Abstract
Volcanic activity is one of the primary sources of mercury in the earth’s ecosystem. In this work, volcanic rocks from four geotectonically distinct localities (the Czech Republic – intraplate, rift-related alkaline basaltic rocks; Iceland – hotspot/rift-related tholeiitic basaltic rocks; Japan – island arc calc-alkaline andesites; and Alaska – continental arc calc-alkaline dacites) were studied. Ultra-trace Hg contents in all samples ranged from 0.3 up to 6 µg/kg. The highest Hg content was determined for volcanic ash from Mount Redoubt (Alaska, USA). In the case of basaltic volcanic rocks, the obtained results are about two orders of magnitude smaller than values formerly assumed for primary mercury contents in basaltic lavas. They are close to predicted Hg contents in the mantle source, i.e. below 0.5 µg/kg. Hg degassing is probably a key process for the resulting Hg contents in material ejected during volcanic eruption, which is previously enriched by Hg in the shallow-crust.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 October 2018
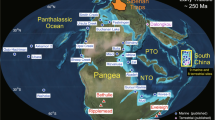
The original version of this article contained a mistake in Fig. 2. The country names have been missed in the figure legend along with the X-axis. The corrected figure is given below.
References
Bagnato E, Aiuppa A, Parello F, Calabrese S, D’Alessandro W, Mather TA, McGonigle AJS, Pyle DM, Wängberg I (2007) Degassing of gaseous (elemental and reactive) and particulate mercury from Mount Etna volcano (Southern Italy). Atmos Environ 41:7377–7388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.05.060
Bagnato E, Aiuppa A, Parello F, Allard P, Shinohara H, Liuzzo M, Giudice G (2011) New clues on the contribution of earth’s volcanism to the global mercury cycle. Bull Volcanol 73:497–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-010-0419-y
Bagnato E, Tamburello G, Avard G, Martinez-Cruz M, Enrico M, Fu X, Sprovieri M, Sonke JE (2014) Mercury fluxes from volcanic and geothermal sources: an update. In: Zellmer GF, Edmonds GF, Straub SM (eds) The role of volatiles in the genesis, evolution and eruption of arc magmas, special publications 410. Geological Society, London, pp 263–285. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP410.2
Boening DW (2000) Ecological effects, transport, and fate of mercury: a general review. Chemosphere 40:1335–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00283-0
Cajz V, Schnabl P, Pécskay Z, Skácelová Z, Venhodová D, Šlechta S, Čížková K (2012) Chronological implications of the paleomagnetic record of the Late Cenozoic volcanic activity along the Moravia-Silesia border (NE Bohemian Massif). Geol Carpath 63:423–435. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10096-012-0033-3
Canil D, Crockford PW, Rossin R, Telmer K (2015) Mercury in some arc crustal rocks and mantle peridotites and relevance to the moderately volatile element budget of the earth. Chem Geol 396:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.12.029
Coombs ML, Sisson TW, Bleick HA, Henton SM, Nye CJ, Payne AL, Cameron CE, Larsen JF, Wallace KL, Bull KF (2013) Andesites of the 2009 eruption of Redoubt Volcano, Alaska. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 259:349–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2012.01.002
Coufalík P, Zvěřina O, Krmíček L, Pokorný R, Komárek J (2015) Ultra-trace analysis of Hg in alkaline lavas and regolith from James Ross Island. Antarct Sci 27:281–290. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954102014000819
Dagsson-Waldhauserova P, Arnalds O, Olafsson H, Skrabalova L, Sigurdardottir GM, Branis M, Hladil J, Skala R, Navratil T, Chadimova L von Lowis of Menar S, Thorsteinsson T, Carlsen HK, Jonsdottir I (2014) Physical properties of suspended dust during moist and low wind conditions in Iceland. Icel Agric Sci 27:25–39
Dissanayake CB, Vincent EA (1975) Mercury in rocks and minerals of the Skaergaard intrusion, East Greenland. Mineral Mag 40:33–42. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1975.040.309.05
Ferrara R, Maserti BE (1990) Atmospheric mercury levels in the Mount Etna volcanic area after an eruptive phase. Environ Technol 11:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593339009384838
Fleischer M (1970) Summary of the literature on the inorganic geochemistry of mercury. In: Mercury in the environment, vol 713. U.S. Goverment Printing Office, Geological Survey Professional Paper, Washington, DC, pp 6–13
Gotoh S, Tokudome S, Koga H (1978) Mercury in soil derived from igneous rock in Northern Kyushu, Japan. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 24:391–406. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.1978.10433118
Gray JE, Gent CA, Snee W (1998) The southwestern Alaska mercury belt and its relationship to the circum-pacific metallogenic mercury province. Polarforschung 68:187–196
Henley RW, Berger BR (2013) Nature’s refineries—metals and metalloids in arc volcanoes. Earth Sci Rev 125:146–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.07.007
Hintelmann H (2010) Organomercurials. Their formation and pathways in the environment. In: Sigel A, Sigel H, Sigel RKO (eds) Organometallics in environment and toxicology: metal ions in life sciences. RSC Publishing, Cambridge, pp 365–401. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781849730822-00365
Martín JAR, Nanos N, Miranda JC, Carbonell G, Gil L (2013) Volcanic mercury in Pinus canariensis. Naturwissenschaften 100:739–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-013-1070-1
Mather TA, Pyle DM, Oppenheimer C (2003) Tropospheric volcanic aerosol. In: Robock A, Oppenheimer C (eds) Volcanism and the earth’s atmosphere, geophysical monograph, American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC 139:189–2012. https://doi.org/10.1029/139GM12
Pirrone N, Cinnirella S, Feng X, Finkelman RB, Friedli HR, Leaner J, Mason R, Mukherjee AB, Stracher GB, Streets DG, Telmer K (2010) Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos Chem Phys 10:5951–5964. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-5951-2010
Pyle DM, Mather TA (2003) The importance of volcanic emissions for the global atmospheric mercury cycle. Atmos Environ 37:5115–5124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2003.07.011
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2014) Composition of the continental crust. In: Holland H, Turekian K (eds) Treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 1–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00301-6
Rytuba JJ (2003) Mercury from mineral deposits and potential environmental impact. Environ Geol 43:326–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0629-5
Schlüter K (2000) Review: evaporation of mercury from soils. An integration and synthesis of current knowledge. Environ Geol 39:249–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050005
Schmincke HU (2004) Volcanism. Springer, Berlin, p 324
Schroeder WH, Munthe J (1998) Atmospheric mercury—an overview. Atmos Environ 32:809–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(97)00293-8
Selin NE (2009) Global biogeochemical cycling of mercury: a review. Annu Rev Environ Resour 34:43–63
Sprovieri F, Pirrone N, Bencardino M, D’Amore F, Carbone F, Cinnirella S, Mannarino V, Landis M, Ebinghaus R, Weigelt A, Brunke EG, Labuschagne C, Martin L, Munthe J, Wängberg I, Artaxo P, Morais F, Barbosa HMJ, Brito J, Cairns W, Barbante C, Diéguez MC, Garcia PE, Dommergue A, Angot H, Magand O, Skov H, Horvat M, Kotnik J, Read KA, Neves LM, Gawlik BM, Sena F, Mashyanov N, Obolkin V, Wip D, Feng XB, Zhang H, Fu X, Ramachandran R, Cossa D, Knoery J, Marusczak N, Nerentorp M, Norstrom C (2016) Atmospheric mercury concentrations observed at ground-based monitoring sites globally distributed in the framework of the GMOS network. Atmos Chem Phys 16:11915–11935. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-11915-2016
Symonds RB, Reed MH (1993) Calculation of multicomponent chemical equilibria in gas-solid-liquid systems: calculation methods, thermochemical data, and applications to studies of high temperature volcanic gases with examples from Mount St. Helens. Am J Sci 293:758–864. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.293.8.758
Symonds RB, Reed MH, Rose WI (1992) Origin, speciation, and fluxes of trace-element gases at Augustine volcano, Alaska: insights into magma degassing and fumarolic processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:633–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(92)90087-Y
Ulrych J, Ackerman L, Balogh K, Hegner E, Jelínek E, Pécskay Z, Přichystal A, Upton BGJ, Zimák J, Foltýnová R (2013) Plio-Pleistocene basanitic and melilititic series of the Bohemian Massif: K-Ar ages, major/trace element and Sr–Nd isotopic data. Chem Erde 73:429–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2013.02.001
WHO (2007) Health risks of heavy metals from long-range transboundary air pollution. World Health Organization, Germany, p 130
Zintwana MP, Cawthorn RG, Ashwal LD, Roelofse F, Cronwright H (2012) Mercury in the Bushveld complex, South Africa, and the Skaergaard intrusion, Greenland. Chem Geol 320–321:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.06.001
Acknowledgements
The research was supported by the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic under project P503/12/0682, by Masaryk University under the project MUNI/A/0886/2016, by the Institute of Analytical Chemistry of the CAS under RVO 68081715, by the Institute of Geology of the CAS under RVO 67985831, and by the BUT project LO1408 “AdMaS UP – Advanced Materials, Structures and Technologies”, supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports CR under the “National Sustainability Programme I”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The country names in the X-axis of Fig. 2 has been corrected.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coufalík, P., Krmíček, L., Zvěřina, O. et al. Model of Mercury Flux Associated with Volcanic Activity. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101, 549–553 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2430-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2430-5