Abstract
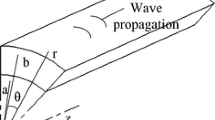
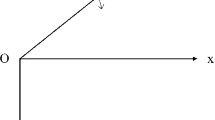
This paper describes a substantiated mathematical theory for Rayleigh waves propagated on some types of metal cylinders. More specifically, it presents not only a new way to express the dispersion relation of Rayleigh waves propagated on the cylindrical surface, but also how it can be used to construct a mathematical equation showing that the applied static mechanical pressure affects the shear modulus of the metal cylinder. All steps, required to conclude the process, consider the equation of motion as a function of radial and circumferential coordinates only, while the axial component can be overlooked without causing any problems. Some numerical experiments are done to illustrate the changes in the Rayleigh circumferential phase velocity in a metal cylindrical section due to static mechanical pressure around its external surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hayes, M., Rivlin, R.S.: A note on the secular equation for Rayleigh waves. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 13, 80–83 (1962)
Sharma, J.N., Pal, M.: Rayleigh–Lamb waves in magneto-thermoelastic homogeneous isotropic plate. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 42, 137–155 (2004)
Kaplunov, J., Nolde, E., Prikazchikov, D.A.: A revisit to the moving load problem using an asymptotic model. Wave Motion 47, 440–451 (2010)
Kaplunov, J., Prikazchikov, D.A.: Asymptotic theory for Rayleigh and Rayleigh-type waves. Adv. Appl. Mech. 50, 1–106 (2017)
Destrad, M., Fu, Y.B.: A wave near the edge of a circular disk. Open Acoust. J. 42, 15–18 (2008)
Guinan, M.W., Steinberg, D.J.: A simple approach to extrapolating measured polycrystalline shear moduli to very high pressure. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 36, 829–829 (1974)
Guinan, M.W., Steinberg, D.J.: A constitutive model for metals applicable at high-strain rate. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 1498–1504 (1979)
Abrikosov, A.A.: Some properties of strongly compressed matter. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 12, 1254 (1961)
Guinan, M.W., Steinberg, D.J.: Pressure and temperature derivatives of the isotropic polycrystalline shear modulus for 65 elements. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 41, 1501–1512 (1973)
Wolf, J.: Air force materials laboratory, Report AFML-TR-68-115 (1972)
Chandrasekharaiah, D.S.: Effects of surface stresses and voids on Rayleigh waves in an elastic solid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 25, 205–211 (1987)
Stein, S., Wysession, M.: An introduction to Seismology, Earthquakes and Structure. Blackweel Publishing Ltd., Oxford (2003)
Duffy, D.G.: Green’s Functions With Applications. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Washington (2001)
Timoshenko, S., Goodier, J.N.: Theory of Elasticity. The Maple Press Company, York (1951)
Watson, G.N.: Theory of Bessel Functions. The Syndics of the Cambridge University Press, Cambriedge (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sebold, J.E., de Lacerda, L.A. Expressions to Rayleigh circumferential phase velocity and dispersion relation for a cylindrical surface under mechanical pressure. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 69, 25 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-018-0918-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-018-0918-9