Abstract
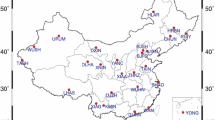
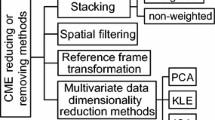
This study uses the daily horizontal and vertical Global Positioning System (GPS) position time series of 41 regionally distributed GPS stations in Southern California covering the period of January 2011 to January 2017 to extract the common mode error (CME) in east-north-up (ENU) components with the principal component analysis (PCA) method. We assume the first component with common spatial responses is CME. Firstly, we focus on the effects of CME on the root mean square (RMS) of the GPS time series. The results indicate that after being filtered, CMEs can reduce the average RMS values by 42.9, 39.1 and 28.8% for ENU components, respectively. Secondly, we investigate the changes in noise type before and after spatio-temporal filtration. The outcome reveals that noise model of the GPS position time series can be mainly described by power law noise (PL) plus white noise (WH). After CME correction, 32, 12 and 13% of the stations’ noise types are altered for ENU components, respectively. Thirdly, we confirm that stations whose noise properties can be best described by PL + WH, PL + WH and FL + WH or RW (Random walk noise) + FL + WH show no obvious differences in velocity and velocity uncertainty. Stations whose noise properties are described by RW + FL + WH, PL + WH and RW + FL + WH show significant differences in velocity and velocity uncertainty. Therefore, for all GPS stations, excluding the ones whose noise properties are described by the RW + FL + WH model, we estimate the noise parameters and velocity before and after spatio-temporal filtration by fitting a PL + WH model. According to our findings, the PCA method does not appear to be efficient for horizontal components. The CME is superimposed on the stochastic process realization for the vertical components. The impact of CME on vertical velocity estimation cannot be ignored, and eliminating CME enhances the credibility of the determined velocity field. Finally, we discuss the correlation between CME and mass loadings. The results of the Pearson correlation analysis and wavelet coherence analysis indicate that CME cannot be interpreted by mass loadings in a regional GPS network and that it may be related to GPS technique errors.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri-Simkooei, A. R., Snellen, M., & Simons, D. G. (2011). Principal component analysis of single-beam echo-sounder signal features for seafloor classification. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 36(2), 259–272.
Barbot, S., Fialko, Y., & Bock, Y. (2009). Postseismic deformation due to the Mw 6.0 Parkfield earthquake: Stress-driven creep on a fault with spatially variable rate-and-state friction parameters. Journal of Geophysical Research, 114, B07405.
Blewitt, G., & Lavallee, D. (2002). Effect of annual signals on geodetic velocity. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107, 9–11.
Bogusz, J., Gruszczynski, M., Figurski, M., & Klos, A. (2015). Spatio-temporal filtering for determination of common mode error in regional GNSS networks. Open Geosciences, 7(1), 140–148.
Bos, M., Fernandes, R., Williams, S., & Bastos, L. (2013). Fast error analysis of continuous GNSS observations with missing data. Journal of Geodesy, 87, 351–360.
Braitenberg, C. (2018). The deforming and rotating Earth—A review of the 18th International Symposium on Geodynamics and Earth Tide, Trieste 2016. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 9, 187–196.
Calais, E., Han, J. Y., DeMets, C., & Nocquet, J. M. (2006). Deformation of the North American plate interior from a decade of continuous GPS measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, B06402.
Dong, D., Fang, P., Bock, Y., et al. (2006). Spatiotemporal filtering using principal component analysis and Karhunen–Loeve expansion approaches for regional GPS network analysis. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, 3405.
Freed, A. M., Bürgmann, R., Calais, E., Freymueller, J., & Hreinsdóttir, S. (2006). Implications of deformation following the 2002 Denali, Alaska, earthquake for postseismic relaxation processes and lithospheric rheology. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, B01401.
Gegout, P., Boy, J. P., Hinderer, J., et al. (2010). Modeling and observation of loading contribution to tune-variable GPS sites positions. In S. P. Mertikass (Ed.), Gravity, geoid and earth observation (pp. 651–659). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Grinsted, A., Moore, J. C., & Jevrejeva, S. (2004). Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Processes Geophysical, 11, 561–566.
Guo, J. Y., Li, W., Yu, H. J., et al. (2015). Impending ionospheric anomaly preceding the Iquique Mw8.2 earthquake in Chile on 2014 April 1. Geophysical Journal International, 203, 1461–1470.
He, X., Montillet, J. P., Hua, X., Yu, K., Jiang, W., & Zhou, F. (2017). Noise analysis for environmental loading effect on GPS position time series. Acta Geodynamica et Geromaterialia, 14(1), 131–143.
Jolliffe, I. T. (2002). Principal component analysis, Springer series in statistics (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Khan, S. A., Wahr, J., Leuliette, E., van Dam, T., Larson, K. M., & Francis, O. (2008). Geodetic measurements of postglacial adjustments in Greenland. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113, B02402.
Klos, A., Bogusz, J., Figurski, M., & Gruszczynski, M. (2016). Error analysis for European IGS stations. Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica, 60(1), 17–34.
Klos, A., Gruszczynska, M., Bos, M.S., Boy, J. P., & Bogusz, J., 2017. Estimates of vertical velocity errors for IGS ITRF2014 stations by applying the improved singular spectrum analysis method and environmental loading models. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 175, 1823–1840.
Kogan, M. G., & Steblov, G. M. (2008). Current global plate kinematics from GPS (1995–2007) with the plate-consistent reference frame. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113, B04416.
Langbein, J. (2012). Estimating rate uncertainty with maximum likelihood: differences between power-law and flicker-random-walk models. Journal of Geodesy, 86, 775.
Li, Z., Yue, J. P., Hu, J. Y., Xiang, Y. F., Chen, J., & Bian, Y. K. (2018). Effect of surface mass loading on geodetic GPS observations. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1851.
Li, Z., Yue, J. P., Li, W., & Lu, D. K. (2017a). Investigating mass loading contributes of annual GPS observations for the Eurasian plate. Journal of Geodynamics, 111, 43–49.
Li, Z., Yue, J. P., Li, W., Lu, D. K., & Li, X. G. (2017b). A comparison of hydrological deformation using GPS and global hydrological model for the Eurasian plate. Advances in Space Research, 60, 587–596.
Marcin, R., & Tomasz, L. (2017). Analysis of seasonal position variation for selected GNSS sites in Poland using loading modelling and GRACE data. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 8, 253–259.
Márquez-Azúa, B., & DeMets, C. (2003). Crustal velocity field of Mexico from continuous GPS measurements to June 2001: Implications for the neotectonics of Mexico. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(B9), 2450.
Mazzotti, S., Dragert, H., Henton, J., Schmidt, M., Hyndman, R., James, T., et al. (2003). Current tectonics of northern Cascadia from a decade of GPS measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(B12), 2554.
Meade, B. J., & Hager, B. H. (2005). Blockmodels of crustal motion in southern California constrained by GPS measurements. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110, B03403.
Melbourne, T. I., Webb, F. H., Stock, J. M., & Reigber, C. (2002). Rapid postseismic transients in subduction zones from continuous GPS. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107(B10), 2241.
Nikolaidis, R., 2002. Observation of geodetic and seismic deformation with the global positioning system (Ph.D. thesis). University of California, San Diego, California.
Prawirodirdjo, L., & Bock, Y. (2004). Instantaneous global plate motion model from 12 years of continuous GPS observations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109, B08405.
Santamaría-Gómez, A., Bouin, M.-N., Collilieux, X., & Wöppelman, G. (2011). Correlated errors in GPS position time series: implications for velocity estimates. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116, B01405.
Savage, J. C., & Langbein, J. (2008). Postearthquake relaxation after the 2004 M6 Parkfield, California, earthquake and rate-and-state friction. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113, B10407.
Sella, G. F., Stein, S., Dixon, T. H., Craymer, M., James, T. S., Mazzotti, S., et al. (2007). Observation of glacial isostatic adjustment in “stable” North America with GPS. Geophysical Research Letter, 34, L02306.
Takayama, H., & Yoshida, A. (2007). Crustal deformation in Kyushu derived from GEONET data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112, B06413.
Wang, W., Zhao, B., Wang, Q., & Yang, S. (2012). Noise analysis of continuous GPS coordinate time series for CMONOC. Advances in Space Research, 49, 943–956.
Wdowinski, S., Bock, Y., Zhang, J., Fang, P., & Genrich, J. (1997). Southern California permanent GPS geodetic array: Spatial filtering of daily positions for estimating coseismic and postseismic displacements induced by the 1992 Landers earthquake. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102(B18), 57–70.
Williams, S. D. P., Bock, Y., Fang, P., et al. (2004). Error analysis of continuous GPS position time series. Journal of Geophysical Research, 109(B3), 412–430.
Zumberge, J. F., Heflin, M. B., & Jefferson, D. C. (1997). Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102, 5005–5017.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant ID 2018B694X14), the Postgraduate Student Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX18_0617). We are very grateful to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory for providing GPS data and the Ecole et Observatoire des Sciences de la Terre/Institut de Physique du Globe de Strasbourg loading service for making publicly available displacement time-series. We thank Machiel S. Bos for providing the Hector software. Some figures in this paper are plotted with the Generic Mapping Tool (GMT) software (Wessel and Smith 1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Yue, J., Li, W. et al. Comprehensive Analysis of the Effects of Common Mode Error on the Position Time Series of a Regional GPS Network. Pure Appl. Geophys. 176, 2565–2579 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-2074-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-2074-8