Abstract
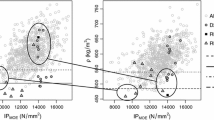
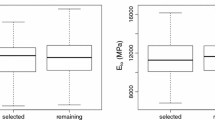
Linear regression models were constructed for chestnut beams of Spanish origin (Asturias, Galicia, Catalonia and Extremadura) using the global modulus of elasticity (MOE g ) and bending strength (MOR), both obtained by destructive tests, as dependent variables, and the results of non-destructive measurements, visual grading parameters and density as independent variables. The variables selected were density, wave velocity, sample length, dynamic modulus of elasticity, maximum knot diameter in relation to height and concentrated knot diameter ratio. Linear regression models were constructed to indirectly estimate the mechanical properties of the beams. Ultrasonic velocity, density and sample length were the best predictors of MOE g (R 2 = 0.740 and 0.734 SE). Regression adjustments for MOR presented low coefficients of determination and high errors. The visual grading parameters of the beams did not play a significant role in the prediction of either MOE g or MOR.
Zusammenfassung
Die Biegefestigkeit (MOR) und der globale Elastizitätsmodul (MOEg) von Kastanienschnittholz spanischer Herkunft (Asturien, Galizien, Katalonien und Extremadura) für Bauzwecke wurden mittels visueller und zerstörungsfreier Verfahren über Regressionsanalysen bestimmt. Elastizitätsmodul und Biegefestigkeit wurden als abhängige Variablen experimentell bestimmt. Als Sortierparameter wurden die Dichte, die Ultraschallgeschwindigkeit, die Prüfkörperlänge, der dynamische E-Modul, der auf die Höhe bezogene maximale Astdurchmesser und die auf den Umfang bezogene Summe der Astdurchmesser einer Astansammlung verwendet. Als am besten für die Vorhersage des globalen E-Moduls geeignet, erwiesen sich Ultraschallgeschwindigkeit, Rohdichte und Prüfkörperlänge (Bestimmtheitsmaß (R2) = 0,740 und Schätzfehler 0,734). Die Regressionsmodelle für Biegefestigkeit ergaben ein niedriges Bestimmtheitsmaß und hohe Schätzfehler. Die visuellen Sortiermerkmale spielten für die Vorhersage von MOEg oder MOR keine bedeutende Rolle.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña L, Díez M, Casado M (2006) Ultrasounds and structural timber quality. Application to Pinus Pinaster Ait. CIDEU 2:7–26
Bucur V (2006) Acoustics of wood. Springer, Heidelberg
Casado M, Acuña L, Vecilla D, Basterra A, Pando V, Relea E (2007) Determination of the strength properties of Pinus sylvestris structural timber through PLG. In: 11th NDT Spanish Conference. Gijón
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112–1:155–159
Divos F (2002) Portable Lumber Grader. In: 13th international symposium on non-destructive testing of wood. Berkeley, USA
Divos F, Sismandy F (2010) Strength Grading of Structural Lumber by Portable Lumber Grading—Effect of knots. In: Final conference of COST action E53. Edinburgh, Scotland
Divos F, Tanaka T (1997) Lumber strength estimation by multiple regression. Holzforschung 51(5):467–471
Esteban M (2003). Determination of strength properties of large cross section structural timber and application to existing softwood structures. Dissertation, Polytechnic University of Madrid
Faggiano B (2009) Mechanical identification by NDT of old chestnut structural timber. In: First international conference PROHITECH. Rome, Italy
Feio A, Lourenço P, Machado J (2007) Non-destructive evaluation of the mechanical behaviour of chestnut wood in tension and compression parallel to grain. Int J Archit Herit 1(3):272–292
Fernández-Golfín J, Conde M, Hermoso E (2007) Improving the prediction of strength and rigidity of structural timber by combining ultrasound techniques with visual grading parameters. Materiales de Construcción 57(288):49–59
Hanhijarvi A, Ranta-Maunus A (2008) Development of strength grading of timber using combined measurement techniques. VTT, Espoo
Hanhijärvi A, Ranta Maunus A, Turk G (2005) Potential of strength grading of timber with combined measurement techniques. Report of the Combigrade—project—phase 1. VTT Publications
Iñiguez G (2007) Classification by non-destructive techniques and evaluation of mechanical properties of softwood large cross section sawn timber for structural use. Dissertation, Polytechnic University of Madrid
Kretschmann DE, Green DW (1999) Mechanical grading of oak timbers. J Mater Civ Eng 11(2):91–97
Nocetti M, Bacher M, Brunetti M, Crivellaro A, van de Kuilen JWG (2010) Machine grading of Italian structural timber: preliminary results on different wood species. In: World conference on timber engineering. Trentino, Italy
Piter JC, Zerbino RL, Blaß HJ (2004) Machine strength grading of Argentinean Eucalyptus grandis. Main grading parameters and analysis of strength profiles according to European standards. Holz als Roh und Werkstoff 62(1):9–15
UNE-EN 408 (2011) Timber structures. Sawn timber and glued laminated timber for structural use. Determination of some physical and mechanical properties
Vega A, Guaita M, Dieste A, Majada J, Fernández I, Baño V (2011) Evaluation of the influence of visual parameters on wave transmission velocity in sawn chestnut timber. In: 17th international nondestructive testing and evaluation of wood symposium. Sopron, Hungary
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Science and Innovation of Spain (MICIN) and the Plan for Science, Technology and Innovation of the Principality of Asturias (PCTI) for funding of the research project “Forest and industrial valorisation of Spanish chestnut” (VALOCAS). Funding of this work was conducted through the lines Singular Strategic Projects (MICIN) and Complementary Support for Singular Strategic Projects carried out in Asturias (PCTI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vega, A., Dieste, A., Guaita, M. et al. Modelling of the mechanical properties of Castanea sativa Mill. structural timber by a combination of non-destructive variables and visual grading parameters. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 70, 839–844 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-012-0626-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-012-0626-7