Abstract
Purpose
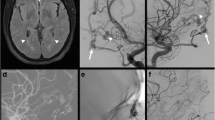
To analyze the angiographic and clinical results of transarterial embolization with Onyx (Medtronic-Covidien, Irvine, CA) in dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) partially fed by arteries arising from the carotid siphon or the vertebral arteries.
Methods
We isolated 40 DAVFs supplied by either the tentorial artery of the internal carotid artery (ICA) or the posterior meningeal artery of the vertebral artery. These DAVFs were embolized with Onyx through the middle meningeal artery or the occipital artery. We reviewed the occurrence of reflux into the arteries of carotid or vertebral origin.
Results
In all the cases, reflux occurred into the first millimeters of the DAVF arterial feeders arising from carotid or vertebral arteries but slowly enough to be controlled by interruption of Onyx injection. Reflux was always minimal and Onyx never reached the ostium of the arteries. No cerebral ischemic complications occurred in our series.
Conclusion
The behavior of Onyx is clearly different from that of cyanoacrylate glue, resulting in superior control during injection. Reflux into arteries arising from the ICA or vertebral artery during DAVF treatment always carries a risk of unintentional non-target embolization of normal cerebral vasculature but Onyx appears to be safe in this situation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cognard C, Januel AC, Silva NA Jr, Tall P. Endovascular treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with cortical venous drainage: new management using Onyx. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:235–41.
Rezende MT, Piotin M, Mounayer C, Spelle L, Abud DG, Moret J. Dural arteriovenous fistula of the lesser sphenoid wing region treated with Onyx: technical note. Neuroradiology. 2006;48:130–4.
Trivelato FP, Abud DG, Ulhôa AC, Menezes Tde J, Abud TG, Nakiri GS, Colli BO, Gusmão SN, Rezende MT (2010) Dural arteriovenous fistulas with direct cortical venous drainage treated with onyx: a case series. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 68:613–618
Abud TG, Nguyen A, Saint-Maurice JP, Abud DG, Bresson D, Chiumarulo L, Enesi E, Houdart E. The use of Onyx in different types of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:2185–91.
Puffer RC, Daniels DJ, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G. Curative Onyx embolization of tentorial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Focus. 2012;32:E4.
Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, Bailly AL, Houdart E, Casasco A, Chiras J, Merland JJ. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology. 1995;194:671–80.
Macdonald JH, Millar JS, Barker CS. Endovascular treatment of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: a single-centre, 14-year experience and the impact of Onyx on local practise. Neuroradiology. 2010;52:387–95.
Lee B, Mehta VA, Amar AP, Tenser MS, Mack WJ. Transarterial embolization of an anterior fossa cranial base dural arteriovenous fistula. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;37:1.
Lv X, Jiang C, Zhang J, Li Y, Wu Z. Complications related to percutaneous transarterial embolization of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas in 40 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30:462–8.
Rabinov JD, Yoo AJ, Ogilvy CS, Carter BS, Hirsch JA. Onyx versus n‑BCA for embolization of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013;5:306–10.
Choo DM, Shankar JJ. Onyx versus nBCA and coils in the treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Interv Neuroradiol. 2016;22:212–6.
Baltsavias G, Valavanis A. Endovascular treatment of 170 consecutive cranial dural arteriovenous fistulae: results and complications. Neurosurg Rev. 2014;37:63–71.
Kim DJ, Willinsky RA, Krings T, Agid R, Terbrugge K. Intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts: transarterial glue embolization-experience in 115 consecutive patients. Radiology. 2011;258:554–61.
Miyamoto N, Naito I, Shimizu T, Yoshimoto Y. Efficacy and limitations of transarterial acrylic glue embolization for intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015;55:163–72.
Tekle WG, Grigoryan M, Tummala RP. Marginal sinus fistula supplied exclusively by vertebral artery feeders. J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2013;6:30–3.
Kim ST, Jeong HW, Seo J. Onyx embolization of dural arteriovenous fistula, using scepter C balloon catheter: a case report. Neurointervention. 2013;8:110–4.
Chapot R, Stracke P, Velasco A, Nordmeyer H, Heddier M, Stauder M, Schooss P, Mosimann PJ. The pressure cooker technique for the treatment of brain AVMs. J Neuroradiol. 2014;41:87–91.
Abud DG, de Castro-Afonso LH, Nakiri GS, Monsignore LM, Colli BO (2016) Modified pressure cooker technique: an easier way to control onyx reflux. J Neuroradiol 43(3):218–222
Gabrieli J, Clarencon F, Di Maria F, Chiras J, Sourour N (2015) Occipital artery: a not so poor artery for the embolization of lateral sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas with onyx. J Neurointerv Surg 9(e1):e8–e9.
Natarajan SK, Ghodke B, Kim LJ, Hallam DK, Britz GW, Sekhar LN. Multimodality treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas in the Onyx era: a single center experience. World Neurosurg. 2010;73:365–79.
Adamczyk P, Amar AP, Mack WJ, Larsen DW. Recurrence of “cured” dural arteriovenous fistulas after Onyx embolization. Neurosurg Focus. 2012;32:E12.
Guedin P, Gaillard S, Boulin A, Condette-Auliac S, Bourdain F, Guieu S, Dupuy M, Rodesch G. Therapeutic management of intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts with leptomeningeal venous drainage: report of 53 consecutive patients with emphasis on transarterial embolization with acrylic glue. J Neurosurg. 2010;112:603–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
T.G. Abud, E. Houdart, J.-P. Saint-Maurice, D.G. Abud, C.E. Baccin, A.D. Nguyen and N. Abdala declare that they have no competing interests.Please confirm or correct the statement on the conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This study was approved by the research ethics committee of Universidade Federal de São Paulo (UNIFESP), registration number 0534/2016, protocol number 1.550.934. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. All procedures were in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Contributors
Thiago G. Abud: analysis and interpretation of cases, writing the article, figure editing.
Emmanuel Houdart: execution of the procedures and clinical follow-up.
Jean-Pierre Saint-Maurice: execution of the procedures and clinical follow-up.
Daniel G. Abud: analysis and interpretation of cases.
Carlos E. Baccin: writing the article.
Andrew D. Nguyen: writing the article.
Nitamar Abdala: supervision and critical revision of the article.
All authors have approved the final version.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abud, T.G., Houdart, E., Saint-Maurice, JP. et al. Safety of Onyx Transarterial Embolization of Skull Base Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas from Meningeal Branches of the External Carotids also Fed by Meningeal Branches of Internal Carotid or Vertebral Arteries. Clin Neuroradiol 28, 579–584 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0615-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0615-7