Abstract
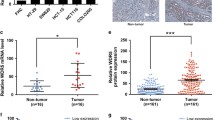
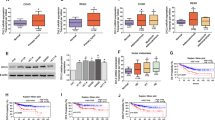
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) play an important role in the metastasis and chemoresistance in the context of colorectal cancer (CRC). Downregulation of death associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) may promote metastasis and chemoresistance of cancer cells through various mechanisms. However, the association between DAPK1 and CSCs or EMT has not been explored. In this study, we demonstrated that DAPK1 was associated with elevated stemness of CSCs in patients with CRC. Silencing of DAPK1 in CRC cell lines promoted the metastasis and chemoresistance due to increased stemness of CSCs and enhanced mesenchymal phenotype, an effect that was mediated via activation of the transcription factor, zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1). Blockade of this signaling pathway attenuated the stemness of CSCs and rescued the EMT process. DAPK1–ZEB1 may lie at the interface of TGF-β and WNT pathways and participate in both CSCs and EMT process. Targeted therapies aimed at DAPK1–ZEB1 pathway may inhibit the chemoresistance and metastasis of CRC.
Key messages
-
Downregulation of DAPK1 promotes chemoresistance and metastasis of CRC.
-
Inhibition of DAPK1 promotes the stemness of cancer stem cells and EMT process.
-
DAPK1–ZEB1 may lie at the interface of TGF-β and WNT pathways.
-
DAPK1–ZEB1 participates in both CSCs and EMT process.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Global Burden of Disease Cancer C, Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H, Moradi-Lakeh M, MF MI, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, Wolfe C, Hamadeh RR, Moore A, Werdecker A, Gessner BD, Te Ao B, McMahon B, Karimkhani C, Yu C, Cooke GS, Schwebel DC, Carpenter DO, Pereira DM, Nash D, Kazi DS, De Leo D, Plass D, Ukwaja KN, Thurston GD, Yun Jin K, Simard EP, Mills E, Park EK, Catala-Lopez F, de Veber G, Gotay C, Khan G, Hosgood HD 3rd, Santos IS, Leasher JL, Singh J, Leigh J, Jonas JB, Sanabria J, Beardsley J, Jacobsen KH, Takahashi K, Franklin RC, Ronfani L, Montico M, Naldi L, Tonelli M, Geleijnse J, Petzold M, Shrime MG, Younis M, Yonemoto N, Breitborde N, Yip P, Pourmalek F, Lotufo PA, Esteghamati A, Hankey GJ, Ali R, Lunevicius R, Malekzadeh R, Dellavalle R, Weintraub R, Lucas R, Hay R, Rojas-Rueda D, Westerman R, Sepanlou SG, Nolte S, Patten S, Weichenthal S, Abera SF, Fereshtehnejad SM, Shiue I, Driscoll T, Vasankari T, Alsharif U, Rahimi-Movaghar V, Vlassov VV, Marcenes WS, Mekonnen W, Melaku YA, Yano Y, Artaman A, Campos I, MacLachlan J, Mueller U, Kim D, Trillini M, Eshrati B, Williams HC, Shibuya K, Dandona R, Murthy K, Cowie B, Amare AT, Antonio CA, Castaneda-Orjuela C, van Gool CH, Violante F, Oh IH, Deribe K, Soreide K, Knibbs L, Kereselidze M, Green M, Cardenas R, Roy N, Tillmann T, Li Y, Krueger H, Monasta L, Dey S, Sheikhbahaei S, Hafezi-Nejad N, Kumar GA, Sreeramareddy CT, Dandona L, Wang H, Vollset SE, Mokdad A, Salomon JA, Lozano R, Vos T, Forouzanfar M, Lopez A, Murray C, Naghavi M (2015) The global burden of cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol 1(4):505–527
Jung B, Staudacher JJ, Beauchamp D (2017) Transforming growth factor beta superfamily signaling in development of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 152(1):36–52
Marin JJ, Sanchez de Medina F, Castano B, Bujanda L, Romero MR, Martinez-Augustin O, Moral-Avila RD, Briz O (2012) Chemoprevention, chemotherapy, and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Drug Metab Rev 44(2):148–172
Zhao J (2016) Cancer stem cells and chemoresistance: the smartest survives the raid. Pharmacol Ther 160:145–158
Zeuner A, Todaro M, Stassi G, De Maria R (2014) Colorectal cancer stem cells: from the crypt to the clinic. Cell Stem Cell 15(6):692–705
Savagner P (2001) Leaving the neighborhood: molecular mechanisms involved during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Bioessays 23(10):912–923
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133(4):704–715
Beck B, Blanpain C (2013) Unravelling cancer stem cell potential. Nat Rev Cancer 13(10):727–738
Steinmann S, Scheibe K, Erlenbach-Wuensch K, Neufert C, Schneider-Stock R (2015) Death-associated protein kinase: a molecule with functional antagonistic duality and a potential role in inflammatory bowel disease (review). Int J Oncol 47(1):5–15
Yuan W, Chen J, Shu Y, Liu S, Wu L, Ji J, Liu Z, Tang Q, Zhou Z, Cheng Y, Jiang B, Shu X (2017) Correlation of DAPK1 methylation and the risk of gastrointestinal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 12(9):e0184959. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184959
Chen HY, Lee YR, Chen RH (2014) The functions and regulations of DAPK in cancer metastasis. Apoptosis 19(2):364–370
Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Ku W, Lee YR, Lin FC, Chang YL, Lin YM, Chen CH, Huang YP, Chiang MJ, Yeh SW, Wu PR, Shen CH, Wu CT, Chen RH (2007) The tumor suppressor DAPK is reciprocally regulated by tyrosine kinase Src and phosphatase LAR. Mol Cell 27(5):701–716
Chen HY, Lin YM, Chung HC, Lang YD, Lin CJ, Huang J, Wang WC, Lin FM, Chen Z, Huang HD, Shyy JY, Liang JT, Chen RH (2012) miR-103/107 promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the metastasis suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res 72(14):3631–3641
Bialik S, Kimchi A (2014) The DAP-kinase interactome. Apoptosis 19(2):316–328
Ogawa T, Liggett TE, Melnikov AA, Monitto CL, Kusuke D, Shiga K, Kobayashi T, Horii A, Chatterjee A, Levenson VV, Koch WM, Sidransky D, Chang X (2012) Methylation of death-associated protein kinase is associated with cetuximab and erlotinib resistance. Cell Cycle 11(8):1656–1663
Jiang Y, Xu P, Yao D, Chen X, Dai H (2017) CD33, CD96 and death associated protein kinase (DAPK) expression are associated with the survival rate and/or response to the chemotherapy in the patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Med Sci Monit 23:1725–1732
Mittag F, Kuester D, Vieth M, Peters B, Stolte B, Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R (2006) DAPK promotor methylation is an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 240(1):69–75
Ivanovska J, Zlobec I, Forster S, Karamitopoulou E, Dawson H, Koelzer VH, Agaimy A, Garreis F, Soder S, Laqua W, Lugli A, Hartmann A, Rau TT, Schneider-Stock R (2015) DAPK loss in colon cancer tumor buds: implications for migration capacity of disseminating tumor cells. Oncotarget 6(34):36774–36788
Zhang P, Sun Y, Ma L (2015) ZEB1: at the crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle 14(4):481–487
Notterman DA, Alon U, Sierk AJ, Levine AJ (2001) Transcriptional gene expression profiles of colorectal adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and normal tissue examined by oligonucleotide arrays. Cancer Res 61(7):3124–3130
Ki DH, Jeung HC, Park CH, Kang SH, Lee GY, Lee WS, Kim NK, Chung HC, Rha SY (2007) Whole genome analysis for liver metastasis gene signatures in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 121(9):2005–2012
Skrzypczak M, Goryca K, Rubel T, Paziewska A, Mikula M, Jarosz D, Pachlewski J, Oledzki J, Ostrowski J (2010) Modeling oncogenic signaling in colon tumors by multidirectional analyses of microarray data directed for maximization of analytical reliability. PLoS One 5(10). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013091
Lo PK, Kanojia D, Liu X, Singh UP, Berger FG, Wang Q, Chen H (2012) CD49f and CD61 identify Her2/neu-induced mammary tumor-initiating cells that are potentially derived from luminal progenitors and maintained by the integrin-TGFbeta signaling. Oncogene 31(21):2614–2626
Sadanandam A, Lyssiotis CA, Homicsko K, Collisson EA, Gibb WJ, Wullschleger S, Ostos LCG, Lannon WA, Grotzinger C, Del Rio M, Lhermitte B, Olshen AB, Wiedenmann B, Cantley LC, Gray JW, Hanahan D (2013) A colorectal cancer classification system that associates cellular phenotype and responses to therapy. Nat Med 19(5):619–625
Chen J, Yuan W, Wu L, Tang Q, Xia Q, Ji J, Liu Z, Ma Z, Zhou Z, Cheng Y, Shu X (2017) PDGF-D promotes cell growth, aggressiveness, angiogenesis and EMT transformation of colorectal cancer by activation of Notch1/Twist1 pathway. Oncotarget 8(6):9961–9973
Aigner K, Dampier B, Descovich L, Mikula M, Sultan A, Schreiber M, Mikulits W, Brabletz T, Strand D, Obrist P, Sommergruber W, Schweifer N, Wernitznig A, Beug H, Foisner R, Eger A (2007) The transcription factor ZEB1 (deltaEF1) promotes tumour cell dedifferentiation by repressing master regulators of epithelial polarity. Oncogene 26(49):6979–6988
Jang CW, Chen CH, Chen CC, Chen JY, Su YH, Chen RH (2002) TGF-beta induces apoptosis through Smad-mediated expression of DAP-kinase. Nat Cell Biol 4(1):51–58
You H, Ding W, Rountree CB (2010) Epigenetic regulation of cancer stem cell marker CD133 by transforming growth factor-beta. Hepatology 51(5):1635–1644
Bae WJ, Lee SH, Rho YS, Koo BS, Lim YC (2016) Transforming growth factor beta1 enhances stemness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells through activation of Wnt signaling. Oncol Lett 12(6):5315–5320
Schneider-Stock R (2014) DAPK: a cancer gene chameleon. Apoptosis 19(2):285
Olsen OE, Wader KF, Hella H, Mylin AK, Turesson I, Nesthus I, Waage A, Sundan A, Holien T (2015) Activin A inhibits BMP-signaling by binding ACVR2A and ACVR2B. Cell Commun Signal 13:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-015-0104-z
Joseph JV, Conroy S, Tomar T, Eggens-Meijer E, Bhat K, Copray S, Walenkamp AM, Boddeke E, Balasubramanyian V, Wagemakers M, den Dunnen WF, Kruyt FA (2014) TGF-beta is an inducer of ZEB1-dependent mesenchymal transdifferentiation in glioblastoma that is associated with tumor invasion. Cell Death Dis 5:e1443
Kahlert UD, Maciaczyk D, Doostkam S, Orr BA, Simons B, Bogiel T, Reithmeier T, Prinz M, Schubert J, Niedermann G, Brabletz T, Eberhart CG, Nikkhah G, Maciaczyk J (2012) Activation of canonical WNT/beta-catenin signaling enhances in vitro motility of glioblastoma cells by activation of ZEB1 and other activators of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett 325(1):42–53
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D, zur Hausen A, Brunton VG, Morton J, Sansom O, Schuler J, Stemmler MP, Herzberger C, Hopt U, Keck T, Brabletz S, Brabletz T (2009) The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol 11(12):1487–1495
Kim ST, Sohn I, Do IG, Jang J, Kim SH, Jung IH, Park JO, Park YS, Talasaz A, Lee J, Kim HC (2014) Transcriptome analysis of CD133-positive stem cells and prognostic value of survivin in colorectal cancer. Cancer Genomics & Proteomics 11(5):259–266
Wu PR, Tsai PI, Chen GC, Chou HJ, Huang YP, Chen YH, Lin MY, Kimchi A, Chien CT, Chen RH (2011) DAPK activates MARK1/2 to regulate microtubule assembly, neuronal differentiation, and tau toxicity. Cell Death Differ 18(9):1507–1520
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N, Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A, Chinnaiyan AM (2004) Large-scale meta-analysis of cancer microarray data identifies common transcriptional profiles of neoplastic transformation and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(25):9309–9314
Yi H, Peng R, Zhang LY, Sun Y, Peng HM, Liu HD, Yu LJ, Li AL, Zhang YJ, Jiang WH, Zhang Z (2017) LincRNA-Gm4419 knockdown ameliorates NF-kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated inflammation in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Death Dis 8(2):e2583
Benderska N, Ivanovska J, Rau TT, Schulze-Luehrmann J, Mohan S, Chakilam S, Gandesiri M, Ziesche E, Fischer T, Soder S, Agaimy A, Distel L, Sticht H, Mahadevan V, Schneider-Stock R (2014) DAPK-HSF1 interaction as a positive-feedback mechanism stimulating TNF-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Sci 127(Pt 24):5273–5287
Acknowledgements
We thank Medjaden Bioscience Limited (Hong Kong, China) for proofreading this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant number 81470789, and 81271199), and Research Fund of Public welfare in Health Industry (grant number 201402015). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Wuhan China). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in accordance with the guidelines in The Declaration of Helsinki 2000. All mouse experiments were conducted with approval of the Institutional Animal Care and Treatment Committee of Tongji Medical College of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, W., Ji, J., Shu, Y. et al. Downregulation of DAPK1 promotes the stemness of cancer stem cells and EMT process by activating ZEB1 in colorectal cancer. J Mol Med 97, 89–102 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1716-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1716-8