Abstract
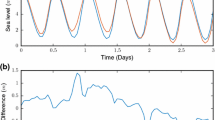
The Argentinean-German Geodetic Observatory is located 13 km from the Río de la Plata, in an area that is frequently affected by storm surges that can vary the level of the river over ±3 m. Water-level information from seven tide gauge stations located in the Río de la Plata are used to calculate every hour an empirical model of water heights (tidal + non-tidal component) and an empirical model of storm surge (non-tidal component) for the period 01/2016–12/2016. Using the SPOTL software, the gravimetric response of the models and the tidal response are calculated, obtaining that for the observatory location, the range of the tidal component (3.6 nm/s2) is only 12% of the range of the non-tidal component (29.4 nm/s2). The gravimetric response of the storm surge model is subtracted from the superconducting gravimeter observations, after applying the traditional corrections, and a reduction of 7% of the RMS is obtained. The wavelet transform is applied to the same series, before and after the non-tidal correction, and a clear decrease in the spectral energy in the periods between 2 and 12 days is identify between the series. Using the same software East, North and Up displacements are calculated, and a range of 3, 2, and 11 mm is obtained, respectively. The residuals obtained after applying the non-tidal correction allow to clearly identify the influence of rain events in the superconducting gravimeter observations, indicating the need of the analysis of this, and others, hydrological and geophysical effects.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, D. C. (2012). SPOTL: some programs for ocean-tide loading. SIO Technical Report, Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
Antokoletz, E., Wziontek, H., & Tocho, C. (2017). First six months of Superconducting Gravimetry in Argentina. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Gravity, Geoid and Height Systems 2016, International Association of Geodesy Symposia, submitted.
Balay, M. (1961). El Río de la Plata entre la atmósfera y el mar. Buenos Aires, Argentina: Servicio de Hidrografía Naval.
Boy, J. P., Longuevergne, L., Boudin, F., Jacob, T., Lyard, F., Llubes, M., et al. (2009). Modelling atmospheric and induced non-tidal oceanic loading contributions to surface gravity and tilt measurements. Journal of Geodynamics, 48(3–5), 182–188.
Campetella, C. M., D’Onofrio, E. E., Cerne, B. S., Fiore, M. E., & Possia, N. E. (2007). Negative storm surges in the port of Buenos Aires city. International Journal of Climatology, 27(8), 1091–1101.
Comisión Administradora del Río de la Plata. (1989). Estudio para la evaluación de la contaminación en el Río de la Plata (p. 422). Buenos Aires: Comisión Administradora del Río de la Plata, Montevideo.
D’Onofrio, E. E. (1984). Desarrollo de un nuevo sistema de procesamiento de información de marea. Informe Técnico Nº25/84, Departamento Oceanografía, Servicio de Hidrografía Naval. 167 pág.
D’Onofrio, E.E., & Fiore, M.M.E. (2003). Estimación de niveles extremos en el Puerto de Buenos Aires contemplando el ascenso del nivel medio. In Paper presented at V Jornadas Nacionales de Ciencias del Mar. Mar del Plata, Argentina.
D’Onofrio, E., Fiore, M., Di Biase, F., Grismeyer, W., & Saladino, A. (2010). Influencia de la marea astronómica sobre las variaciones del nivel del Río Negro en la zona de Carmen de Patagones. Geoacta, 35(2), 92–104. (ISSN 1852-7744).
D’Onofrio, E. E., Fiore, M. M. E., & Pousa, J. L. (2008). Changes in the regime of storm surges at Buenos Aires, Argentina. Journal of Coastal Research, 24(1A), 260–265.
D’Onofrio, E. E., Fiore, M. M. E., & Romero, S. I. (1999). Return periods of extreme water levels estimated for some vulnerables areas of Buenos Aires. Continental Shelf Research, 19, 1681–1693.
D’Onofrio, E., Oreiro, F., Di Biase, F., Grismeyer, W., & Fiore, M. (2009). Estudio de las principales ondas componentes de la marea astronómica en el Río de la Plata. In Resúmenes VII Jornadas Nacionales de Ciencias del Mar, Bahía Blanca, Provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina (Poster).
D’Onofrio, E., Oreiro, F., & Fiore, M. (2012). Simplified empirical astronomical tide model—An application for the Río de la Plata Estuary. Computers & Geosciences, 44, 196–202. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2011.09.019.
Dehant, V., Defraigne, P., & Wahr, J. M. (1999). Tides for a convective Earth. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104(B1), 1035–1058.
Dragani, W., & Romero, S. (2004). Impact of a possible local wind change on the wave climate in the upper Río de la Plata. International Journal of Climatology, 24, 1149–1157.
Escobar, G., Vargas, W., & Bischoff, S. A. (2004). Wind Tides in the Río de la Plata Estuary: Meteorological conditions. International Journal of Climatology, 24, 1159–1169.
Farrell, W. E. (1972). Deformation of the earth by surface loads. Reviews of Geophysics, 10(3), 761–797.
Fiore, M. M. E., D’Onofrio, E. E., Pousa, J. L., Schnack, E. J., & Bértola, G. R. (2009). Storm surges and coastal impacts at Mar del Plata, Argentina. Continental Shelf Research, 29(14), 1643–1649.
Fratepietro, F., Baker, T. F., Williams, S. D. P., & Van Camp, M. (2006). Ocean loading deformations caused by storm surges on the northwest European shelf. Geophysical Research Letters, 33, L06317. doi:10.1029/2005GL025475.
Geng, J., Williams, S. D. P., Teferle, F. N., & Dodson, A. H. (2012). Detecting storm surge loading deformations around the southern North Sea using subdaily GPS. Geophysical Journal International, 191(2), 569–578.
Goodkind, J. M. (1999). The superconducting gravimeter. Review of Scientific Instruments, 70, 4131–4152.
Guerrero, R. A., Acha, E. M., Framiñan, M. B., & Lasta, C. A. (1997). Physical oceanography of the Río de la Plata Estuary, Argentina. Continental Shelf Research, 17(7), 727–742.
Hinderer, J., Crossley, D., & Warburton, R. (2007). Gravimetric methods—Superconducting gravity meters. In G. Schubert (Ed.), Treatise on geophysics (pp. 65–122). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Klügel, T., & Wziontek, H. (2009). Correcting gravimeters and tiltmeters for atmospheric mass attraction using operational weather models. Journal of Geodynamics, 48(3–5), 204–210. doi:10.1016/j.jog.2009.09.010.
Nordman, M., Virtanen, H., Nyberg, S., & Mäkinen, J. (2015). Non-tidal loading by the Baltic Sea: Comparison of modelled deformation with GNSS time series. GeoResJ, 7, 14–21.
Oreiro, F., D’Onofrio, E., & Fiore, M. M. E. (2016). Vinculación de las referencias altimétricas utilizadas en las cartas náuticas con el elipsoide WGS84 para el Río de la Plata. Geoacta, 40(2), 109–120. (ISSN 1852-7744).
Petrov, L. (2015). The International mass loading service. arXiv preprint 1503.00191.
Pousa, J. L., D’Onofrio, E. E., Fiore, M. M. E., & Kruse, E. (2013). Environmental impacts and simultaneity of positive and negative storm surges on the coast of the Province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Environmental Earth Sciences, 68, 2325–2335.
Schüller, K. (2015). Theoretical basis for Earth Tide analysis with the new ETERNA34-ANA-V4.0 program, Bulletin d’Informations des Marees Terrestres 149, 12024. http://www.eas.slu.edu/GGP/BIM_Recent_Issues/bim149-2015/schuller_theoretical_basis_Eterna-ANA_v4_BIM149.pdf. Accessed 20 Feb 2017.
SHN (Servicio de Hidrografía Naval). (2017). Tablas de Marea, Pub. H- 610. Argentina. Servicio de Hidrografía Naval, Ministerio de Defensa.
Simionato, C. G., Dragani, W., Meccia, V., & Nuñez, M. (2004a). A numerical study of the barotropic circulation of the Río de La Plata estuary: sensitivity to bathymetry, the Earth’s rotation and low frequency wind variability. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 61, 261–273.
Simionato, C. G., Dragani, W., Nuñez, M. N., & Engel, M. (2004b). A set of 3-D nested models for tidal propagation from the Argentinean continental shelf to the Río de la Plata estuary—Part I M2. Journal of Coastal Research, 20(3), 893–912.
Tocho, C. (2016). Gravimetría superconductora en Argentina. Geoacta, 41(1), 77–78. (Asociación Argentina de Geofísicos y Geodestas).
Virtanen, H. (2004). Loading effects in Metsähovi from the atmosphere and the Baltic Sea. Journal of Geodynamics, 38, 407–422.
Virtanen, H., & Mäkinen, J. (2003). The effect of the Baltic sea level on gravity at the Metsähovi station. Journal of Geodynamics, 35, 553–565.
Wziontek, H., Nowak, I., Hase, H., Häfner, M., Güntner, A., Reich, M., et al. (2016). A new gravimetric reference station in South America: The installation of the Superconducting Gravimeter SG038 at the Argentinian-German Geodetic Observatory AGGO, EGU General Assembly 2016. Geophysical Research Abstracts, 18, EGU2016–12612.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oreiro, F.A., Wziontek, H., Fiore, M.M.E. et al. Non-Tidal Ocean Loading Correction for the Argentinean-German Geodetic Observatory Using an Empirical Model of Storm Surge for the Río de la Plata. Pure Appl. Geophys. 175, 1739–1753 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-017-1651-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-017-1651-6