Abstract
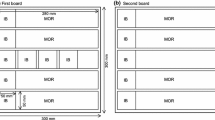
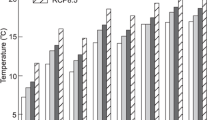
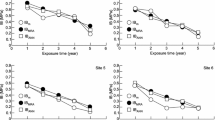
An outdoor test on particleboards subjected to various climatic conditions was conducted in Japan. The significant climatic factors that reduce the particleboard strength (bending strength and internal bond strength) were investigated using multiple regression analysis. The climatic factors that reduce strength were temperature, sunshine duration, and/or precipitation. These three factors were not always significant; the significant climatic factors were different for each exposure time. In addition, the effects of climatic factors on strength reduction were different. Thus, multiple regression analysis using each climatic factor separately was not powerful. Therefore, the three climatic factors were combined into a first principal component using principal component analysis. The principal component score is referred to as the climate deterioration index (CDI). Strength at each exposure time decreased linearly with increasing CDI. The CDI is simpler and more useful as a climate index than individual climatic factors for predicting the strength reduction. In addition, both the relationship between CDI and strength reduction at each exposure time using analysis of covariance and the effects of CDI and exposure time were significant.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki S (2014) Statistical analysis using R (in Japanese). Ohmsha, Tokyo, p 143
Crawley MJ (2012) Statics: an introduction using R (Japanese version). (Translator; Nomakuchi K, Kikuchi Y) Kyoritsu Shuppan, Tokyo, pp 201–209
Crawley MJ (2012) Statics: An introduction using R (Japanese version). (Translator; Nomakuchi K, Kikuchi Y) Kyoritsu Shuppan, Tokyo, pp 226–227
Gatchell CJ, Heebink BG, Hefty FV (1966) Influence of component variables on properties of particleboard for exterior use. Forest Prod J 16(4):46–59
Hann RA, Black JM, Blomquist RF (1962) How durable is particleboard? Forest Prod J 12:577–584
Japan Meteorological Agency (2014) http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/index.html. Accessed 1 April 2014
Japanese Industrial Standards (2003) JIS standard specification for particleboard. JIS A 5908. Japanese Standards Association, Tokyo
Kawai S, Suda H, Sasaki H (1987) Production technology for low density particleboard IV. Effects of particle density and compaction ratio on board properties. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 33:385–392
Kojima Y, Suzuki S (2011a) Evaluating the durability of wood-based panels using internal bonding strength results from accelerated aging treatments. J Wood Sci 57:7–13
Kojima Y, Suzuki S (2011b) Evaluating the durability of wood-based panels using bending properties after accelerated aging treatments. J Wood Sci 57:126–133
Kojima Y, Norita H, Suzuki S (2009) Evaluating the durability of wood-based panels using thickness swelling results from accelerated aging treatments. Forest Prod J 59(5):35–41
Kojima Y, Shimoda T, Suzuki S (2012) Modified method for evaluating weathering intensity using outdoor exposure tests on wood-based panels. J Wood Sci 58:525–531
Korai H (2012) Durability of medium density fiberboard subjected to outdoor exposure (in Japanese). Mokuzai Gakkaishi 58:347–356
Korai H, Hattori K (2013) Effects of surface coating on durability improvement of particleboard subjected to outdoor exposure (in Japanese). Mokuzai Gakkaishi 59:361–366
Korai H, Saotome H (2014) Effects of water soaking and outdoor exposure on nail joint properties of particleboard. J Wood Sci 60:134–140
Korai H, Watanabe K (2015) Effectiveness of principal component analysis for analyzing particleboard subjected to outdoor exposure. J Wood Sci 61:35–39
Korai H, Sekino N, Saotome H (2012) Effects of outdoor exposure angle on the deterioration of wood-based board properties. Forest Prod J 62:184–190
Korai H, Adachi K, Saotome H (2013) Deterioration of wood-based boards subjected to outdoor exposure in Tsukuba. J Wood Sci 59:24–34
Korai H, Saotome H, Ohmi M (2014a) Effects of water soaking and outdoor exposure on modulus of rupture and internal bond strength of particleboard. J Wood Sci 60:127–133
Korai H, Watanabe K, Nogami H, Fukino M, Fujimoto Y (2014b) Simple and useful index for analyzing particleboard subjected to outdoor exposure. J Adhes Soc Jpn 50:260–267
River BH (1994) Outdoor aging of wood-based panels and correlation with laboratory aging. Forest Prod J 44(11/12):55–65
Sekino N, Sato H, Adachi K (2014) Evaluation of particleboard deterioration under outdoor exposure using several different types of weathering intensity. J Wood Sci 60:141–151
Suchsland O (1973) Hygroscopic thickness swelling and related properties of selected commercial particleboards. Forest Prod J 22(7):26–30
Suzuki S (2001) Evaluation of wood-based panel durability (in Japanese). Wood Indus 56:7–12
Watanabe K, Korai H, Matsumoto Y, Hayashi T (2014) Predicting internal bond strength of particleboard under outdoor exposure based on climate data. Comparison of multiple liner regression and artificial network. J Wood Sci. doi:10.1007/s10086-014-1446-7
Wong ED, Zhang M, Wang Q, Kawai S (1998) Effects of mat moisture content and press closing speed on the formation of density profile and properties of particleboard. J Wood Sci 44:287–295
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (21380108) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. The authors are grateful for the grant received. The outdoor exposure test was conducted as part of a project organized by the Research Working Group on Wood-based Panels from the Japan Wood Research Society. The authors express their thanks to all participants of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korai, H., Watanabe, K. Comparison between climatic factors and climate deterioration index on strength reduction of particleboards subjected to various climatic conditions in Japan. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 73, 563–571 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-015-0918-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-015-0918-9