Abstract
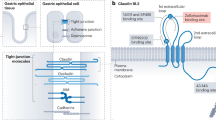
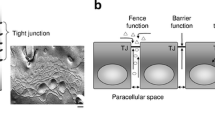
Claudins are a family of integral tight junction proteins that regulate paracellular permeability in polarized epithelia. Overexpression or reduction of claudins can both promote and limit cancer progression, revealing complex dichotomous roles for claudins depending on cellular context. In contrast, recent studies demonstrating tumor formation in claudin knockout mouse models indicate a role for several claudin family members in suppressing tumor initiation. For example, intestine-specific claudin-7 knockout mice spontaneously develop atypical hyperplasia and intestinal adenomas, while claudin-18 knockout mice develop carcinomas in the lung and stomach. Claudin-4, -11, and -15 knockout mice show increased cell proliferation and/or hyperplasia in urothelium, Sertoli cells, and small intestinal crypts, respectively, possibly a precursor to cancer development. Pathways implicated in both cell proliferation and tumorigenesis include Yap/Taz and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R)/Akt pathways, among others. Consistent with the tumor suppressive role of claudins shown in mice, in humans, claudin-low breast cancer has been described as a distinct entity with a poor prognosis, and claudin-18-Rho GTPase activating protein 26 (CLDN18-ARHGAP26) fusion protein as a driver gene aberration in diffuse-type gastric cancer due to effects on RhoA. Paradoxically, claudins have also garnered interest as targets for therapy, as they are sometimes aberrantly expressed in cancer cells, which may or may not promote cancer progression. For example, a chimeric monoclonal antibody which targets cells expressing claudin-18.2 through antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity has shown promise in multiple phase II studies. In this review, we focus on new findings supporting a tumor suppressive role for claudins during cancer initiation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao X, Surma MA, Simons K (2012) Polarized sorting and trafficking in epithelial cells. Cell Res 22:793–805
Shilova ON, Shilov ES, Lieber A, Deyev SM (2018) Disassembling a cancer puzzle: cell junctions and plasma membrane as targets for anticancer therapy. J Control Release 286:125–136
Coopman P, Djiane A (2016) Adherens junction and E-cadherin complex regulation by epithelial polarity. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:3535–3553
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2014) Architecture of tight junctions and principles of molecular composition. Semin Cell Dev Biol 36:157–165
Mineta K, Yamamoto Y, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka H, Tada Y, Saito K, Tamura A, Igarashi M, Endo T, Takeuchi K, Tsukita S (2011) Predicted expansion of the claudin multigene family. FEBS Lett 585:606–612
Koval M (2013) Claudin heterogeneity and control of lung tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 75:551–567
Holmes JL, Van Itallie CM, Rasmussen JE, Anderson JM (2006) Claudin profiling in the mouse during postnatal intestinal development and along the gastrointestinal tract reveals complex expression patterns. Gene Expr Patterns 6:581–588
Garcia-Hernandez V, Quiros M, Nusrat A (2017) Intestinal epithelial claudins: expression and regulation in homeostasis and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1397:66–79
Kwon MJ (2013) Emerging roles of claudins in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14:18148–18180
Singh AB, Dhawan P (2015) Claudins and cancer: fall of the soldiers entrusted to protect the gate and keep the barrier intact. Semin Cell Dev Biol 42:58–65
Osanai M, Takasawa A, Murata M, Sawada N (2017) Claudins in cancer: bench to bedside. Pflugers Arch 469:55–67
Tabaries S, Siegel PM (2017) The role of claudins in cancer metastasis. Oncogene 36:1176–1190
Singh AB, Sharma A, Dhawan P (2010) Claudin family of proteins and cancer: an overview. J Oncol 2010:541957
Chao YC, Pan SH, Yang SC, Yu SL, Che TF, Lin CW, Tsai MS, Chang GC, Wu CH, Wu YY, Lee YC, Hong TM, Yang PC (2009) Claudin-1 is a metastasis suppressor and correlates with clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 179:123–133
Huang J, Zhang L, He C, Qu Y, Li J, Zhang J, Du T, Chen X, Yu Y, Liu B, Zhu Z (2015) Claudin-1 enhances tumor proliferation and metastasis by regulating cell anoikis in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 6:1652–1665
Huang YH, Bao Y, Peng W, Goldberg M, Love K, Bumcrot DA, Cole G, Langer R, Anderson DG, Sawicki JA (2009) Claudin-3 gene silencing with siRNA suppresses ovarian tumor growth and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:3426–3430
Shang X, Lin X, Alvarez E, Manorek G, Howell SB (2012) Tight junction proteins claudin-3 and claudin-4 control tumor growth and metastases. Neoplasia 14:974–985
Ahmad R, Kumar B, Chen Z, Chen X, Muller D, Lele SM, Washington MK, Batra SK, Dhawan P, Singh AB (2017) Loss of claudin-3 expression induces IL6/gp130/Stat3 signaling to promote colon cancer malignancy by hyperactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Oncogene 36:6592–6604
Tanaka H, Takechi M, Kiyonari H, Shioi G, Tamura A, Tsukita S (2015) Intestinal deletion of claudin-7 enhances paracellular organic solute flux and initiates colonic inflammation in mice. Gut 64:1529–1538
Zhou B, Flodby P, Luo J, Castillo DR, Liu Y, Yu FX, McConnell A, Varghese B, Li G, Chimge NO, Sunohara M, Koss MN, Elatre W, Conti P, Liebler JM, Yang C, Marconett CN, Laird-Offringa IA, Minoo P, Guan K, Stripp BR, Crandall ED, Borok Z (2018) Claudin-18-mediated YAP activity regulates lung stem and progenitor cell homeostasis and tumorigenesis. J Clin Investig 128:970–984
Hagen SJ, Ang LH, Zheng Y, Karahan SN, Wu J, Wang YE, Caron TJ, Gad AP, Muthupalani S, Fox JG (2018) Loss of tight junction protein claudin 18 promotes progressive neoplasia development in mouse stomach. Gastroenterology 155:1852–1867
Alexandre MD, Lu Q, Chen YH (2005) Overexpression of claudin-7 decreases the paracellular Cl-conductance and increases the paracellular Na+ conductance in LLC-PK1 cells. J Cell Sci 118:2683–2693
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Namorado Mdel C, Martin D, Sierra G, Reyes JL (2006) The tight junction proteins claudin-7 and -8 display a different subcellular localization at Henle’s loops and collecting ducts of rabbit kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:2391–2398
Tatum R, Zhang Y, Salleng K, Lu Z, Lin JJ, Lu Q, Jeansonne BG, Ding L, Chen YH (2010) Renal salt wasting and chronic dehydration in claudin-7-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:F24–F34
Ding L, Lu Z, Foreman O, Tatum R, Lu Q, Renegar R, Cao J, Chen YH (2012) Inflammation and disruption of the mucosal architecture in claudin-7-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 142:305–315
Li WJ, Xu C, Wang K, Li TY, Wang XN, Yang H, Xing T, Li WX, Chen YH, Gao H, Ding L (2018) Severe intestinal inflammation in the small intestine of mice induced by controllable deletion of claudin-7. Dig Dis Sci 63:1200–1209
Hahn-Stromberg V, Askari S, Ahmad A, Befekadu R, Nilsson TK (2017) Expression of claudin 1, claudin 4, and claudin 7 in colorectal cancer and its relation with CLDN DNA methylation patterns. Tumour Biol 39:1010428317697569
Akizuki R, Shimobaba S, Matsunaga T, Endo S, Ikari A (2017) Claudin-5, -7, and -18 suppress proliferation mediated by inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt in human lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1864:293–302
Lu Z, Kim DH, Fan J, Lu Q, Verbanac K, Ding L, Renegar R, Chen YH (2015) A non-tight junction function of claudin-7-Interaction with integrin signaling in suppressing lung cancer cell proliferation and detachment. Mol Cancer 14:120
Niimi T, Nagashima K, Ward JM, Minoo P, Zimonjic DB, Popescu NC, Kimura S (2001) claudin-18, a novel downstream target gene for the T/EBP/NKX2.1 homeodomain transcription factor, encodes lung- and stomach-specific isoforms through alternative splicing. Mol Cell Biol 21:7380–7390
Linares GR, Brommage R, Powell DR, Xing W, Chen ST, Alshbool FZ, Lau KH, Wergedal JE, Mohan S (2012) Claudin 18 is a novel negative regulator of bone resorption and osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Miner Res 27:1553–1565
Micke P, Mattsson JS, Edlund K, Lohr M, Jirstrom K, Berglund A, Botling J, Rahnenfuehrer J, Marincevic M, Ponten F, Ekman S, Hengstler J, Woll S, Sahin U, Tureci O (2014) Aberrantly activated claudin 6 and 18.2 as potential therapy targets in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 135:2206–2214
Li G, Flodby P, Luo J, Kage H, Sipos A, Gao D, Ji Y, Beard LL, Marconett CN, DeMaio L, Kim YH, Kim KJ, Laird-Offringa IA, Minoo P, Liebler JM, Zhou B, Crandall ED, Borok Z (2014) Knockout mice reveal key roles for claudin 18 in alveolar barrier properties and fluid homeostasis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 51:210–222
LaFemina MJ, Sutherland KM, Bentley T, Gonzales LW, Allen L, Chapin CJ, Rokkam D, Sweerus KA, Dobbs LG, Ballard PL, Frank JA (2014) Claudin-18 deficiency results in alveolar barrier dysfunction and impaired alveologenesis in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 51:550–558
Luo J, Chimge NO, Zhou B, Flodby P, Castaldi A, Firth AL, Liu Y, Wang H, Yang C, Marconett CN, Crandall ED, Offringa IA, Frenkel B, Borok Z (2018) CLDN18.1 attenuates malignancy and related signaling pathways of lung adenocarcinoma in vivo and in vitro. Int J Cancer 143:3169–3180
Shimobaba S, Taga S, Akizuki R, Hichino A, Endo S, Matsunaga T, Watanabe R, Yamaguchi M, Yamazaki Y, Sugatani J, Ikari A (2016) Claudin-18 inhibits cell proliferation and motility mediated by inhibition of phosphorylation of PDK1 and Akt in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:1170–1178
Hayashi D, Tamura A, Tanaka H, Yamazaki Y, Watanabe S, Suzuki K, Suzuki K, Sentani K, Yasui W, Rakugi H, Isaka Y, Tsukita S (2012) Deficiency of claudin-18 causes paracellular H + leakage, up-regulation of interleukin-1beta, and atrophic gastritis in mice. Gastroenterology 142:292–304
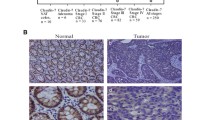
Oshima T, Shan J, Okugawa T, Chen X, Hori K, Tomita T, Fukui H, Watari J, Miwa H (2013) Down-regulation of claudin-18 is associated with the proliferative and invasive potential of gastric cancer at the invasive front. PLoS ONE 8:e74757
Jun KH, Kim JH, Jung JH, Choi HJ, Chin HM (2014) Expression of claudin-7 and loss of claudin-18 correlate with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Int J Surg 12:156–162
Matsusaka K, Ushiku T, Urabe M, Fukuyo M, Abe H, Ishikawa S, Seto Y, Aburatani H, Hamakubo T, Kaneda A, Fukayama M (2016) Coupling CDH17 and CLDN18 markers for comprehensive membrane-targeted detection of human gastric cancer. Oncotarget 7:64168–64181
Yamaga K, Murota H, Tamura A, Miyata H, Ohmi M, Kikuta J, Ishii M, Tsukita S, Katayama I (2018) Claudin-3 loss causes leakage of sweat from the sweat gland to contribute to the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 138:1279–1287
Tanaka H, Imasato M, Yamazaki Y, Matsumoto K, Kunimoto K, Delpierre J, Meyer K, Zerial M, Kitamura N, Watanabe M, Tamura A, Tsukita S (2018) Claudin-3 regulates bile canalicular paracellular barrier and cholesterol gallstone core formation in mice. J Hepatol 69:1308–1316
Schlingmann B, Molina SA, Koval M (2015) Claudins: gatekeepers of lung epithelial function. Semin Cell Dev Biol 42:47–57
Kooij G, Kopplin K, Blasig R, Stuiver M, Koning N, Goverse G, van der Pol SM, van Het Hof B, Gollasch M, Drexhage JA, Reijerkerk A, Meij IC, Mebius R, Willnow TE, Muller D, Blasig IE, de Vries HE (2014) Disturbed function of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier aggravates neuro-inflammation. Acta Neuropathol 128:267–277
Kage H, Flodby P, Gao D, Kim YH, Marconett CN, DeMaio L, Kim KJ, Crandall ED, Borok Z (2014) Claudin 4 knockout mice: normal physiological phenotype with increased susceptibility to lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L524–L536
Fujita H, Hamazaki Y, Noda Y, Oshima M, Minato N (2012) Claudin-4 deficiency results in urothelial hyperplasia and lethal hydronephrosis. PLoS ONE 7:e52272
Gong Y, Yu M, Yang J, Gonzales E, Perez R, Hou M, Tripathi P, Hering-Smith KS, Hamm LL, Hou J (2014) The Cap1-claudin-4 regulatory pathway is important for renal chloride reabsorption and blood pressure regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E3766–E3774
Morita K, Sasaki H, Fujimoto K, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Claudin-11/OSP-based tight junctions of myelin sheaths in brain and Sertoli cells in testis. J Cell Biol 145:579–588
Gow A, Southwood CM, Li JS, Pariali M, Riordan GP, Brodie SE, Danias J, Bronstein JM, Kachar B, Lazzarini RA (1999) CNS myelin and sertoli cell tight junction strands are absent in Osp/claudin-11 null mice. Cell 99:649–659
Gow A, Davies C, Southwood CM, Frolenkov G, Chrustowski M, Ng L, Yamauchi D, Marcus DC, Kachar B (2004) Deafness in claudin 11-null mice reveals the critical contribution of basal cell tight junctions to stria vascularis function. J Neurosci 24:7051–7062
Mazaud-Guittot S, Meugnier E, Pesenti S, Wu X, Vidal H, Gow A, Le Magueresse-Battistoni B (2010) Claudin 11 deficiency in mice results in loss of the Sertoli cell epithelial phenotype in the testis. Biol Reprod 82:202–213
Tamura A, Kitano Y, Hata M, Katsuno T, Moriwaki K, Sasaki H, Hayashi H, Suzuki Y, Noda T, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (2008) Megaintestine in claudin-15-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 134:523–534
Furuse M, Hata M, Furuse K, Yoshida Y, Haratake A, Sugitani Y, Noda T, Kubo A, Tsukita S (2002) Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier: a lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 156:1099–1111
Muto S, Hata M, Taniguchi J, Tsuruoka S, Moriwaki K, Saitou M, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Fujimura A, Imai M, Kusano E, Tsukita S, Furuse M (2010) Claudin-2-deficient mice are defective in the leaky and cation-selective paracellular permeability properties of renal proximal tubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:8011–8016
Tamura A, Hayashi H, Imasato M, Yamazaki Y, Hagiwara A, Wada M, Noda T, Watanabe M, Suzuki Y, Tsukita S (2011) Loss of claudin-15, but not claudin-2, causes Na+ deficiency and glucose malabsorption in mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology 140:913–923
Tsai PY, Zhang B, He WQ, Zha JM, Odenwald MA, Singh G, Tamura A, Shen L, Sailer A, Yeruva S, Kuo WT, Fu YX, Tsukita S, Turner JR (2017) IL-22 upregulates epithelial claudin-2 to drive diarrhea and enteric pathogen clearance. Cell Host Microbe 21(671–681):e674
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, Seo Y, Sasaki H, Hashimoto N, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Size-selective loosening of the blood–brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 161:653–660
Breiderhoff T, Himmerkus N, Stuiver M, Mutig K, Will C, Meij IC, Bachmann S, Bleich M, Willnow TE, Muller D (2012) Deletion of claudin-10 (Cldn10) in the thick ascending limb impairs paracellular sodium permeability and leads to hypermagnesemia and nephrocalcinosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:14241–14246
Breiderhoff T, Himmerkus N, Drewell H, Plain A, Gunzel D, Mutig K, Willnow TE, Muller D, Bleich M (2018) Deletion of claudin-10 rescues claudin-16-deficient mice from hypomagnesemia and hypercalciuria. Kidney Int 93:580–588
Ben-Yosef T, Belyantseva IA, Saunders TL, Hughes ED, Kawamoto K, Van Itallie CM, Beyer LA, Halsey K, Gardner DJ, Wilcox ER, Rasmussen J, Anderson JM, Dolan DF, Forge A, Raphael Y, Camper SA, Friedman TB (2003) Claudin 14 knockout mice, a model for autosomal recessive deafness DFNB29, are deaf due to cochlear hair cell degeneration. Hum Mol Genet 12:2049–2061
Gong Y, Renigunta V, Himmerkus N, Zhang J, Renigunta A, Bleich M, Hou J (2012) Claudin-14 regulates renal Ca(+)(+) transport in response to CaSR signalling via a novel microRNA pathway. EMBO J 31:1999–2012
Miyamoto T, Morita K, Takemoto D, Takeuchi K, Kitano Y, Miyakawa T, Nakayama K, Okamura Y, Sasaki H, Miyachi Y, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2005) Tight junctions in Schwann cells of peripheral myelinated axons: a lesson from claudin-19-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 169:527–538
Hagen SJ (2017) Non-canonical functions of claudin proteins: beyond the regulation of cell–cell adhesions. Tissue Barriers 5:e1327839
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N, Sibley RK (1991) Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med 325:1127–1131
Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer C, Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Allen C, Al-Raddadi R, Alvis-Guzman N, Amoako Y, Artaman A, Ayele TA, Barac A, Bensenor I, Berhane A, Bhutta Z, Castillo-Rivas J, Chitheer A, Choi JY, Cowie B, Dandona L, Dandona R, Dey S, Dicker D, Phuc H, Ekwueme DU, Zaki MS, Fischer F, Furst T, Hancock J, Hay SI, Hotez P, Jee SH, Kasaeian A, Khader Y, Khang YH, Kumar A, Kutz M, Larson H, Lopez A, Lunevicius R, Malekzadeh R, McAlinden C, Meier T, Mendoza W, Mokdad A, Moradi-Lakeh M, Nagel G, Nguyen Q, Nguyen G, Ogbo F, Patton G, Pereira DM, Pourmalek F, Qorbani M, Radfar A, Roshandel G, Salomon JA, Sanabria J, Sartorius B, Satpathy M, Sawhney M, Sepanlou S, Shackelford K, Shore H, Sun J, Mengistu DT, Topor-Madry R, Tran B, Ukwaja KN, Vlassov V, Vollset SE, Vos T, Wakayo T, Weiderpass E, Werdecker A, Yonemoto N, Younis M, Yu C, Zaidi Z, Zhu L, Murray CJL, Naghavi M, Fitzmaurice C (2017) The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA Oncol 3:1683–1691
Danese S, Mantovani A (2010) Inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal cancer: a paradigm of the Yin–Yang interplay between inflammation and cancer. Oncogene 29:3313–3323
Fan R, Kim NG, Gumbiner BM (2013) Regulation of Hippo pathway by mitogenic growth factors via phosphoinositide 3-kinase and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:2569–2574
Zhu H, Wang DD, Yuan T, Yan FJ, Zeng CM, Dai XY, Chen ZB, Chen Y, Zhou T, Fan GH, Ying M, Cao J, Luo P, Liu XJ, Hu Y, Peng Y, He Q, Yang B (2018) Multikinase inhibitor CT-707 targets liver cancer by interrupting the hypoxia-activated IGF-1R-YAP axis. Cancer Res 78:3995–4006
Tumaneng K, Schlegelmilch K, Russell RC, Yimlamai D, Basnet H, Mahadevan N, Fitamant J, Bardeesy N, Camargo FD, Guan KL (2012) YAP mediates crosstalk between the Hippo and PI(3)K-TOR pathways by suppressing PTEN via miR-29. Nat Cell Biol 14:1322–1329
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2018) Phosphorylation of tight junction transmembrane proteins: many sites, much to do. Tissue Barriers 6:e1382671
Pope JL, Ahmad R, Bhat AA, Washington MK, Singh AB, Dhawan P (2014) Claudin-1 overexpression in intestinal epithelial cells enhances susceptibility to adenamatous polyposis coli-mediated colon tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer 13:167
Ahmad R, Chaturvedi R, Olivares-Villagomez D, Habib T, Asim M, Shivesh P, Polk DB, Wilson KT, Washington MK, Van Kaer L, Dhawan P, Singh AB (2014) Targeted colonic claudin-2 expression renders resistance to epithelial injury, induces immune suppression, and protects from colitis. Mucosal Immunol 7:1340–1353
Turksen K, Troy TC (2002) Permeability barrier dysfunction in transgenic mice overexpressing claudin 6. Development 129:1775–1784
Kuhn S, Koch M, Nubel T, Ladwein M, Antolovic D, Klingbeil P, Hildebrand D, Moldenhauer G, Langbein L, Franke WW, Weitz J, Zoller M (2007) A complex of EpCAM, claudin-7, CD44 variant isoforms, and tetraspanins promotes colorectal cancer progression. Mol Cancer Res 5:553–567
Pitule P, Vycital O, Bruha J, Novak P, Hosek P, Treska V, Hlavata I, Soucek P, Kralickova M, Liska V (2013) Differential expression and prognostic role of selected genes in colorectal cancer patients. Anticancer Res 33:4855–4865
Herschkowitz JI, Simin K, Weigman VJ, Mikaelian I, Usary J, Hu Z, Rasmussen KE, Jones LP, Assefnia S, Chandrasekharan S, Backlund MG, Yin Y, Khramtsov AI, Bastein R, Quackenbush J, Glazer RI, Brown PH, Green JE, Kopelovich L, Furth PA, Palazzo JP, Olopade OI, Bernard PS, Churchill GA, Van Dyke T, Perou CM (2007) Identification of conserved gene expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and human breast tumors. Genome Biol 8:R76
Yao F, Kausalya JP, Sia YY, Teo AS, Lee WH, Ong AG, Zhang Z, Tan JH, Li G, Bertrand D, Liu X, Poh HM, Guan P, Zhu F, Pathiraja TN, Ariyaratne PN, Rao J, Woo XY, Cai S, Mulawadi FH, Poh WT, Veeravalli L, Chan CS, Lim SS, Leong ST, Neo SC, Choi PS, Chew EG, Nagarajan N, Jacques PE, So JB, Ruan X, Yeoh KG, Tan P, Sung WK, Hunziker W, Ruan Y, Hillmer AM (2015) Recurrent fusion genes in gastric cancer: CLDN18-ARHGAP26 induces loss of epithelial integrity. Cell Rep 12:272–285
Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, Demeter J, Perou CM, Lonning PE, Brown PO, Borresen-Dale AL, Botstein D (2003) Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8418–8423
Dawson SJ, Rueda OM, Aparicio S, Caldas C (2013) A new genome-driven integrated classification of breast cancer and its implications. EMBO J 32:617–628
Knight JF, Lesurf R, Zhao H, Pinnaduwage D, Davis RR, Saleh SM, Zuo D, Naujokas MA, Chughtai N, Herschkowitz JI, Prat A, Mulligan AM, Muller WJ, Cardiff RD, Gregg JP, Andrulis IL, Hallett MT, Park M (2013) Met synergizes with p53 loss to induce mammary tumors that possess features of claudin-low breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E1301–E1310
Zawistowski JS, Nakamura K, Parker JS, Granger DA, Golitz BT, Johnson GL (2013) MicroRNA 9-3p targets beta1 integrin to sensitize claudin-low breast cancer cells to MEK inhibition. Mol Cell Biol 33:2260–2274
Matsunuma R, Chan DW, Kim BJ, Singh P, Han A, Saltzman AB, Cheng C, Lei JT, Wang J, Roberto da Silva L, Sahin E, Leng M, Fan C, Perou CM, Malovannaya A, Ellis MJ (2018) DPYSL3 modulates mitosis, migration, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in claudin-low breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E11978–E11987
Hoadley KA, Yau C, Wolf DM, Cherniack AD, Tamborero D, Ng S, Leiserson MDM, Niu B, McLellan MD, Uzunangelov V, Zhang J, Kandoth C, Akbani R, Shen H, Omberg L, Chu A, Margolin AA, Van’t Veer LJ, Lopez-Bigas N, Laird PW, Raphael BJ, Ding L, Robertson AG, Byers LA, Mills GB, Weinstein JN, Van Waes C, Chen Z, Collisson EA, Cancer Genome Atlas Research N, Benz CC, Perou CM, Stuart JM (2014) Multiplatform analysis of 12 cancer types reveals molecular classification within and across tissues of origin. Cell 158:929–944
Doherty GJ, Ahlund MK, Howes MT, Moren B, Parton RG, McMahon HT, Lundmark R (2011) The endocytic protein GRAF1 is directed to cell-matrix adhesion sites and regulates cell spreading. Mol Biol Cell 22:4380–4389
Shu Y, Zhang W, Hou Q, Zhao L, Zhang S, Zhou J, Song X, Zhang Y, Jiang D, Chen X, Wang P, Xia X, Liao F, Yin D, Chen X, Zhou X, Zhang D, Yin S, Yang K, Liu J, Fu L, Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhang J, An Y, Cheng H, Zheng B, Sun H, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Xie D, Ouyang L, Wang P, Zhang W, Qiu M, Fu X, Dai L, He G, Yang H, Cheng W, Yang L, Liu B, Li W, Dong B, Zhou Z, Wei Y, Peng Y, Xu H, Hu J (2018) Prognostic significance of frequent CLDN18-ARHGAP26/6 fusion in gastric signet-ring cell cancer. Nat Commun 9:2447
Tanaka A, Ishikawa S, Ushiku T, Yamazawa S, Katoh H, Hayashi A, Kunita A, Fukayama M (2018) Frequent CLDN18-ARHGAP fusion in highly metastatic diffuse-type gastric cancer with relatively early onset. Oncotarget 9:29336–29350
Singh P, Toom S, Huang Y (2017) Anti-claudin 18.2 antibody as new targeted therapy for advanced gastric cancer. J Hematol Oncol 10:105
Sahin U, Schuler M, Richly H, Bauer S, Krilova A, Dechow T, Jerling M, Utsch M, Rohde C, Dhaene K, Huber C, Tureci O (2018) A phase I dose-escalation study of IMAB362 (Zolbetuximab) in patients with advanced gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction cancer. Eur J Cancer 100:17–26
Cherradi S, Ayrolles-Torro A, Vezzo-Vie N, Gueguinou N, Denis V, Combes E, Boissiere F, Busson M, Canterel-Thouennon L, Mollevi C, Pugniere M, Bibeau F, Ychou M, Martineau P, Gongora C, Del Rio M (2017) Antibody targeting of claudin-1 as a potential colorectal cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:89
Hashimoto Y, Tada M, Iida M, Nagase S, Hata T, Watari A, Okada Y, Doi T, Fukasawa M, Yagi K, Kondoh M (2016) Generation and characterization of a human-mouse chimeric antibody against the extracellular domain of claudin-1 for cancer therapy using a mouse model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477:91–95
Romani C, Cocco E, Bignotti E, Moratto D, Bugatti A, Todeschini P, Bandiera E, Tassi R, Zanotti L, Pecorelli S, Sartori E, Odicino FE, de Marco A, Santin AD, Ravaggi A, Mitola S (2015) Evaluation of a novel human IgG1 anti-claudin3 antibody that specifically recognizes its aberrantly localized antigen in ovarian cancer cells and that is suitable for selective drug delivery. Oncotarget 6:34617–34628
Sahin U, Koslowski M, Dhaene K, Usener D, Brandenburg G, Seitz G, Huber C, Tureci O (2008) Claudin-18 splice variant 2 is a pan-cancer target suitable for therapeutic antibody development. Clin Cancer Res 14:7624–7634
Hashimoto Y, Okada Y, Shirakura K, Tachibana K, Sawada M, Yagi K, Doi T, Kondoh M (2019) Anti-claudin antibodies as a concept for development of claudin-directed drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 368:179–186
Hashimoto Y, Yagi K, Kondoh M (2016) Current progress in a second-generation claudin binder, anti-claudin antibody, for clinical applications. Drug Discov Today 21:1711–1718
Hashimoto Y, Kawahigashi Y, Hata T, Li X, Watari A, Tada M, Ishii-Watabe A, Okada Y, Doi T, Fukasawa M, Kuniyasu H, Yagi K, Kondoh M (2016) Efficacy and safety evaluation of claudin-4-targeted antitumor therapy using a human and mouse cross-reactive monoclonal antibody. Pharmacol Res Perspect 4:e00266
Li X, Iida M, Tada M, Watari A, Kawahigashi Y, Kimura Y, Yamashita T, Ishii-Watabe A, Uno T, Fukasawa M, Kuniyasu H, Yagi K, Kondoh M (2014) Development of an anti-claudin-3 and -4 bispecific monoclonal antibody for cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 351:206–213
Fujiwara-Tani R, Sasaki T, Luo Y, Goto K, Kawahara I, Nishiguchi Y, Kishi S, Mori S, Ohmori H, Kondoh M, Kuniyasu H (2018) Anti-claudin-4 extracellular domain antibody enhances the antitumoral effects of chemotherapeutic and antibody drugs in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 9:37367–37378
Hashimoto Y, Hata T, Tada M, Iida M, Watari A, Okada Y, Doi T, Kuniyasu H, Yagi K, Kondoh M (2018) Safety evaluation of a human chimeric monoclonal antibody that recognizes the extracellular loop domain of claudin-2. Eur J Pharm Sci 117:161–167
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Hastings Foundation, research grants R35HL135747 (ZB) and HL114959 (BZ), from the National Institutes of Health and by The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) KAKENHI research grant JP16K09574 (HK). Z. Borok is Hastings Professor and Edgington Chair in Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kage, H., Flodby, P., Zhou, B. et al. Dichotomous roles of claudins as tumor promoters or suppressors: lessons from knockout mice. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76, 4663–4672 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03238-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03238-7