Abstract.
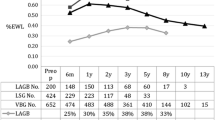
Morbid obesity (body mass index > 40 kg/m2) is a risk factor for cardiovascular, pulmonary, metabolic, neoplastic, and psychologic sequelae. In the present prospective clinical study 65 patients (11 men, 54 women) underwent vertical banded gastroplasty (Mason procedure) from June 1994 to October 1997. The median age was 41 ± 5.3 years (range 18–69; n = 65). Preoperative body weight was 135 ± 23 kg (96–229; n = 65), excess body weight in kg was 75 ± 6.9 (44–155; n = 65) or in % 126 ± 10 (78–223; n = 65) and BMI was 49 ± 7.4 kg/m2 (39–69; n = 65). Mean hospital stay was 9.7 ± 2.4 days (6–18; n = 65). Hospital mortality was 0 % (0/65). Early complications were vomiting (30 %) and problems in wound healing (15 %; n = 65). Late complications (> 30 days) were incisional hernias (13.8 %) and staple-line disruptions (12.3 %; n = 65) with a reoperation rate of 23 % (15/65). Median follow-up was 15.0 ± 5.2 months (2–42) with a follow up rate of 100 %. Mean weight loss after 12 months was 38.5 ± 17 kg (30–98; n = 34) (P < 0.0001) and loss of excessive body weight 65 ± 10 % (57–86; n = 34), respectively (P < 0.0001). Cardiovascular risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia) were significantly improved within 12 months (n = 34). Vertical banded gastroplasty (Mason procedure) – well established for 20 years – is a good, safe therapy for morbid obesity if strict indications for operation are observed and if there is multidisciplinary long-term follow-up. Co-morbid risk factors are considerably reduced and a long-term weight loss of more than 50 % can be achieved without the risk of pathological metabolic changes.
Zusammenfassung.
Die morbide Adipositas (Body Mass Index > 40 kg/m2) hat kardiovasculäre, pulmonale, metabolische, neoplastische und psychische Krankheiten zur Folge. Im Rahmen der vorliegenden prospektiven klinischen Studie wurden 65 Patienten im Zeitraum von Juni 1994 bis Oktober 1997 mittels vertikaler Gastroplastik nach Mason operiert (11 Männer, 54 Frauen). Das Durchschnittsalter betrug 41 ± 5,3 Jahre (Range 18–69; n = 65). Das durchschnittliche präoperative Gewicht betrug 135 ± 23 kg (96–229; n = 65), das Übergewicht nach Broca in kg 75 ± 6,9 (44–155; n = 65) oder in % 126 ± 10 (78–223; n = 65) (excess body weight) und der BMI 49 ± 7,4 kg/m2 (39–69; n = 65). Die Hospitalisationszeit betrug 9,7 ± 2,4 Tage (6–18; n = 65). Die Krankenhausmortalität war 0 % (0/65). Erbrechen respektive Regurgitation (30 %) und Wundheilungsstörungen (15 %) waren die häufigsten postoperativen Morbiditätsfaktoren (n = 65). Spätkomplikationen (> 30 Tage) waren Narbenhernien (13,8 %) und Klammernahteröffnungen (12,3 %; n = 65); die Reoperationsrate betrug 23 % (15/65). Der mediane Follow-up betrug 15,0 ± 5,2 Monate (2–42) bei einer Follow-up Rate von 100 %. Die mittlere Gewichtsreduktion nach 12 Monaten betrug 38,5 ± 17 kg (30–98; p < 0,0001; n = 34), der Verlust an Übergewicht 65 ± 10 % (57–86; p < 0,0001; n = 34). Die kardiovasculären Risikofaktoren (Hypertonie, Diabetes, Hyperlipidämie) konnten 12 Monate postoperativ signifikant verbessert werden (n = 34). Die vertikale Gastroplastik nach Mason, eine seit 20 Jahren etablierte Methode in der bariatrischen Chirurgie, stellt bei strenger Indikation und intensiver interdisziplinärer Nachbetreuung eine gute und sichere Therapie der morbiden Adipositas dar. Mit dieser Methode kann die internistische Co-Morbidität beträchtlich gesenkt und eine Gewichtsreduktion von mehr als 50 % des Übergewichts ohne Risiko von metabolischen Langzeitschäden auch langfristig gehalten werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naef, M., Sadowski, C., de Marco, D. et al. Die vertikale Gastroplastik nach Mason zur Behandlung der morbiden Adipositas . Chirurg 71, 448–455 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001040051081
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001040051081