Tsuga heterophylla
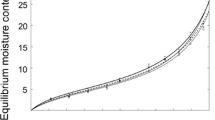
), Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), western red cedar (Thuja plicata), sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis), and lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta). Enthalpy and entropy show a strong negative relation to the moisture content, the absolute desorption values always being higher than the adsorption ones, but with no clear trend between and within the species. Furthermore, it is shown that the linear plot of compensation between enthalpy and entropy correlates well for water sorption in wood; that water adsorption or desorption are irreversible, and that both are enthalpy-driven mechanisms.
Tsuga heterophyll
, Pseudotsuga menziesi, Thuja plicata, Picea sitchensis), und Pinus contorta. Enthalpie und Entropie steigen mit fallender Feuchte. Die Desorptionswerte sind immer etwas höher als die Adsorptionswerte. Zwischen den Holzarten gab es keine signifikanten Unterschiede. Die lineare Kompensation zwischen Enhalpie und Entropie korrelliert gut mit der Sorption. Absorption und Desorption sind irreversible, Enthalpie-getriebene Prozesse.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koumoutsakos, A., Avramidis, S. Enthalpy-entropy compensation in water sorption by various wood species. Holz als Roh- und Werkstoff 57, 379–382 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001070050363
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001070050363