Abstract
Based on the optimization design technology and fuzzy uncertainty theory, this paper proposes a novel inverse analysis method for membership function identification in steady-state heat transfer problem with fuzzy modeling parameters. The system subjective uncertainties associated with expert opinions are quantified as fuzzy parameters, which can be converted into interval variables by level-cut strategy. By means of the errors between measured and calculated temperature data, the parameter identification process is executed as a nested-loop optimization model. To avoid the considerable computational cost caused by nested-loop, an interval vertex method is presented to replace the inner-loop for predicting the temperature response bounds. The eventual membership functions of input fuzzy parameters are constructed by using the fuzzy decomposition theorem. Comparing results with traditional Monte Carlo method, a numerical example about 3D air cooling system is provided to verify the feasibility of proposed method for fuzzy parameter identification in engineering.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abonyi J (2003) Fuzzy Model Identification for Control. Springer Science Business Media, New York
Agarwal H, Mozumder CK, Renaud JE, Watson LT (2007) An inverse-measure-based unilevel architecture for reliability-based design optimization. Struct Multidiscip O 33(3):217–227
Akkaram S, Beeson D, Agarwal H, Wiggs G (2007) Inverse modeling technology for parameter estimation. Struct Multidiscip O 34(2):151–164
Ben-Haim Y, Elishakoff I (2013) Convex Models of Uncertainty in Applied Mechanics. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Bilal M, Hussain A, Jaffar MA, Choi T, Mirza AM (2014) Estimation and optimization based ill-posed inverse restoration using fuzzy logic. Multimed Tools Appl 69(3):1067–1087
Blackwell B, Beck JV (2010) A technique for uncertainty analysis for inverse heat conduction problems. Int J Heat Mass Tran 53(4):753–759
Cao SG, Rees NW (1995) Identification of dynamic fuzzy models. Fuzzy Sets Syst 74(3):307–320
Capasso V, Engl HW, Kindermann S (2008) Parameter identification in a random environment exemplified by a multiscale model for crystal growth. Multiscale Model Sim 7(2):814–841
Carrera J, Alcolea A, Medina A, Hidalgo J, Slooten LJ (2005) Inverse problem in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol J 13(1):206–222
Choi CK, Yoo HH (2016) Stochastic inverse method to identify parameter random fields in a structure. Struct Multidiscip O 54(6):1557–1571
Fletcher R (2013) Practical Methods of Optimization. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Fujimoto RM (2000) Parallel and Distributed Simulation Systems. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Jiang C, Liu G, Han X (2008) A novel method for uncertainty inverse problems and application to material characterization of composites. Exp Mech 48(4):539–548
Klimke A (2006) Uncertainty Modeling Using Fuzzy Arithmetic and Sparse Grids. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Stuttgart, Shaker Verlag, Aachen
Korycki R (2001) Two-dimensional shape identification for the unsteady conduction problem. Struct Multidiscip O 21(3):229–238
Ku CJ, Cermak JE, Chou LS (2007) Random decrement based method for modal parameter identification of a dynamic system using acceleration responses. J Wind Eng Ind Aerod 95(6):389–410
Lai Y, Jiang X, Fang L (2012) Isight Optimization Theory and Examples. Beihang University Press, Beijing
Li S (2015) Engineering Fuzzy Mathematics with Applications. Harbin Institute of Technology Press, Harbin
Liu J, Sun X, Han X, Jiang C, Yu D (2015a) Dynamic load identification for stochastic structures based on Gegenbauer polynomial approximation and regularization method. Mech Syst Signal Pr 56:35–54
Liu J, Sun X, Li K, Jiang C, Han X (2015b) A probability density function discretization and approximation method for the dynamic load identification of stochastic structures. J Sound Vib 357:74–94
Moens D, Hanss M (2011) Non-probabilistic finite element analysis for parametric uncertainty treatment in applied mechanics recent advances. Finite Elem Anal Des 47(1):4–16
Nayak S, Chakraverty S (2013) Non-probabilistic approach to investigate uncertain conjugate heat transfer in an imprecisely defined plate. Int J Heat Mass Tran 67:445–454
Nazin SA, Polyak BT (2005) Interval parameter estimation under model uncertainty. Math Comp Model Dyn 11(2):225–237
Nicolai BM, Egea JA, Scheerlinck N, Banga JR, Datta AK (2011) Fuzzy finite element analysis of heat conduction problems with uncertain parameters. J Food Eng 103:38–46
Rice JA (1995) Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis. Duxbury Press, Belmont
Rump SM (1992) On the solution of interval linear systems. Computing 47(3–4):337–353
Selimefendigil F, Öztop HF (2012) Fuzzy-based estimation of mixed convection heat transfer in a square cavity in the presence of an adiabatic inclined fin. Int Commun Heat Mass 39(10):1639–1646
Sepahvand K, Marburg S (2015) Non-sampling inverse stochastic numerical-experimental identification of random elastic material parameters in composite plates. Mech Syst Signal Pr 54:172–181
Stavroulakis GE (2013) Inverse and Crack Identification Problems in Engineering Mechanics. Springer, Berlin
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 15(1):116–132
Tao W (2001) Numerical Heat Transfer. Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, Xi’an
Theodoridis D, Boutalis Y, Christodoulou M (2012) Dynamical recurrent neuro-fuzzy identification schemes employing switching parameter hopping. Int J Neural Syst 22(2):1250004
Wang C, Qiu Z (2015a) Interval analysis of steady-state heat convection–diffusion problem with uncertain-but-bounded parameters. Int J Heat Mass Tran 91:355–362
Wang C, Qiu Z (2015b) Hybrid uncertain analysis for temperature field prediction with random, fuzzy and interval parameters. Int J Therm Sci 98:124–134
Wang C, Qiu Z (2015c) Improved numerical prediction and reliability-based optimization of transient heat conduction problem with interval parameters. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51(1):113–123
Wang X, Yang C, Wang L, Yang H (2013) Membership-set identification method for structural damage based on measured natural frequencies and static displacements. Struct Health Monit 12(1):23–34
Wang X, Xia Y, Zhou X, Yang C (2014) Structural damage measure index based on non-probabilistic reliability model. J Sound Vib 333(5):1344–1355
Wang C, Qiu Z, Yang Y (2016a) Uncertainty propagation of heat conduction problem with multiple random inputs. Int J Heat Mass Tran 99:95–101
Wang C, Qiu Z, Yang Y (2016b) Collocation methods for uncertain heat convection-diffusion problem with interval input parameters. Int J Therm Sci 107:230–236
Wang C, Qiu Z, Xu M (2017) Collocation methods for fuzzy uncertainty propagation in heat conduction problem. Int J Heat Mass Tran 107:631–639
Wendlandt WW (1974) Thermal Methods of Analysis. Wiley Interscience, New York
Xia B, Yu D, Liu J (2013) Interval and subinterval perturbation methods for a structural-acoustic system with interval parameters. J Fluid Struct 38:146–163
Xue Y, Yang H (2013a) Interval estimation of convection-diffusion heat transfer problems. Numer Heat Tr B-Fund 64(3):263–273
Xue Y, Yang H (2013b) Interval identification of thermal parameters for convection-diffusion heat transfer problems. Asia-Pacific Congress for Computational Mechanics, Singapore
Yilmaz S, Oysal Y (2010) Fuzzy wavelet neural network models for prediction and identification of dynamical systems. IEEE T Neural Network 21(10):1599–1609
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zhang W, Liu J, Cho C, Han X (2015) A hybrid parameter identification method based on Bayesian approach and interval analysis for uncertain structures. Mech Syst Signal Pr 60:853–865
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, 111 Project (No. B07009), and National Natural Science Foundation of PR China (No.11432002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Fuzzy set theory
Appendix: Fuzzy set theory
Definition 1 (fuzzy sets)
Given the definition domain R, a fuzzy set X can be defined as
where μ X (x) is the membership function representing the degree a sample x belongs to the set R.
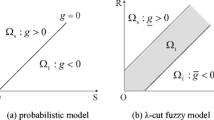
Definition 2 (level-cut strategy)
Given a fuzzy set X, for any λ ∈ [0, 1] the normal set
is defined as the λ-cut set, where λ is called the cut level. Usually, the cut sets are considered as intervals of confidence, since in case of convex fuzzy sets, they are closed intervals associated with a gradation of confidence between [0,1].
Definition 3 (fuzzy decomposition theorem)
Based on the λ-cut sets, any fuzzy set X defined in the domain R can be visually expressed by the normal sets
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Matthies, H.G. & Qiu, Z. Optimization-based inverse analysis for membership function identification in fuzzy steady-state heat transfer problem. Struct Multidisc Optim 57, 1495–1505 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1821-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1821-2