Abstract
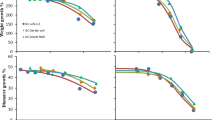
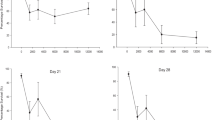
The bioaccumulation of and resistance to different heavy metals in soil was tested using Mongoloniscus sinensis, a terrestrial isopod endemic to china, and results show that: (1) the median lethal concentration (LC50) of Pb, Zn, Cd in the filter paper contact test after 48 h was 197.6, 503.7, 448.0 µg cm− 2, LC50 of Pb–Zn compounds was 173.8 and 440.8 µg cm− 2 and after 14 days of soil contamination LC50 was 2917.0, 2977.9, 5048.4 mg kg− 1, LC50 of Pb–Zn compounds was 1219 and 1463 mg kg− 1. Thus Zn turned out to be less toxic than Cd in the filter paper contact test, while their sequence of toxicity was reversed during the soil exposure test, which shows that M. sinensis can tolerate a dose of Zn and Cd. (2) analysis of body burdens showed that the sequence of internalized metal concentrations was Pb < Cd < Zn, which indicates that heavy metals in soil can be enriched and absorbed by M. sinensis, and that it is much more efficient at absorbing Zn and Cd than Pb.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costa D, Bouchon D, VanStraalen NM, Sousa JP, Ribeiro R (2013) Copper tolerance and genetic diversity of Porcellionides sexfasciatus (Isopoda) in a highly contaminated mine habitat. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:884–888
Dallinger R, Berger B, Birkel S (1992) Terrestrial isopods: useful biological indicators of metal pollution. Oecol 89:32–41
Drobne D, Hopkin SP (1994) Ecotoxicological laboratory test for assessing the effects chemicals on terrestrial isopods. Bull Environ ContamToxicol 53(3):390–397
Gerhardt A (1993) Review of impact of heavy metals on stream inverte2 brates with special emphasis on acid conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 66:289–314
Ghemari C, Waterlot C, Ayari A et al (2017) Assessment of heavy metals in soil and terrestrial isopod Porcellio laevis, in Tunisian industrialized areas. Environ Earth Sci 76(17):623
Godet JP, Demuynck S, Waterlot C, Lemière S, Souty-Grosset C, Sheifler R, Douay F, Lepreˆtre A, Pruvot C (2011) Growth and metal accumulation in Porcellio scaber exposed to poplar litter from Cd-, Pb- and Zn-contaminated sites. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:451–458
Hames CAC, Hopkin SP (1989) The structure and function of the digestive system of terrestrial isopods. Proc Zoolo Soc London 217(4):599–627
Heikens A, Peijnenburg WJGM, Hendriks AJ (2001) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Environ Pollut 113(3):385–393
Hodkinson ID, Jackson JK (2005) Terrestrial and aquatic invertebrates as bioindicators for environmental monitoring, with particular reference to mountain ecosystems. Environ Manage 35:649–666
Hopkin SP (1989) Ecophysiology of metals in terrestrial invertebrates. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, London
Hopkin SP, Hardisty GN, Martin MH (1986) The woodlouse Porcellio scaber as ‘biological indicator’ of zinc, cadmium, lead and copper pollution. Environ Pollut 11B:271–290
Hopkin SP, Hames CAC, Bragg S (1989) Terrestrial isopods as biological indicators of zinc pollution in the Reading area south east England. Monitore Zoologico Italiano 4:477–488
Hopkin SP, Jones DT, Dietrich D (1993) The isopod Porcellio scaber as a monitor of the bioavailability of metals in terrestrial ecosystems: towards a global ‘woodlouse watch’ scheme. Sci Total Environ 134(05):357–365
Hussein MA, Obuid-Allah AH, Mohammad AH, Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Abd El-Wakeil KF (2006) Seasonal variation in heavy metal accumulation in subtropical population of the terrestrial isopod, Porcellio laevis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:168–174
Köhler HR, Hüttenrauch K, Berkus M, Grǎff S, Alberti G (1996) Cellular hepatopancreatic reactions in Porcellio scaber (Isopoda) as biomarkers for the evaluation of heavy metal toxicity in soils. Appl Soil Ecol 3(1):1–15
Li M, Niu X, Li Y, An J (2016) Toxicological effects of Cd pollution on three Species of woodlouse (Crustacea: Isopoda) and their avoidance behaviors. Acta Pedol Sin 53(3):703–712
Lin X, Zhang L, Wei C (2008) Determination of Copper, lead, zinc and iron in tea by wet digestion method. Prev Med Trib 14(4):324–326
Longo G, Trovato M, Mazzei V, Ferrante M, Conti GO (2013) Ligia italica (isopoda, oniscidea) as bioindicator of mercury pollution of marine rocky coasts. PLoS ONE 32(8):e58548
Loureiro S, Sampaio A, Brandão A, Nogueira AJ, Soares M (2006) Feeding behaviour of the terrestrial isopod Porcellionides pruinosus brandt, 1833 (crustacea, isopoda) in response to changes in food quality and contamination. Sci Total Environ 369(1–3):119–128
Mazzei V, Longo G, Brundo MV, Copat C, Oliveri Conti G, Ferrante M (2013) Effects of heavy metal accumulation on some reproductive characters in Armadillidium granulatum Brandt (Crustacea, Isopoda, Oniscidea). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98(3):66–73
Mazzei V, Longo G, Brundo MV, Copat C, Oliveri Conti G, Ferrante M (2014) Bioaccumulation of cadmium and lead and its effects on hepatopancreas morphology in three terrestrial isopod Crustacean species. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:269–279
Moraïtou-Apostolopoulou M, Verriopoulos G (1982) Individual and combined toxicity of three heavy metals, Cu, Cd and Cr for the marine copepod Tisbe holothuriae. Hydrobiol 87(1):83–87
Schill RO, Köhler HR (2004) Energy reserve and metal-storage granules in the hepatopancreas of Oniscus asellus and Porcellio scaber (Isopoda) from a metal gradient at Avonmouth, UK. Ecotoxicology 13(8):787–796
Sun Z, Wang H, Wang J, Liu J, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Wu Ch (2009) Single and joint toxicity of mercury, cadmium and selenium on juvenile sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicas. Oceanol Et Limnol Sinica 40(2):228–234
Tourinho PS, van Gestel CAM, Jurkschat K, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2015) Effects of soil and dietary exposures to Ag nanoparticles and AgNO3 in the terrestrial isopod Porcellionides pruinosus. Environ Pollut 205:170–177
Vijver MG, Vink JPM, Jager T, Straalen NMV, Wolterbeek HT, Gestel CAMV (2006) Kinetics of Zn and Cd accumulation in the isopod Porcellio scaber, exposed to contaminated soil and/or food. Soil Biol Biochem 38(7):1554–1563
Wang Zh, Wu H, Wang Y et al (2014) Acute toxic and joint toxic experiments of Cd2+ and Cu2+ on Tegillarca granosa. Mar Sci 38(8):16–20
Wieser W, Busch G, Bijchel L (1976) Isopods as indicators of the copper content of soil and litter. Oecol 23:107–114
Witzel B (1998) Uptake, storage and loss of cadmium and lead in the woodlouse Porcellio scaber (Crustacea, Isopoda). Water Air Soil Pollut 108(1–2):51–68
Xiu R, Gao S, Xu Y, Ren M, Zheng J, Fu Y (1995) Study on joint toxicity of fluoride and selenium to fish. Chin Environ Sci 15(5):348–350
Xu D, Wen Y, Li L, Zhong X (2011) Effects of perfluorooctane sulfonate on acute lethality and avoidance behavior of earthworm. Chin J Appl Ecol 22(1):215–220
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Fund Program for the Scientific Activities of Selected Returned Overseas Professionals in Shanxi Province (Grant No. 2016010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, T., Wang, M., Li, M. et al. Toxicity of Heavy Metals to Mongoloniscus sinensis (Dollfus, 1901) (Crustacea: Isopoda: Oniscidea). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102, 25–31 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2480-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2480-8