Abstract
Key message
Engineered chromosomes 1BS and 1RS offer a new alternative in the development of hybrid systems in bread wheat and triticale.
Abstract
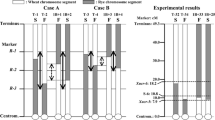
In the cytoplasmic male sterility system for hybrid wheat based on the cytoplasm of Triticum timopheevi fertility restoration is difficult, with few good restorer genes available. In the system based on the cytoplasms of Aegilops kotschyi, Ae. uniaristata and Ae. mutica, essentially all chromosomes 1B carry locus Rf multi that restores male fertility; male sterility manifests itself in wheats with the 1RS.1BL translocation where 1BS chromosome arm is missing. To generate male sterile wheats without the 1RS.1BL translocation, the 1BS arm was cytogenetically engineered to replace the segment with Rf multi with two short inserts of rye chromatin. Conversely, to enhance fertility restoration by doubling the number of restorers present for eventual use in wheat and triticale, a region of 1BS with Rf multi was inserted into 1RS. Alloplasmic wheats with Rf multi removed were completely male sterile; alloplasmic wheats with engineered 1RS carrying Rf multi and without normal 1B were male fertile. An exception to the ubiquitous presence of Rf multi is T. spelta var. duhamelianum; four accessions tested in this study gave inconsistent results but some did not restore male fertility. Engineered chromosomes 1BS and 1RS and chromosomes 1B of T. spelta offer a new alternative for practical application of a cytoplasmic male sterility system in the development of hybrid wheat and hexaploid triticale.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curtis CA, Lukaszewski AJ (1993) Localization of genes in rye that restore male fertility to hexaploid wheat with timopheevi cytoplasm. Plant Breed 111:106–112
Edwards IB (2001) Hybrid wheat. In: Bonjean AP, Angus WJ (eds) The world wheat book. A history of wheat breeding. Lavoisier Publishing, Paris, pp 1019–1045
Goral H (2013) Męska płodność pszenżyta ozimego w zależności od rodzaju cytoplazmy i formy ojcowskiej (in Polish; Male fertility of winter triticales depending on the type of cytoplasm and the male parent). Bul Inst Aklim Hodowli Roslin 269:15–20
Hohn C, Lukaszewski AJ (2016) Engineering the 1BS chromosome arm in wheat to remove the Rf multi locus restoring male fertility in cytoplasms of Aegilops kotschyi, Ae. uniaristata and Ae. mutica. Theor Appl Genet 129:1769–1774
Kobayashi M, Tsunewaki K (1980) Haploid induction and its genetic mechanism in alloplasmic common wheat. J Hered 71:9–14
Lukaszewski AJ (1995) Chromatid and chromosome type breakage-fusion-bridge cycles in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genetics 140:1069–1085
Lukaszewski AJ (2000) Manipulation of the 1RS.1BL translocation in wheat by induced homoeologous recombination. Crop Sci 40:216–225
Massoudi-Nejad A, Nasuda S, McIntosh RA, Endo TR (2002) Transfer of rye chromosome segments to wheat by gametocidal system. Chromosome Res 10:349–357
Mukai Y, Tsunewaki K (1979) Basic studies on hybrid wheat breeding. VIII. A new male sterility-fertility restoration system in common wheat utilizing the cytoplasms of Aegilops kotschyi and Ae. variabilis. Theor Appl Genet 54:153–160
Nalepa S (1991) Hybrid triticale: present and future In: Proc. 2nd Int Triticale Symp, Passo Fundo, Brazil, Oct. 1–5, 1990, CIMMYT, pp 402–407
Tahir CM, Tsunewaki K (1969) Monosomic analysis of Triticum spelta var. duhamelianum, a fertility-restorer for T. timopheevi cytoplasm. Jpn J Genet 44:1–9
Tsunewaki K (1988) Cytoplasmic variation in Triticum and Aegilops. In: Miller TE, Koebner RMD (eds), Proc. 7th Int Wheat Genet Symp. Cambridge UK, July 13–19, 1988, pp 53–62
Tsunewaki K (2015) Fine mapping of the first multi-fertility-restoring gene, Rf multi, of wheat for three Aegilops plasmons, using 1BS–1RS recombinant lines. Theor Appl Genet 128:723–732
Wilson JA, Ross WM (1962) Male-sterility interaction of the Triticum aestivum nucleus and Triticum timopheevi cytoplasm. Wheat Inf Serv 14:29–30
Acknowledgements
This project was supported in part by funding from USDA—NIFA #CA-R-BPS-5411-H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Dr. P. Heslop-Harrison.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukaszewski, A.J. Chromosomes 1BS and 1RS for control of male fertility in wheats and triticales with cytoplasms of Aegilops kotschyi, Ae. mutica and Ae. uniaristata . Theor Appl Genet 130, 2521–2526 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2973-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2973-6