Abstract
Background and Purpose
In unenhanced computed tomography (CT) of acute ischemic stroke, the density of occluding clots is associated with the content of red blood cells and successful recanalization with stent thrombectomy. However, no CT marker for fibrin content is established. In order to improve clot diagnostics, we conducted an in vitro study to investigate thrombus composition of histologically defined ovine blood clots with unenhanced and contrast-enhanced CT using spectral detector CT (SDCT).
Methods
Ovine blood clot types containing defined amounts of red blood cells (RBC; pure fibrin clots: RBC 0% ± 0, fibrin 100% ± 0), mixed clots (RBC 35.1% ± 4.11, fibrin 79.2% ± 5.6) and red clots (RBC 99.05% ± 1.14, fibrin 0.95% ± 1.14) were scanned in a SDCT (IQon®, Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) (a) in a tube containing saline, (b) 5 min and (c) 3 days after exposure to a 1:50 dilution of iohexol (Accupaque-350®, GE-Healthcare, Boston, MA, USA). The attenuation of the clots was measured in Hounsfield units (HU) in conventional CT datasets as well as virtual noncontrast reconstructions (VNC) of nonenhanced and contrast-enhanced SDCT in a blinded and randomized fashion. Statistical analysis was conducted with ANOVA, Spearman’s correlation, linear and multivariable regression models.
Results
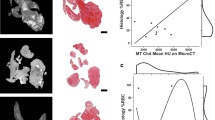
In unenhanced scans, clots differed in density with linear interrelation (fibrin 23.6 ± 1.1, mixed 34.9 ± 1.6, red 46.7 ± 1.6, mean HU ± SD). The blood clots did not show any overlap of density in the native scans and VNC at different time points (p < 0.0001 for each setting and clot type). However, they could not be differentiated after initial contrast exposure (fibrin 108.5 ± 7.8, mixed 105.3 ± 3.5, red 104.8 ± 3.8, mean HU ± SD). After prolonged exposure, the fibrin rich clots showed a significant increase of density due to further uptake of contrast medium (fibrin 163.6 ± 3.6, mixed 138.3 ± 4.1, red 109.6 ± 5.4, mean HU ± SD). In multivariable models, native CT density and contrast enhancement were independent variables associated with thrombus type (p < 0.01 each).
Conclusion
The fibrin content in blood clots is strongly associated with contrast uptake. As previously shown, the density of the clot formations in native CT scans is dependent on the RBC. Our data show that CT density and relative enhancement of clots are independent determinants of clot composition. Using both variables in the CT workup of acute ischemic stroke has the potential to have a decisive impact on patient stratification for treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morales-Vidal S, Biller, J. Stroke pathophysiology. In: Ovbiagele, B, editor. Stroke Management and Recovery Stroke. London: Future Medicine; 2013. p. 6–20. doi:10.2217/ebo.12.443
Niesten JM, van der Schaaf IC, van Dam L, Vink A, Vos JA, Schonewille WJ, de Bruin PC, Mali WP, Velthuis BK. Histopathologic composition of cerebral thrombi of acute stroke patients is correlated with stroke subtype and thrombus attenuation. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88882.
Duffy S, Farrell M, McArdle K, Thornton J, Vale D, Rainsford E, Morris L, Liebeskind DS, MacCarthy E, Gilvarry M. Novel methodology to replicate clot analogs with diverse composition in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017;9(5):486-91.
Marder VJ, Chute DJ, Starkman S, Abolian AM, Kidwell C, Liebeskind D, Ovbiagele B, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Jahan R, Vespa PM, Selco S, Rajajee V, Kim D, Sanossian N, Saver JL. Analysis of thrombi retrieved from cerebral arteries of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2006;37:2086–93.
Kim SK, Yoon W, Kim TS, Kim HS, Heo TW, Park MS. Histologic analysis of retrieved clots in acute ischemic stroke: correlation with stroke etiology and gradient-echo MRI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36:1756–62.
Jang IK, Gold HK, Ziskind AA, Fallon JT, Holt RE, Leinbach RC, May JW, Collen D. Differential sensitivity of erythrocyte-rich and platelet-rich arterial thrombi to lysis with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator. A possible explanation for resistance to coronary thrombolysis. Circulation. 1989;79:920–8.
Kirchhof K, Sikinger M, Welzel T, Zoubaa S, Sartor K. Does the result of thrombolysis with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA) in rabbits depend on the erythrocyte- and fibrin-content of a thrombus? Rofo. 2004;176:98–105.
Almekhlafi MA, Hu WY, Hill MD, Auer RN. Calcification and endothelialization of thrombi in acute stroke. Ann Neurol. 2008;64:344–8.
Yuki I, Kan I, Vinters HV, Kim RH, Golshan A, Viñuela FA, Sayre JW, Murayama Y, Viñuela F. The impact of thromboemboli histology on the performance of a mechanical thrombectomy device. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:643–8.
Boeckh-Behrens T, Schubert M, Förschler A, Prothmann S, Kreiser K, Zimmer C, Riegger J, Bauer J, Neff F, Kehl V, Pelisek J, Schirmer L, Mehr M, Poppert H. The impact of histological clot composition in embolic stroke. Clin Neuroradiol. 2016;26:189–97.
Kirchhof K, Welzel T, Mecke C, Zoubaa S, Sartor K. Differentiation of white, mixed, and red thrombi: value of CT in estimation of the prognosis of thrombolysis phantom study. Radiology. 2003;228:126–30.
Liebeskind DS, Sanossian N, Yong WH, Starkman S, Tsang MP, Moya AL, Zheng DD, Abolian AM, Kim D, Ali LK, Shah SH, Towfighi A, Ovbiagele B, Kidwell CS, Tateshima S, Jahan R, Duckwiler GR, Viñuela F, Salamon N, Villablanca JP, Vinters HV, Marder VJ, Saver JL. CT and MRI early vessel signs reflect clot composition in acute stroke. Stroke. 2012;42(5):1237–43.
Puig J, Pedraza S, Demchuk A, Daunis-I-Estadella J, Termes H, Blasco G, Soria G, Boada I, Remollo S, Baños J, Serena J, Castellanos M. Quantification of thrombus Hounsfield units on noncontrast CT predicts stroke subtype and early recanalization after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:90–6.
Cline B, Vos J, Carpenter J, Rai A. Pathological analysis of extracted clots in embolectomy patients with acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013;5:A15–A6.
Kim J, Park JE, Nahrendorf M, Kim DE. Direct thrombus imaging in stroke. J Stroke. 2016;18:286–96.
Mokin M, Morr S, Natarajan SK, Lin N, Snyder KV, Hopkins LN, Siddiqui AH, Levy EI. Thrombus density predicts successful recanalization with Solitaire stent retriever thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;7:104–7.
Moftakhar P, English JD, Cooke DL, Kim WT, Stout C, Smith WS, Dowd CF, Higashida RT, Halbach VV, Hetts SW. Density of thrombus on admission CT predicts revascularization efficacy in large vessel occlusion acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2013;44:243–5.
Brinjikji W, Duffy S, Burrows A, Hacke W, Liebeskind D, Majoie CB, Dippel DW, Siddiqui AH, Khatri P, Baxter B, Nogeuira R, Gounis M, Jovin T, Kallmes DF. Correlation of imaging and histopathology of thrombi in acute ischemic stroke with etiology and outcome: a systematic review. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016 May 10. [Epub ahead of print]
Santos EM, Marquering HA, den Blanken MD, Berkhemer OA, Boers AM, Yoo AJ, Beenen LF, Treurniet KM, Wismans C, van Noort K, Lingsma HF, Dippel DW, van der Lugt A, van Zwam WH, Roos YB, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Niessen WJ, Majoie CB; MR CLEAN Investigators. Thrombus permeability is associated with improved functional outcome and recanalization in patients with ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2016;47(3):732–41.
Brinjikji W, McDonald JS, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ. Rescue treatment of thromboembolic complications during endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Stroke. 2013;44(5):1343–7.
Leys D, Pruvo JP, Godefroy O, Rondepierre P, Leclerc X. Prevalence and significance of hyperdense middle cerebral artery in acute stroke. Stroke. 1992;23:317–23.
Froehler MT, Tateshima S, Duckwiler G, Jahan R, Gonzalez N, Vinuela F, Liebeskind D, Saver JL, Villablanca JP; UCLA Stroke Investigators.. The hyperdense vessel sign on CT predicts successful recanalization with the merci device in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013;100:130–4.
Tomsick T, Brott T, Barsan W, Broderick J, Haley EC, Spilker J, Khoury J. Prognostic value of the hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign and stroke scale score before ultraearly thrombolytic therapy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996;17:79–85.
Guidelines for Management of Ischaemic Stroke and Transient Ischaemic Attack 2008. Eur Stroke Organ Exec Comm ESO Writ Comm 2012;25:1–126.
Muir KW, Buchan A, von Kummer R, Rother J, Baron JC. Imaging of acute stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:755–68.
Jones CI, Goodall AH. Differential effects of the iodinated contrast agents Ioxaglate, Iohexol and Iodixanol on thrombus formation and fibrinolysis. Thromb Res. 2004;112:65–71.
McDonald MM, Archeval-Lao JM, Cai C, Peng H, Sangha N, Parker SA, Wetzel J, Riney SA, Cherches MF, Guthrie GJ, Roper TC, Kawano-Castillo JF, Pandurengan R, Rahbar MH, Grotta JC. Iodinated contrast does not alter clotting dynamics in acute ischemic stroke as measured by thromboelastography. Stroke. 2014;45:462–6.
Gabriel DA, Jones MR, Reece NS, Boothroyd E, Bashore T. Platelet and fibrin modification by radiographic contrast media. Circ Res. 1991;68:881–7.
Johnson TR, Krauss B, Sedlmair M, Grasruck M, Bruder H, Morhard D, Fink C, Weckbach S, Lenhard M, Schmidt B, Flohr T, Reiser MF, Becker CR. Material differentiation by dual energy CT : initial experience. Eur Radiol. 2007;17(6):1510–7.
Turk AS, Frei D, Fiorella D, Mocco J, Baxter B, Siddiqui A, Spiotta A, Mokin M, Dewan M, Quarfordt S, Battenhouse H, Turner R, Chaudry I. ADAPT FAST study: a direct aspiration first pass technique for acute stroke thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2014;6:260–4.
Maus V, Behme D, Kabbasch C, Borggrefe J, Tsogkas I, Nikoubashman O, Wiesmann M, Knauth M, Mpotsaris A, Psychogios MN. Maximizing first-pass complete reperfusion with SAVE. Clin Neuroradiol. 2017 Feb 13. [Epub ahead of print]
Siller-Matula JM, Plasenzotti R, Spiel A, Quehenberger P, Jilma B. Interspecies differences in coagulation profile. Thromb Haemost. 2008;100:397–404.
Kim EY, Lee SK, Kim DJ, Suh SH, Kim J, Heo JH, Kim DI. Detection of thrombus in acute ischemic stroke: value of thin-section noncontrast-computed tomography. Stroke. 2005;36:2745–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Truman for editing of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was kindly supported by Neuravi Ltd. The company produces the predefined ovine blood clots for scientific purposes and provided them to our working group. The authors did not receive further funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
J. Borggrefe, J. Kottlors, M. Mirza, V.-F. Neuhaus, N. Abdullayev, V. Maus, C. Kabbasch, D. Maintz and A. Mpotsaris declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borggrefe, J., Kottlors, J., Mirza, M. et al. Differentiation of Clot Composition Using Conventional and Dual-Energy Computed Tomography. Clin Neuroradiol 28, 515–522 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0599-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0599-3