mohammadiha O, Beheshti H (2014) Optimization of functionally graded foam-filled conical tubes under axial impact loading. J Mech Sci Technol 28(5):1741–1752
Nicolaou ZG, Motter AE (2012) Mechanical metamaterials with negative compressibility transitions. Nat Mater 11(7):608–613
Patel NM, Kang B-S, Renaud JE, Tovar A (2009) Crashworthiness design using topology optimization. J Mech Des 131(6):061013
Puglisi G, Truskinovsky L (2000) Mechanics of a discrete chain with bi-stable elements. J Mech Phys Solids 48(1):1–27
Rafsanjani A, Akbarzadeh A, Pasini D (2015) Snapping mechanical metamaterials under tension. Adv Mater 27(39):5931–5935
Rojas-Labanda S, Stolpe M (2015) Automatic penalty continuation in structural topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52(6):1205–1221
Shan S, Kang SH, Raney JR, Wang P, Fang L, Candido F, Lewis JA, Bertoldi K (2015) Multistable architected materials for trapping elastic strain energy. Adv Mater 27(29):4296–4301
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1031–1055
Tran AV, Zhang X, Zhu B (2017) The development of a new piezoresistive pressure sensor for low pressure. IEEE Trans Ind Electron PP(99):1–1
van Dijk NP, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2014) Element deformation scaling for robust geometrically nonlinear analyses in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 50(4):537–560
Wang R, Zhang X (2018) Parameters optimization and experiment of a planar parallel 3-dof nanopositioning system. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 65(3):2388–2397
Wang F, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2011) On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):767–784
Wang F, Sigmund O, Jensen JS (2014a) Design of materials with prescribed nonlinear properties. J Mech Phys Solids 69:156– 174
Wang F, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O, Jensen JS (2014b) Interpolation scheme for fictitious domain techniques and topology optimization of finite strain elastic problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 276:453–472
Yoon GH, Kim YY (2005) Element connectivity parameterization for topology optimization of geometrically nonlinear structures. Int J Solids Struct 42(7):1983–2009
Zheng X, Lee H, Weisgraber TH, Shusteff M, DeOtte J, Duoss EB, Kuntz JD, Biener MM, Ge Q, Jackson JA et al (2014) Ultralight, ultrastiff mechanical metamaterials. Science 344(6190):1373–1377
Zheng X, Smith W, Jackson J, Moran B, Cui H, Chen D, Ye J, Fang N, Rodriguez N, Weisgraber T et al (2016) Multiscale metallic metamaterials. Nat Mater 15:1100–1106
Zhu B, Zhang X, Fatikow S (2015) Structural topology and shape optimization using a level set method with distance-suppression scheme. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 283:1214–1239
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. U1501247 and U1609206). This support is greatly appreciated. Additionally, the authors thank Dr. K. Svanberg at KTH (Stockholm, Sweden) for providing the MMA code for academic research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kurt Maute
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(AVI 399 KB)
(AVI 429 KB)
(AVI 451 KB)
(AVI 720 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Zhang, X. & Zhu, B. Design of buckling-induced mechanical metamaterials for energy absorption using topology optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 58, 1395–1410 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1970-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-1970-y