Abstract.
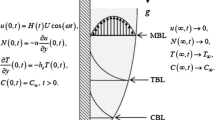
A boundary layer analysis is used to study the effect of buoyancy-induced streamwise pressure gradients on heat transfer and laminar forced convective flow of a micropolar fluid over a horizontal plate. In particular, self-similar solution is given for the case of a wall temperature that is inversely proportional to the square root of the distance from the leading edge. Such a solution does not exist if the buoyancy parameter is smaller than a certain critical value, which is negative (decelerated flow), but not yet small enough to satisfy the separation criterion of vanishing shear stress at the wall. The effects of the buoyancy force and material parameters on the friction factor, total heat transfer, displacement thickness, and wall couple stress as well as the details of the velocity, microrotation and temperature fields are discussed. The micropolar properties of the fluid are found to play an important role in controlling flow separation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
November 21, 1994; revised: October 31, 1995 and August 27, 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassanien, I. Combined forced and free convection in boundary layer flow of a micropolar fluid over a horizontal plate. Z. angew. Math. Phys. 48, 571–583 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000330050047
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000330050047