Abstract
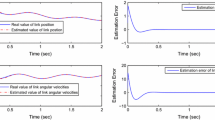
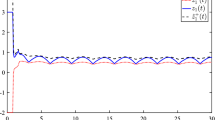
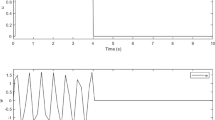
This paper considers the design problem of exponential reduced-order observers for nonlinear systems satisfying incremental quadratic constraints governed by an incremental multiplier matrix. Sufficient existence conditions of the exponential full-order observers are established and formulated in terms of matrix inequalities. Then, it is shown that the conditions under which an exponential full-order observer exists also guarantee the existence of an exponential reduced-order observer. Moreover, with a proper parameterization of the multiplier matrix, the design of reduced-order observers is reduced to solving linear matrix inequalities of the Lyapunov matrix and observer gain matrices. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed design method is illustrated by an example.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abbaszadeh, H.J. Marquez, Nonlinear observer design for one-sided Lipschitz systems, in Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference , pp. 5284–5289 (2010)
B. Açıkmeşe, M. Corless, Stability analysis with quadratic Lyapunov functions: some necessary and sufficient multiplier conditions. Syst. Control Lett. 57(1), 78–94 (2008)
B. Açıkmeşe, M. Corless, Observers for systems with nonlinearities satisfying incremental quadratic constraints. Automatica 47(7), 1339–1348 (2011)
M. Arcak, Circle-Criterion Observers and Their Feedback Applications: An Overview (Birkhäuser Boston, Boston, 2006)
M. Arcak, P. Kokotović, Observer-based control of systems with slope-restricted nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 46(7), 1146–1150 (2001)
M. Arcak, P. Kokotović, Nonlinear observers: a circle criterion design and robustness analysis. Automatica 37(12), 1923–1930 (2001)
L. Bai, Q. Zhou, L. Wang, Z. Yu, H. Li, Observer-based adaptive control for stochastic nonstrict-feedback systems with unknown backlash-like hysteresis. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 31, 1481–1490 (2017)
A. Ben-Israel, T.N.E. Greville, Generalized inverses. CMS Books Math. 34(3), 406–413 (2003)
T.N. Dinh, V. Andrieu, M. Nadri, U. Serres, Continuous-discrete time observer design for Lipschitz systems with sampled measurements. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60(3), 787–792 (2015)
X. Fan, M. Arcak, Observer design for systems with multivariable monotone nonlinearities. Syst. Control Lett. 50(4), 319–330 (2003)
H.K. Khalil, Noninear Systems (Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, 1996)
A.J. Krener, W. Respondek, Nonlinear observers with linearizable error dynamics. SIAM J. Control Optim. 23(2), 197–216 (1985)
H. Li, Y. Gao, P. Shi, H.K. Lam, Observer-based fault detection for nonlinear systems with sensor fault and limited communication capacity. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 61(9), 2745–2751 (2016)
Z. Liu, L. Zhao, H. Xiao, C. Gao, Adaptive \(H_{\infty }\) integral sliding mode control for uncertain singular time-delay systems based on observer. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(11), 4365–4387 (2017)
L. Magnis, N. Petit, Angular velocity nonlinear observer from vector measurements. Automatica 75, 46–53 (2017)
G. Phanomchoeng, R. Rajamani, Observer design for Lipschitz nonlinear systems using Riccati equations, in Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference pp. 6060–6065 (2010)
M. Pourgholi, V.J. Majd, A nonlinear adaptive resilient observer design for a class of Lipschitz systems using LMI. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 30(6), 1401–1415 (2011)
D.M. Raimondo, G. Roberto Marseglia, R.D. Braatz, J.K. Scott, Closed-loop input design for guaranteed fault diagnosis using set-valued observers. Automatica 74, 107–117 (2016)
R. Rajamani, Observers for Lipschitz nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 43(3), 397–401 (1998)
A. Selivanov, E. Fridman, Observer-based input-to-state stabilization of networked control systems with large uncertain delays. Automatica 74, 63–70 (2016)
H. Su, H. Wu, X. Chen, Observer-based discrete-time nonnegative edge synchronization of networked systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 28(10), 2446–2455 (2017)
H. Su, H. Wu, X. Chen, M.Z.Q. Chen, Positive edge consensus of complex networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2765678
F.E. Thau, Observing the state of non-linear dynamic systems. Int. J. Control 17(3), 471–479 (1973)
L. Wang, M. Basin, H. Li, R. Lu, Observer-based composite adaptive fuzzy control for nonstrict-feedback systems with actuator failures. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2017.2774185
Y. Wang, R. Rajamani, D.M. Bevly, Observer design for parameter varying differentiable nonlinear systems, with application to slip angle estimation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 62(4), 1940–1945 (2017)
Y. Wu, R. Lu, P. Shi, H. Su, Z. Wu, Adaptive output synchronization of heterogeneous network with an uncertain leader. Automatica 76, 183–192 (2017)
Y. Wu, X. Meng, L. Xie, R. Lu, H. Su, Z. Wu, An input-based triggering approach to leader-following problems. Automatica 75, 221–228 (2017)
X. Xia, W. Gao, Nonlinear observer design by observer error linearization. SIAM J. Control Optim. 27(1), 199–216 (1989)
W. Zhang, H. Su, H. Wang, Z. Han, Full-order and reduced-order observers for one-sided Lipschitz nonlinear systems using Riccati equations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17(12), 4968–4977 (2012)
W. Zhang, H. Su, F. Zhu, G.M. Azar, Unknown input observer design for one-sided Lipschitz nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(2), 1469–1479 (2015)
W. Zhang, H. Su, F. Zhu, S.P. Bhattacharyya, Improved exponential observer design for one-sided Lipschitz nonlinear systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 26(18), 3958–3973 (2016)
W. Zhang, H. Su, F. Zhu, M. Wang, Observer-based \(H_{\infty }\) synchronization and unknown input recovery for a class of digital nonlinear systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 32(6), 2867–2881 (2013)
Q. Zhou, H. Li, L. Wang, R. Lu, Prescribed performance observer-based adaptive fuzzy control for nonstrict-feedback stochastic nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2017.2738155
Q. Zhou, L. Wang, C. Wu, H. Li, Adaptive fuzzy tracking control for a class of pure-feedback nonlinear systems with time-varying delay and unknown dead zone. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 329, 36–60 (2017)
Q. Zhou, D. Yao, J. Wang, C. Wu, Robust control of uncertain semi-Markovian jump systems using sliding mode control method. Appl. Math. Comput. 286, 72–87 (2016)
F. Zhu, Z. Han, A note on observers for Lipschitz nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 47(10), 1751–1754 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 51505273, the State Key Laboratory of Robotics and System (HIT) under Grant SKLRS-2014-MS-10, the Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Advanced Robotics Fund Projects under Grant JAR201401 and the Fund of MOE Key Laboratory of Image Processing and Intelligence Control (Huazhong University of Science and Technology) under Grant No. IPIC2015-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, W. et al. Exponential Reduced-Order Observers for Nonlinear Systems Satisfying Incremental Quadratic Constraints. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 3725–3738 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0745-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0745-4