Abstract
Key message
A repertoire of the genomic regions involved in quantitative resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in winter oilseed rape was established from combined linkage-based QTL and genome-wide association (GWA) mapping.
Abstract
Linkage-based mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) and genome-wide association studies are complementary approaches for deciphering the genomic architecture of complex agronomical traits. In oilseed rape, quantitative resistance to blackleg disease, caused by L. maculans, is highly polygenic and is greatly influenced by the environment. In this study, we took advantage of multi-year data available on three segregating populations derived from the resistant cv Darmor and multi-year data available on oilseed rape panels to obtain a wide overview of the genomic regions involved in quantitative resistance to this pathogen in oilseed rape. Sixteen QTL regions were common to at least two biparental populations, of which nine were the same as previously detected regions in a multi-parental design derived from different resistant parents. Eight regions were significantly associated with quantitative resistance, of which five on A06, A08, A09, C01 and C04 were located within QTL support intervals. Homoeologous Brassica napus genes were found in eight homoeologous QTL regions, which corresponded to 657 pairs of homoeologous genes. Potential candidate genes underlying this quantitative resistance were identified. Genomic predictions and breeding are also discussed, taking into account the highly polygenic nature of this resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamery S, Tirnaz S, Bayer P, Tollenaere R, Chaloub B, Edwards D, Batley J (2017) Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis of NBS-LRR resistance genes in Brassica napus. Crop Pasture Sci 69:72–93
Allard A, Bink MCAM, Martinez S, Kelner J, Legave J, Guardo M, Di Pierro EA, Laurens F, Van De Weg EW, Costes E (2016) Detecting QTLs and putative candidate genes involved in budbreak and flowering time in an apple multiparental population. J Exp Bot 67:2875–2888
Aubertot JN, Schott JJ, Penaud A, Brun H, Doré T (2004) Methods for sampling and assessment in relation to the spatial pattern of phoma stem canker (Leptosphaeria maculans) in oilseed rape. Eur J Plant Pathol 110:183–192
Avia K, Coelho SM, Montecinos GJ, Cormier A, Lerck F, Mauger S, Faugeron S, Valero M, Cock JM, Boudry P (2017) High-density genetic map and identification of QTLs for responses to temperature and salinity stresses in the model brown alga. Ectocarpus Sci Rep 7:43241
Balesdent MH, Fudal I, Ollivier B, Bally P, Grandaubert J, Eber F, Chèvre AM, Leflon M, Rouxel T (2013) The dispensable chromosome of Leptosphaeria maculans shelters an effector gene conferring avirulence towards Brassica rapa. New Phytol 198:887–898
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Soft 67:1–48
Becker MG, Zhang X, Walker PL, Wan JC, Millar JL, Khan D et al (2017) Transcriptome analysis of the Brassica napus-Leptosphaeria maculans pathosystem identifies receptor, signalling and structural genes underlying plant resistance. Plant J 90:573–586
Bian Y, Holland JB (2017) Data from: enhancing genomic prediction with genome-wide association studies in multiparental maize populations. Dryad Digit Repos. https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.cd3hv
Broman KW, Wu H, Sen S, Churchill GA (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19:889–890
Brun H, Levivier S, Somda I, Ruer D, Renard M, Chevre AM (2000) A field method for evaluating the potential durability of new resistance sources: application to the Leptosphaeria maculans-Brassica napus pathosystem. Phytopathol 90:961–966
Brun H, Chèvre AM, Fitt BD, Powers S, Besnard AL, Ermel M, Huteau V, Marquer B, Eber F, Renard M, Andrivon D (2010) Quantitative resistance increases the durability of qualitative resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. New Phytol 185:285–299
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu S, Parkin IAP, Tang H, Wang X et al (2014) Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345:950–953
Clarke WE, Higgins EE, Plieske J, Wieseke R, Sidebottom C et al (2016) A high-density SNP genotyping array for Brassica napus and its ancestral diploid species based on optimised selection of singlelocus markers in the allotetraploid genome. Theor Appl Genet 129:1887–1899
de Givry S, Bouchez M, Chabrier P, Milan D, Schiex T (2005) CARTHAGENE: multipopulation integrated genetic and radiation hybrid mapping. Bioinformatics 21:1703–1704
Delourme R, Pilet-Nayel ML, Archipiano M, Horvais R, Tanguy X, Rouxel T, Brun H, Renard M, Balesdent MH (2004) A cluster of major specific resistance genes to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. Phytopathol 94:578–583
Delourme R, Chevre AM, Brun H, Rouxel T, Balesdent MH, Dias JS et al (2006) Major gene and polygenic resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Eur J Plant Pathol 114:41–52
Delourme R, Falentin C, Fomeju BF, Boillot M, Lassalle G et al (2013) High-density SNP-based genetic map development and linkage disequilibrium assessment in Brassica napus L. BMC Genomics 14:120
Delourme R, Bousset L, Ermel E, Duffé P, Besnard AL, Marquer B, Fudal I, Linglin J, Chadoeuf J, Brun H (2014) Quantitative resistance affects the speed of frequency increase but not the diversity of the virulence alleles overcoming a major resistance gene to Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape. Infect Genet Evol 27:490–499
Endelman JB (2011) Ridge regression and other kernels for genomic selection with R package rrBLUP. Plant Genome 4:250–255
Evans N, Baierl A, Semenov MA, Gladders P, Fitt BDL (2008) Range and severity of a plant disease increased by global warming. J R Soc Interface 5:525–531
Fitt BDL, Brun H, Barbetti MJ, Rimmer SR (2006) World-wide importance of phoma stem canker (Leptosphaeria maculans and L. biglobosa) on oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Eur J Plant Pathol 114:3–15
Foisset N, Delourme R, Barret P, Renard M (1995) Localization of agronomic traits on a B. napus map. In: Proceedings of 9th international Rapeseed congress, vol 4. Cambridge, UK, pp 1199–1201
Foisset N, Delourme R, Barret P, Hubert N, Landry BS, Renard M (1996) Molecular mapping analysis in Brassica napus using isozyme, RAPD and RFLP markers on a doubled haploid progeny. Theor Appl Genet 93:1017–1025
Fopa Fomeju B, Falentin C, Lassalle G, Manzanares-Dauleux M, Delourme R (2014) Homologous duplicated regions are involved in quantitative resistance of Brassica napus to stem canker. BMC Genomics 15:498
Fopa Fomeju B, Falentin C, Lassalle G, Manzanares-Dauleux M, Delourme R (2015) Comparative genomic analysis of duplicated homoeologous regions involved in the resistance of Brassica napus to stem canker. Front Plant Sci 6:772
Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, Blumenstiel B, Higgins J, DeFelice M et al (2002) The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296:2225–2229
Goh L, Yap VB (2009) Effects of normalization on quantitative traits in association test. BMC Bioinform 10:415
Gore MA, Fang DD, Poland JA, Zhang J, Percy RG, Cantrell RG et al (2014) Linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus analysis of agronomic and fiber quality traits in cotton. Plant Genome. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2013.07.0023
Haddadi P, Ma L, Wang H, Borhan MH (2016) Genome-wide transcriptomic analyses provide insights into the lifestyle transition and effector repertoire of Leptosphaeria maculans during the colonization of Brassica napus seedlings. Mol Plant Pathol 17:1196–1210
Huang YJ, Pirie EJ, Evans N, Delourme R, King GJ, Fitt BDL (2009) Quantitative resistance to symptomless growth of Leptosphaeria maculans (phoma stem canker) in Brassica napus (oilseed rape). Plant Pathol 58:314–323
Huang YJ, Jestin C, Welham SJ, King GJ, Manzanares-Dauleux MJ, Fitt BDL, Delourme R (2016) Identification of environmentally stable QTL for resistance against Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Theor Appl Genet 129:169–180
Ichimura K, Shinozaki K, Tena G, Sheen J, Henry Y, Champion A et al (2002) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: a new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci 7:301–308
Jestin C, Lodé M, Vallée P, Domin C, Falentin C, Horvais R, Coedel S, Manzanares-Dauleux MJ, Delourme R (2011) Association mapping of quantitative resistance for Leptosphaeria maculans in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Mol Breed 27:271–287
Jestin C, Vallée P, Domin C, Manzanares-Dauleux MJ, Delourme R (2012) Assessment of a new strategy for selective phenotyping applied to complex traits in Brassica napus. Open J Genet 2:190–201
Jestin C, Bardol N, Lodé M, Duffé P, Domin C, Vallée P, Mangin B, Manzanares-Dauleux MJ, Delourme R (2015) Connected populations for detecting quantitative resistance factors to phoma stem canker in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Mol Breed 35:1–16
Kang HM, Zaitlen NA, Wade CM, Kirby A, Heckerman D, Daly MJ, Eskin E (2008) Efficient control of population structure in model organism association mapping. Genetics 178:1709–1723
Kruijer W, Boer MP, Malosetti M, Flood PJ, Engel B, Kooke R, Keurentjes JJ, van Eeuwijk FA (2015) Marker-based estimation of heritability in immortal populations. Genetics 199:379–398
Kushalappa AC, Gunnaiah R (2013) Metabolo-proteomics to discover plant biotic stress resistance genes. Trends Plant Sci 18:522–531
Kushalappa AC, Yogendra KN, Karre S (2016) Plant innate immune response: qualitative and quantitative resistance. Crit Rev Plant Sci 35:38–55
Larkan NJ, Raman H, Lydiate DJ, Robinson SJ, Yu F, Barbulescu DM, Raman R, Luckett DJ, Burton W, Wratten N, Salisbury PA, Rimmer SR, Borhan MH (2016) Multi-environment QTL studies suggest a role for cysteine-rich protein kinase genes in quantitative resistance to blackleg disease in Brassica napus. BMC Plant Biol 16:183
Lay FT, Anderson MA (2005) Defensins-components of the innate immune system in plants. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:85–101
Li H, Sivasithamparam K, Barbetti MJ (2003) Breakdown of a Brassica rapa subsp. sylvestris single dominant blackleg resistance gene in B. napus rapeseed by Leptosphaeria maculans field isolates in Australia. Plant Dis 87:752
Long Y, Wang Z, Sun Z, Fernando DWG, McVetty PBE, Li G (2011) Identification of two blackleg resistance genes and fine mapping of one of these two genes in a Brassica napus canola cultivar ‘Surpass 400’. Theor Appl Genet 122:1223–1231
Lowe RG, Cassin A, Grandaubert J, Clark BL, Van De Wouw AP, Rouxel T et al (2014) Genomes and transcriptomes of partners in plant-fungal-interactions between canola (Brassica napus) and two Leptosphaeria species. PLoS ONE 9:e103098
Marcroft SJ, Purwantara A, Salisbury P, Potter TD, Wratter N, Khangura R et al (2002) Reaction of a range of Brassica species under Australian conditions to the fungus, Leptosphaeria maculans, the causal agent of blackleg. Aust J Exp Agric 42:587–594
Mitchell-Olds T, Schmitt J (2006) Genetic mechanisms and evolutionary significance of natural variation in Arabidopsis. Nature 441:947–952
Nawrot R, Barylski J, Nowicki G, Broniarczyk J, Buchwald W, Gózdzicka-Józefiak A (2014) Plant antimicrobial peptides. Folia Microbiol 59:181–196
Nordborg M, Weigel D (2010) Next-generation genetics in plants. Nature 456:10–13
Pilet ML, Delourme R, Foisset N, Renard M (1998) Identification of loci contributing to quantitative field resistance to blackleg disease, causal agent Leptosphaeria maculans (Desm.) Ces. et de Not., in Winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 96:23–30
Pilet ML, Duplan G, Archipiano M, Barret P, Baron C, Horvais R, Tanguy X, Lucas MO, Renard M, Delourme R (2001) Stability of QTL for field resistance to blackleg across two genetic backgrounds in oilseed rape. Crop Sci 41:197–205
Pilet-Nayel ML, Moury B, Caffier V, Montarry J, Kerlan MC, Fournet S, Durel CE, Delourme R (2017) Quantitative resistance to plant pathogens in pyramiding strategies for durable crop protection. Front Plant Sci 8:1838
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MAR, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PIW, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Rabbi IY, Hamblin MT, Kumar PL, Gedil M, Ikpan AS, Jannink J-L, Kulakow P (2014) High-resolution mapping of resistance to cassava mosaic geminiviruses in cassava using genotyping-by-sequencing and its implications for breeding. Virus Res 186:87–96
Raman R, Taylor B, Marcroft S, Stiller J, Eckermann P, Coombes N et al (2012) Molecular mapping of qualitative and quantitative loci for resistance to Leptosphaeria maculans; causing blackleg disease in canola (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:405–418
Raman H, Raman R, Larkan N (2013) Genetic dissection of blackleg resistance loci in rapeseed (Brassica napus L). In: Andersen SB (ed) Plant breeding from laboratories to fields. InTech, Luton. https://doi.org/10.5772/53611. ISBN 978-953-51-1090-3
Raman H, Raman R, Coombes N, Song J, Prangnell R, Bandaranayake C et al (2016) Genome-wide association analyses reveal complex genetic architecture underlying natural variation for flowering time in canola. Plant Cell Environ 39:1228–1239
Rimmer SR (2006) Resistance genes to Leptosphaeria maculans in Brassica napus. Can J Plant Pathol 28:S288–S297
Rouxel T, Penaud A, Pinochet X, Brun H, Gout L, Delourme R et al (2003) A 10-year survey of populations of Leptosphaeria maculans in France indicates a rapid adaptation towards the Rlm1 resistance gene of oilseed rape. Eur J Plant Pathol 109:871–881
Schwender H, Ickstadt K (2008) Imputing missing genotypes with k nearest neighbors. Technical report, SFB 475, Department of Statistics, University of Dortmund
Tan B, Grattapaglia D, Martins GS, Zamprogno Ferreira K, Sundberg B, Ingvarsson PK (2017) Evaluating the accuracy of genomic prediction of growth and wood traits in two Eucalyptus species and their F1 hybrids. BMC Plant Biol 17:110
Thomma BP, Cammue BP, Thevissen K (2002) Plant defensins. Planta 216:193–202
West JS, Kharbanda PD, Barbetti MJ, Fitt BDL (2001) Epidemiology and management of Leptosphaeria maculans (phoma stem canker) on oilseed rape in Australia, Canada and Europe. Plant Pathol 50:10–27
Wong JH, Xia L, Ng TB (2007) A review of defensins of diverse origins. Curr Protein Pept Sci 8:446–459
Yu F, Lydiate DJ, Rimmer SR (2005) Identification of two novel genes for blackleg resistance in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 110:969–979
Yu F, Lydiate DJ, Rimmer SR (2008) Identification and mapping of a third blackleg resistance locus in Brassica napus derived from B rapa subsp sylvestris. Genome 51:64–72
Yu F, Gugel RK, Kutcher HR, Peng G, Rimmer SR (2013) Identification and mapping of a novel blackleg resistance locus LepR4 in the progenies from Brassica napus × B rapa subsp sylvestris. Theor Appl Genet 126:307–315
Zhang X, Huang C, Wu D et al (2017) High-throughput phenotyping and QTL mapping reveals the genetic architecture of maize plant growth. Plant Physiol 173:1554–1564
Zheng X, Levine D, Shen J, Gogarten SM, Laurie C, Weir BS (2012) A high-performance computing toolset for relatedness and principal component analysis of SNP data. Bioinformatics 28:3326–3328
Acknowledgements
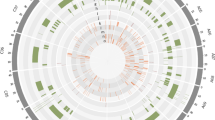
We would like to acknowledge Gilles Lassalle and Anne Laperche for the script that was used to choose the markers for QTL analysis and Mathieu Rousseau-Gueutin, Jérôme Morice for Circos representation of homoeologous relationships between the QTL regions. The authors are grateful to Claude Domin and the INRA Experimental Unit (UE La Motte, Le Rheu) for field experimentations. The authors would like to thank the BrACySol biological resource center (INRA Ploudaniel, France) for providing the seeds used in this study. This work was supported by the French ‘Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique’—Department of ‘Biologie et Amélioration des Plantes’, Terres Inovia and PROMOSOL. VK was funded through the European PLANT-KBBE-IV research program in the French-German Project GEWIDIS (Exploiting genome-wide diversity for disease resistance improvement in oilseed rape; ANR13-KBBE-0004-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Heiko C. Becker.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, V., Paillard, S., Fopa-Fomeju, B. et al. Multi-year linkage and association mapping confirm the high number of genomic regions involved in oilseed rape quantitative resistance to blackleg. Theor Appl Genet 131, 1627–1643 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3103-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3103-9