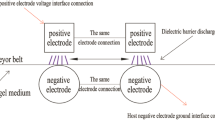
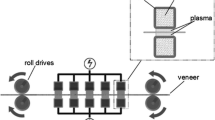
Abstract
This study investigated the effect of a plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure on the absorption characteristics of beech veneers by using a dielectric barrier discharge on the DMDHEU (1,3-dimethylol-4,5-dihydroxyethylene urea). Immersion tests with varying immersion durations showed that plasma treatment significantly accelerated the DMDHEU-solution uptake of the veneers. Additionally, improved bulking characteristics were observed for plasma-treated and DMDHEU-immersed veneers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acda MN, Devera EE, Cabangon RJ, Ramos HJ (2012) Effects of plasma modification on adhesion properties of wood. Int J Adhes Adhes 32:70–75
Avramidis G, Militz H, Avar I, Viöl W, Wolkenhauer A (2012) Improved absorption characteristics of thermally modified beech veneer produced by plasma treatment. Eur J Wood Prod 70:545–549
Blanchard V, Blanchet P, Riedl B (2009) Surface energy modification by radiofrequency inductive and capacitive plasmas at low pressures on sugar maple: an exploratory study. Wood Fiber Sci 41:245–254
Busnel F, Blanchard V, Pregent J, Stafford L, Riedl B, Blanchet P, Sarkissian A (2010) Modification of sugar maple (Acer saccharum) and black spruce (Picea mariana) wood surfaces in a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) at atmospheric pressure. J Adhes Sci Technol 24:1401–1413
Furuno T, Imamura Y, Kajita H (2004) The modification of wood by treatment with low molecular weight phenol-formaldehyde resin: a properties enhancement with neutralized phenolic-resin and resin penetration into wood cell walls. Wood Sci Technol 37:349–361
Haase JG, Evans PD (2010) Plasma modification of wood surfaces to improve the performance of clear coatings. In: Hill CAS, Militz H, Andersons B (eds) The Fifth European Conference on Wood Modification, Riga, Latvia, 2010. Latvian State Institut of Wood Chemistry, pp 271–274
Hill CAS (2007) Wood modification: chemical, thermal and other processes. John Wiley & Sons, Beijing
Jamali A, Evans PD (2011) Etching of wood surfaces by glow discharge plasma. Wood Sci Technol 45:169–182
Klarhofer L, Viol W, Maus-Friedrichs W (2010) Electron spectroscopy on plasma treated lignin and cellulose. Holzforschung 64:331–336
Kogelschatz U, Eliasson B, Egli W (1997) Dielectric-barrier discharges. Princ Appl J Phys IV 7:47–66
Král P, Ráhel’ J, Stupavská M, Šrajer J, Klímek P, Mishra P, Wimmer R (2015) XPS depth profile of plasma-activated surface of beech wood (Fagus sylvatica) and its impact on polyvinyl acetate tensile shear bond strength. Wood Sci Technol 49:319–330
Lecoq E, Clément F, Panousis E, Loiseau J-F, Held B, Castetbon A, Guimon C (2008) Pinus Pinaster surface treatment realized in spatial and temporal afterglow DBD conditions. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 42:47–53
Militz H (1993) Treatment of timber with water soluble dimethylol resins to improve their dimensional stability and durability. Wood Sci Technol 27:347–355
Niemz P (1993) Physik des Holzes und der Holzwerkstoffe. DRW-Verlag, Stuttgart
Odrášková M, Ráhel’ J, Zahoranová A, Tiňo R, Černák M (2008) Plasma activation of wood surface by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28:203–211
Ohmae K, Minato K, Norimoto M (2002) The Analysis of dimensional changes due to chemical treatments and water soaking for Hinoki (Chamaecyparis obtusa) Wood. Holzforschung 56(1):98–102
Rehn P, Wolkenhauer A, Bente M, Förster S, Viöl W (2003) Wood surface modification in dielectric barrier discharges at atmospheric pressure. Surf Coat Technol 174–175:515–518
Rowell RM (1983) Chemical modification of wood. For Prod Abstr 6(12):363–382
Sakai K, Matsunaga M, Minato K, Nakatsubo F (1999) Effects of impregnation of simple phenolic and natural polycyclic compounds on physical properties of wood. J Wood Sci 45:227–232
Verma P, Junga U, Militz H, Mai C (2009) Protection mechanisms of DMDHEU treated wood against white and brown rot fungi. Holzforschung 63(3):371–378
Wagenführ A, Scholz F (2008) Taschenbuch der Holztechnik. Fachbuchverlag, Leipzig
Wascher R, Avramidis G, Vetter U, Damm R, Peters F, Militz H, Viöl W (2014) Plasma induced effects within the bulk material of wood veneers. Surf Coat Technol 259:62–67
Wepner F (2006) Entwicklung eines Modifizierungsverfahrens für Buchenfurniere (Fagus sylvatica L.) auf Basis von zyklischen N-Methylol-Verbindungen. Thesis, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Cai Y, Militz H, Viol W (2007a) Investigation of wood and timber surface modification by dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Process Polym 4:S470–S474
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Militz H, Viöl W (2007b) Wood modification by atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. In: Hill CAS, Jones D, Militz H, GA O (eds) The third European conference on wood modification, Cardiff, wales, Biocomposites Centre, University of Wales, Bangor, pp 271–274
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Militz H, Viol W (2008) Plasma treatment of heat treated beech wood—investigation on surface free energy. Holzforschung 62:472–474
Xie Y, Krause A, Mai C, Militz H, Richter K, Urban K, Evans PD (2005) Weathering of wood modified with the N-methylol compound 1,3-dimethylol-4,5-dihydroxyethyleneurea. Polym Degrad Stabil 89:189–199
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), under the supervision of Dr.-Ing. Karen Otten in Jülich, Germany, and the joint research project “PlaNaWood” (Grant no. 03X5519B). The authors would like to thank Viktor Seifert and Roger Skarsten.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wascher, R., Leike, N., Avramidis, G. et al. Improved DMDHEU uptake of beech veneers after plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 73, 433–437 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-015-0916-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-015-0916-y