Abstract
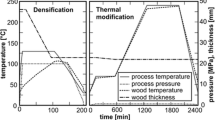
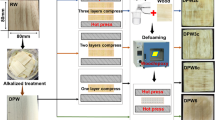
The mechanical properties of densified wood relevant for structural composites were studied. Low density hybrid poplar (Populus deltoides × Populus trichocarpa) was densified using the viscoelastic thermal compression (VTC) process to three different degrees of densification (63, 98, and 132%). The modulus of rupture (MOR) and the modulus of elasticity (MOE) of the control (undensified) wood and of the VTC wood were determined. The bonding performance of the control and VTC wood, using two phenol-formaldehyde (PF) adhesives, was studied. Four different 3-layer composites were also prepared from undensified and VTC wood, and tested in four-point bending. The results showed that the bending properties of the VTC wood (MOR and MOE) were significantly improved due to the increased density. The bonding performance of VTC wood with PF adhesives was comparable with or better than in the case of the control wood. Increased density of the face layers in the 3-layer VTC composites was advantageous for their mechanical performance.
Zusammenfassung
Die für tragende Verbundwerkstoffe relevanten mechanischen Eigenschaften von verdichtetem Holz wurden untersucht. Das Holz der Hybridpappel (Populus deltoides × Populus trichocarpa), einer Holzart mit geringer Dichte, wurde mit viskoelastischer thermischer Verdichtung (VTC) in drei verschiedenen Graden (63, 98, und 132%) verdichtet. Die Biegefestigkeit und der Elastizitätsmodul einer Referenzprobe und des VTC Holzes wurden bestimmt. Das Verklebungsverhalten mit Phenolformaldehyd (PF)-Harz einer Referenzprobe und des VTC Holzes wurden untersucht. Vier verschiedene dreilagige Schichthölzer wurden aus unverdichtetem und aus VTC Holz hergestellt und anschließend im 4-Punkt-Biegeversuch geprüft. Die Biegefestigkeit und der Elastizitätsmodul des verdichteten Holzes wurden durch die Verdichtung signifikant verbessert. Das Verklebungsverhalten des VTC Holzes mit PF-Harz war vergleichbar oder besser als das der Referenzprobe. Die erhöhte Verdichtung der Deckschicht des dreilagigen VTC Schichtholzes wirkte sich vorteilhaft auf die mechanischen Eigenschaften aus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blomberg J, Persson B (2004) Plastic deformation in small clear pieces of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) during densification with the CaLignum process. J Wood Sci 50:307–314
Dwianto W, Morooka T, Norimoto M, Kitajima T (1999) Stress relaxation of Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don) wood in radial compression under high temperature steam. Holzforschung 53(5):541–546
EN 302-1 (2004) Adhesives for load bearing timber structures. Adhesives for load-bearing timber structures Test methods: Part 1: Determination of bond strength in longitudinal tensile shear strength
Gdoutos EE, Daniel IM, Wang KA, Abot JL (2001) Nonlinear behavior of composite sandwich beams in three-point bending. Exp Mech 41(2):182–189
Grossman PUA (1976) Requirements for a model that exhibits mechano-sorptive behavior. Wood Sci Technol 10:163–168
Inoue M, Norimoto M, Tanahashi M, Rowell MR (1993) Steam or heat fixation of compressed wood. Wood Fiber Sci 25(3):224–235
Janowiak JJ, Bukowski SW (2000) Toughness properties for several composite lumber materials. Forest Prod J 50(5):51–54
Kamke FA, Sizemore H (2005) Viscoelastic thermal compression of wood. U.S. Patent Application No. US2005/006004AI, Jan. 13
Kamke FA (2006) Densified radiata pine for structural composites. Maderas: Cienc Tecnol 8(2):83–92
Kawasaki T, Zhang M, Wang Q, Komatsu K, Kawai S (2006) Elastic moduli and stiffness optimization in four-point bending of wood-based sandwich panel for use as structural insulated walls and floors. J Wood Sci 52:302–310
Kutnar A, Kamke FA, Sernek M (2008) Density profile and morphology of viscoelastic thermal compressed (VTC) Wood. Wood Sci Technol DOI 10.1007/s00226-008-0198-1
Navi P, Girardet F (2000) Effects of thermo-hydro-mechanical treatment on the structure and properties of wood. Holzforschung 54(3):287–293
Seborg RM, Millet M, Stamm AJ (1945) Heat-stabilized compressed wood. Staypak. Mech Eng 67:25–31
Sernek M, Kamke FA, Glasser WG (2004) Comparative analysis of inactivated wood surfaces. Holzforschung 58:22–31
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutnar, A., Kamke, F.A. & Sernek, M. The mechanical properties of densified VTC wood relevant for structural composites . Holz Roh Werkst 66, 439–446 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-008-0259-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-008-0259-z