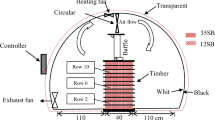
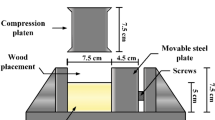
Abstract
The development of twist in Norway spruce boards (Picea abies Karst.) during normal temperature kiln drying was researched. Tangentially oriented boards were sawn from diametrical radial planks, from which the basic wood properties, i.e. linear shrinkage and grain angle, were determined. The unrestrained boards were kiln dried using a selected drying schedule. During the controlled drying process the moisture content (MC) and twist of the boards were measured. Twist was generally induced by the shrinkage of wood below the fibre saturation point, and increased in proportional to the decrease in MC. The earlier appearance of twist, with regard to MC and drying time, was confirmed in the case of boards sawn from the central part of logs. The final twist amounted to between 10 and 20°/m in the case of boards close to the pith, and decreased to less than 4°/m in the case of boards sawn at a radius of 70 mm from the centre of the logs. Ring curvature had the highest impact on the final twist of the dried boards, followed by grain angle and tangential shrinkage.
Zusammenfassung
Untersucht wurde die Entwicklung der Verdrehung von Fichtenholz während der technischen Trocknung unter üblichen Temperaturen. Kernbohlen wurden in Bretter mit tangentialem Jahrringverlauf aufgetrennt und deren Eigenschaften, d. h. lineares Schwindmaß und Faserabweichung, wurden bestimmt. Die Proben wurden unbehindert gelagert und mit einem ausgewählten Trocknungsprogramm getrocknet. Während des Trocknungsverlaufes wurden die Holzfeuchte (MC) und die Verdrehung der Bretter gemessen. Die Verdrehung wurde im Allgemeinen durch Schwinden des Holzes unterhalb Fasersättigung verursacht und sie nahm mit abnehmender Holzfeuchte proportional zu. Die Bretter aus dem marknahen Bereich verdrehten sich früher, d. h. bei hoher Holzfeuchte und kürzerer Trocknungszeit. Am Ende betrug die Verdrehung bei marknahen Brettern 10–20°/m, während Bretter mit einem Markabstand von 70 mm nur eine Verdrehung von 4°/m aufwiesen. Den größten Einfluss auf die endgültige Verdrehung der getrockneten Bretter hatte der vom Markabstand abhängige Jahrringverlauf gefolgt von der Faserabweichung und dem tangentialen Schwindmaß.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arganbright DG, Venturino JA, Gorvad M (1978) Warp reduction in young-growth ponderosa pine studs dried by different methods with top-load restraint. For Prod J 28(8):47–52
Bäckström M, Johansson M (2006) Analytical model of twist in Norway spruce (Picea abies) timber. Scand J For Res 21:54–62
Bäckström M, Kliger R (2006) Restraining moisture related twist in timber structures. Holz Roh- Werkst 64:235–242
Balodis V (1972) Influence of grain angle on twist in seasoned boards. Wood Sci 5:44–50
Booker RE (2005) Geometric model to predict twist in unrestrained boards. Wood Sci Technol 39:269–289
Chong ET, Fogg PJ (1989) Differences in moisture content and shrinkage between innerwood and outerwood of two shortleaf pine trees. For Prod J 39(3):13–18
Cown DJ, McCounchie DL (1983) Radiata pine wood properties survey (1977–1982). FRI Report, New Zeland Forest Service, 50 pp
Danborg F (1994) Spiral grain in plantation trees of Picea abies. Can J For Res 24:1662–1671
Donaldson LA, Burdon RD (1995) Clonal variation and repeatability of microfibril angle in Pinus radiata. NZ J For Sci 25:164–174
Feist WC, Tarkow H (1967) A new procedure for measuring fiber saturation points. For Prod J 17(10):65–68
Forsberg D, Warensjö M (2001) Grain angle variation: a major determination of twist in sawn Picea abies Karst. Scand J For Res 16:269–277
Frühwald E (2006) Improvement of shape stability by high-temperature treatment of Norway spruce: effect of drying at 120°C with and without restraint of twist. Holz Roh- Werkst 64:24–29
Frühwald E (2007) Effect of high temperature drying and restraint on twist of Norway spruce. Drying Technol 25:489–496
Gorišek Ž, Straže A (2005) Influence of wood structure on the warping quality in Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.) during kiln drying. In: Jambreković V (ed) International conference: wood in the construction industry, proceedings, Zagreb, 124 pp
Gorišek Ž, Straže A, Pervan S (2004) Juvenile wood in spruce (Picea abies Karst.)—limitation of use. In: Jambreković V (ed) International conference: wood in the construction industry, proceedings, Zagreb, 92 pp
Gorišek Ž, Straže A, Gornik-Bučar D, Bučar B (2006) Influence of some anatomical and physical properties of wood on warp during kiln drying of spruce (Picea abies Karst.) and silver fir (Abies alba Mill.). In: Teischinger A (ed) COST E40, proceedings, Biel: 67–72
Harris JM (1977) Shrinkage and density of radiata pine compression wood in relation to its anatomy and mode of formation. NZ J For Sci 7:91–106
Harris JM, Meylan BA (1965) The influence of microfibril angle on longitudinal and tangential in Pinus radiata. Holzforschung 19:144–153
Johansson M, Perstorper M, Kliger R (2001) Distortion of Norway spruce timber, part 2: modelling twist. Holz Roh- Werkst 59:155–162
Kellogg RM, Wangaard FF (1969) Variation in the cell-wall density of wood. Wood Fiber 1:180–204
Kliger R, Bengtsson C, Johansson M (2005) Comparison between HT and LT-dried spruce timber in terms of shape stability and dimensional stability. Holzforschung 59:647–653
Mackay JFG (1973) The influence of drying conditions and other factors on twist and torque in Pinus radiata studs. Wood Fiber 4:264–271
Milota MR (2000) Warp and shrinkage of hem-fir stud lumber dried at conventional and high temperature drying. For Prod J 50(11/12):79–84
Ormarsson S (1995) A finite element study of the shape stability of wand timber subjected to the moisture variations. Report TVSM-3017, Lund Univ of Tech, 91 pp
Ormarsson S, Dahlblom O, Petersen H (1998) A numerical study of the shape stability of sawn timber subjected to moisture variation, part 1: theory. Wood Sci Technol 32:325–334
Ormarsson S, Dahlblom O, Petersson H (1999) A numerical study of shape stability of sawn timber subjected to moisture variation, part 2: simulation of drying board. Wood Sci Technol 33:407–423
Pang S, Pearson H (2004) Experimental investigation and practical application of superheated steam drying technology for softwood timber. Drying Tech 22(9):2079–2094
Pang S, Simpson IG, Haslett AN (2001) Cooling and steam conditioning after high-temperature drying of Pinus radiata board: experimental investigation and mathematical modelling. Wood Sci Technol 35:487–502
Perstorper M, Pellican PJ, Kliger R, Johansson G (1995) Quality of timber products from Norway spruce, part 1: optimization, key variables and experimental study. Wood Sci Technol 29:157–170
Perstorper M, Johansson M, Kliger R, Johansson G (2001) Distortion of Norway spruce timber, part 1: variation of relevant wood properties. Holz Roh- Werkst 59:94–103
Price EW, Koch P (1980) Kiln time and temperature affect shrinkage warp and mechanical properties of southern pine lumber. For Prod J 47(1):41–47
Sandland MK, Tronstad S (2001) Possibilities to control deformations in wood during drying to meet the requirements from timber end-users. In: Welling J (ed) COST E15, proceedings, Helsinki, 10 pp
Sepulveda P (2001) Measurement of spiral grain with computed tomography. J. Wood Sci 47:289–293
Shelly JR, Arganbright DG, Birnbach M (1979) Severe warp development in young-growth ponderosa pine studs. Wood Fiber 11:50–56
Stamm AJ (1971) Review of nine methods for determining the fiber saturation points of wood and wood products. Wood Sci 4:114–128
Stevens WC (1963) The transverse shrinkage of wood. For Prod J 13:386–389
Stevens WC, Johnston DD (1960) Distortion caused by spiral grain. Timber Technol 68:217–218
Straže A, Gorišek Ž (2000) Density in mechanical properties of the juvenile and adult wood of Norway spruce wood (Picea abies Karst.) and silver fir (Abies alba Mill.). Wood (Les) 52(6):185–190
Thiam M, Milota MR, Leichti RJ (2002) Effect of high-temperature drying on bending and shear strengths of western hemlock lumber. For Prod J 52(4):64–68
Vorreiter L (1963) Fasersättigungsfeuchte und höchste Wasseraufnahme der Hölzer. Holzforschung 17:139–146
Warensjo M, Rune G (2004) Effect of compression wood and grain angle on deformations on studs from 22-year-old Scots pine trees. Scand J For Res 19(5):48–54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Straže, A., Kliger, R., Johansson, M. et al. The influence of material properties on the amount of twist of spruce wood during kiln drying. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 69, 239–246 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0422-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-010-0422-1