Abstract
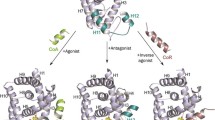
The estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ, NR3B3) is a constitutively active nuclear receptor which has been proposed to act as a mediator of the low-dose effects of a number of environmental endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) such as the xenoestrogen bisphenol-A (BPA). To better characterize the ability of exogenous compounds to bind and activate ERRγ, we used a combination of cell-based, biochemical, structural and computational approaches. A purposely created stable cell line allowed for the determination of the EC50s for over 30 environmental ERRγ ligands, including previously unknown ones. Interestingly, affinity constants (Kds) of the most potent compounds measured by isothermal titration calorimetry were in the 50–500 nM range, in agreement with their receptor activation potencies. Crystallographic analysis of the interaction between the ERRγ ligand-binding domain (LBD) and compounds of the bisphenol, alkylphenol and naphthol families revealed a partially shared binding mode and minimal alterations of the receptor conformation upon ligand binding. Further biophysical characterizations coupled to molecular dynamics simulations suggested a mechanism through which ERRγ ligands would exhibit their agonistic properties by preserving the transcriptionally active form of the receptor while rigidifying some loop regions with associated functions. This unique mechanism contrasts with the classical one involving a ligand-induced repositioning and stabilization of the C-terminal activation helix H12.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horard B, Vanacker JM (2003) Estrogen receptor-related receptors: orphan receptors desperately seeking a ligand. J Mol Endocrinol 31(3):349–357
Wei W, Schwaid AG, Wang X, Wang X, Chen S, Chu Q, Saghatelian A, Wan Y (2016) Ligand activation of ERRalpha by cholesterol mediates statin and bisphosphonate effects. Cell Metab 23(3):479–491
Casaburi I, Chimento A, De Luca A, Nocito M, Sculco S, Avena P, Trotta F, Rago V, Sirianni R, Pezzi V (2018) Cholesterol as an endogenous ERRalpha agonist: a new perspective to cancer treatment. Front Endocrinol 9:525
Goyanka R, Das S, Samuels HH, Cardozo T (2010) Nuclear receptor engineering based on novel structure activity relationships revealed by farnesyl pyrophosphate. Protein Eng Des Sel 23(11):809–815
Greschik H, Wurtz JM, Sanglier S, Bourguet W, van Dorsselaer A, Moras D, Renaud JP (2002) Structural and functional evidence for ligand-independent transcriptional activation by the estrogen-related receptor 3. Mol Cell 9(2):303–313
Eichner LJ, Giguere V (2011) Estrogen related receptors (ERRs): a new dawn in transcriptional control of mitochondrial gene networks. Mitochondrion 11(4):544–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2011.03.121
Misra J, Kim DK, Choi HS (2017) ERRgamma: a junior orphan with a senior role in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metabol TEM 28(4):261–272
Deblois G, Giguere V (2013) Oestrogen-related receptors in breast cancer: control of cellular metabolism and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 13(1):27–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3396
Dufour CR, Wilson BJ, Huss JM, Kelly DP, Alaynick WA, Downes M, Evans RM, Blanchette M, Giguere V (2007) Genome-wide orchestration of cardiac functions by the orphan nuclear receptors ERRalpha and gamma. Cell Metab 5(5):345–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.03.007
Maehara K, Hida T, Abe Y, Koga A, Ota K, Kutoh E (2003) Functional interference between estrogen-related receptor alpha and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/9-cis-retinoic acid receptor alpha heterodimer complex in the nuclear receptor response element-1 of the medium chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase gene. J Mol Endocrinol 31(1):47–60
Audet-Walsh E, Giguere V (2015) The multiple universes of estrogen-related receptor alpha and gamma in metabolic control and related diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36(1):51–61
Ranhotra HS (2012) The estrogen-related receptors: orphans orchestrating myriad functions. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 32(2):47–56. https://doi.org/10.3109/10799893.2011.647350
Tremblay AM, Wilson BJ, Yang XJ, Giguere V (2008) Phosphorylation-dependent sumoylation regulates estrogen-related receptor-alpha and -gamma transcriptional activity through a synergy control motif. Mol Endocrinol (Baltim Md) 22(3):570–584. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0357
Riggins RB (2014) The pERK of being a target: kinase regulation of the orphan nuclear receptor ERRgamma. Receptors Clin Investig 1:5
Misawa A, Inoue S (2015) Estrogen-related receptors in breast cancer and prostate cancer. Front Endocrinol 6:83. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00083
Ariazi EA, Jordan VC (2006) Estrogen-related receptors as emerging targets in cancer and metabolic disorders. Curr Top Med Chem 6(3):203–215
Ariazi EA, Clark GM, Mertz JE (2002) Estrogen-related receptor alpha and estrogen-related receptor gamma associate with unfavorable and favorable biomarkers, respectively, in human breast cancer. Can Res 62(22):6510–6518
Suzuki T, Miki Y, Moriya T, Shimada N, Ishida T, Hirakawa H, Ohuchi N, Sasano H (2004) Estrogen-related receptor alpha in human breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor. Can Res 64(13):4670–4676
Ijichi N, Shigekawa T, Ikeda K, Horie-Inoue K, Fujimura T, Tsuda H, Osaki A, Saeki T, Inoue S (2011) Estrogen-related receptor gamma modulates cell proliferation and estrogen signaling in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 123(1–2):1–7
Tiraby C, Hazen BC, Gantner ML, Kralli A (2011) Estrogen-related receptor gamma promotes mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition and suppresses breast tumor growth. Can Res 71(7):2518–2528
Rochester JR (2013) Bisphenol A and human health: a review of the literature. Reprod Toxicol 42:132–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2013.08.008
Okada H, Tokunaga T, Liu X, Takayanagi S, Matsushima A, Shimohigashi Y (2008) Direct evidence revealing structural elements essential for the high binding ability of bisphenol A to human estrogen-related receptor-gamma. Environ Health Perspect 116(1):32–38. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10587
Takayanagi S, Tokunaga T, Liu X, Okada H, Matsushima A, Shimohigashi Y (2006) Endocrine disruptor bisphenol A strongly binds to human estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) with high constitutive activity. Toxicol Lett 167(2):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2006.08.012
Tohme M, Prud’homme SM, Boulahtouf A, Samarut E, Brunet F, Bernard L, Bourguet W, Gibert Y, Balaguer P, Laudet V (2014) Estrogen-related receptor gamma is an in vivo receptor of bisphenol A. FASEB J 28(7):3124–3133. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-240465
Greschik H, Flaig R, Renaud JP, Moras D (2004) Structural basis for the deactivation of the estrogen-related receptor by diethylstilbestrol or 4-hydroxytamoxifen and determinants of selectivity. J Biol Chem 279(32):33639–33646. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M402195200
Coward P, Lee D, Hull MV, Lehmann JM (2001) 4-Hydroxytamoxifen binds to and deactivates the estrogen-related receptor gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(15):8880–8884. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.151244398
Matsushima A, Kakuta Y, Teramoto T, Koshiba T, Liu X, Okada H, Tokunaga T, Kawabata S, Kimura M, Shimohigashi Y (2007) Structural evidence for endocrine disruptor bisphenol A binding to human nuclear receptor ERR gamma. J Biochem 142(4):517–524
Abad MC, Askari H, O’Neill J, Klinger AL, Milligan C, Lewandowski F, Springer B, Spurlino J, Rentzeperis D (2008) Structural determination of estrogen-related receptor gamma in the presence of phenol derivative compounds. J steroid Biochem Mol Biol 108(1–2):44–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.06.006
Seimandi M, Lemaire G, Pillon A, Perrin A, Carlavan I, Voegel JJ, Vignon F, Nicolas JC, Balaguer P (2005) Differential responses of PPARalpha, PPARdelta, and PPARgamma reporter cell lines to selective PPAR synthetic ligands. Anal Biochem 344(1):8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2005.06.010
Kabsch W (2010) Xds. Acta Crystallogr 66(Pt 2):125–132
Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkoczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH (2010) PHENIX: a comprehensive python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr A 66(Pt 2):213–221
Emsley P, Cowtan K (2004) Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr A 60(Pt 12 Pt 1):2126–2132
Chen VB, Arendall WB 3rd, Headd JJ, Keedy DA, Immormino RM, Kapral GJ, Murray LW, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2010) MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr A 66(Pt 1):12–21
Pogenberg V, Guichou JF, Vivat-Hannah V, Kammerer S, Perez E, Germain P, de Lera AR, Gronemeyer H, Royer CA, Bourguet W (2005) Characterization of the interaction between retinoic acid receptor/retinoid X receptor (RAR/RXR) heterodimers and transcriptional coactivators through structural and fluorescence anisotropy studies. J Biol Chem 280(2):1625–1633
Maier JA, Martinez C, Kasavajhala K, Wickstrom L, Hauser KE, Simmerling C (2015) ff14SB: improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J Chem Theory Comput 11:3696–3713
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general AMBER force field. J Comput Chem 25:1157–1174
Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E (2015) GROMACS: high performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 1–2:19–25
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577
Bussi G, Donadio D, Parrinello M (2007) Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J Chem Phys 126:014101
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52:7182–7190
Matsushima A, Teramoto T, Okada H, Liu X, Tokunaga T, Kakuta Y, Shimohigashi Y (2008) ERRgamma tethers strongly bisphenol A and 4-alpha-cumylphenol in an induced-fit manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 373(3):408–413
Delfosse V, Maire AL, Balaguer P, Bourguet W (2014) A structural perspective on nuclear receptors as targets of environmental compounds. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36(1):88–101
Levin ER (2015) Extranuclear steroid receptors are essential for steroid hormone actions. Annu Rev Med 66:271–280
Nadal A, Fuentes E, Ripoll C, Villar-Pazos S, Castellano-Munoz M, Soriano S, Martinez-Pinna J, Quesada I, Alonso-Magdalena P (2018) Extranuclear-initiated estrogenic actions of endocrine disrupting chemicals: is there toxicology beyond paracelsus? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 176:16–22
Prossnitz ER, Barton M (2011) The G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPER in health and disease. Nat Rev 7(12):715–726
le Maire A, Bourguet W, Balaguer P (2010) A structural view of nuclear hormone receptor: endocrine disruptor interactions. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(8):1219–1237
Delfosse V, Grimaldi M, Pons JL, Boulahtouf A, le Maire A, Cavailles V, Labesse G, Bourguet W, Balaguer P (2012) Structural and mechanistic insights into bisphenols action provide guidelines for risk assessment and discovery of bisphenol A substitutes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(37):14930–14935. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203574109
Delfosse V, Grimaldi M, Cavailles V, Balaguer P, Bourguet W (2014) Structural and functional profiling of environmental ligands for estrogen receptors. Environ Health Perspect 122(12):1306–1313. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1408453
Alaynick WA, Kondo RP, Xie W, He W, Dufour CR, Downes M, Jonker JW, Giles W, Naviaux RK, Giguere V, Evans RM (2007) ERRgamma directs and maintains the transition to oxidative metabolism in the postnatal heart. Cell Metab 6(1):13–24
Narkar VA, Fan W, Downes M, Yu RT, Jonker JW, Alaynick WA, Banayo E, Karunasiri MS, Lorca S, Evans RM (2011) Exercise and PGC-1alpha-independent synchronization of type I muscle metabolism and vasculature by ERRgamma. Cell Metab 13(3):283–293
Wang T, McDonald C, Petrenko NB, Leblanc M, Wang T, Giguere V, Evans RM, Patel VV, Pei L (2015) Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) and ERRgamma are essential coordinators of cardiac metabolism and function. Mol Cell Biol 35(7):1281–1298
Alaynick WA, Way JM, Wilson SA, Benson WG, Pei L, Downes M, Yu R, Jonker JW, Holt JA, Rajpal DK, Li H, Stuart J, McPherson R, Remlinger KS, Chang CY, McDonnell DP, Evans RM, Billin AN (2010) ERRgamma regulates cardiac, gastric, and renal potassium homeostasis. Mol Endocrinol (Baltim Md) 24(2):299–309
Luo Y, Kumar P, Mendelson CR (2013) Estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) regulates oxygen-dependent expression of voltage-gated potassium (K+) channels and tissue kallikrein during human trophoblast differentiation. Mol Endocrinol (Baltim Md) 27(6):940–952
Kim DK, Kim JR, Koh M, Kim YD, Lee JM, Chanda D, Park SB, Min JJ, Lee CH, Park TS, Choi HS (2011) Estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) is a novel transcriptional regulator of phosphatidic acid phosphatase, LIPIN1, and inhibits hepatic insulin signaling. J Biol Chem 286(44):38035–38042
Kim DK, Ryu D, Koh M, Lee MW, Lim D, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Cho WJ, Lee CH, Park SB, Koo SH, Choi HS (2012) Orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) is key regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. J Biol Chem 287(26):21628–21639
Menale C, Piccolo MT, Cirillo G, Calogero RA, Papparella A, Mita L, Del Giudice EM, Diano N, Crispi S, Mita DG (2015) Bisphenol A effects on gene expression in adipocytes from children: association with metabolic disorders. J Mol Endocrinol 54(3):289–303
Le Magueresse-Battistoni B, Multigner L, Beausoleil C, Rousselle C (2018) Effects of bisphenol A on metabolism and evidences of a mode of action mediated through endocrine disruption. Mol Cell Endocrinol 475:74–91
Ren Y, Jiang H, Ma D, Nakaso K, Feng J (2011) Parkin degrades estrogen-related receptors to limit the expression of monoamine oxidases. Hum Mol Genet 20(6):1074–1083
Kim DK, Kim YH, Hynx D, Wang Y, Yang KJ, Ryu D, Kim KS, Yoo EK, Kim JS, Koo SH, Lee IK, Chae HZ, Park J, Lee CH, Biddinger SB, Hemmings BA, Choi HS (2014) PKB/Akt phosphorylation of ERRgamma contributes to insulin-mediated inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetologia 57(12):2576–2585
Heckler MM, Thakor H, Schafer CC, Riggins RB (2014) ERK/MAPK regulates ERRgamma expression, transcriptional activity and receptor-mediated tamoxifen resistance in ER + breast cancer. FEBS J 281(10):2431–2442
Misra J, Kim DK, Jung YS, Kim HB, Kim YH, Yoo EK, Kim BG, Kim S, Lee IK, Harris RA, Kim JS, Lee CH, Cho JW, Choi HS (2016) O-GlcNAcylation of orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor gamma promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 65(10):2835–2848
Bruck N, Vitoux D, Ferry C, Duong V, Bauer A, de The H, Rochette-Egly C (2009) A coordinated phosphorylation cascade initiated by p38MAPK/MSK1 directs RARalpha to target promoters. EMBO J 28(1):34–47
Gaillard E, Bruck N, Brelivet Y, Bour G, Lalevee S, Bauer A, Poch O, Moras D, Rochette-Egly C (2006) Phosphorylation by PKA potentiates retinoic acid receptor alpha activity by means of increasing interaction with and phosphorylation by cyclin H/cdk7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(25):9548–9553
Le Goff P, Montano MM, Schodin DJ, Katzenellenbogen BS (1994) Phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor. Identification of hormone-regulated sites and examination of their influence on transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 269(6):4458–4466
Shang Y, Hu X, DiRenzo J, Lazar MA, Brown M (2000) Cofactor dynamics and sufficiency in estrogen receptor-regulated transcription. Cell 103(6):843–852
Xin QL, Qiu JT, Cui S, Xia GL, Wang HB (2016) Transcriptional activation of nuclear estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor and its regulation. Sheng Li Xue Bao 68(4):435–454
Chebaro Y, Amal I, Rochel N, Rochette-Egly C, Stote RH, Dejaegere A (2013) Phosphorylation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha induces a mechanical allosteric regulation and changes in internal dynamics. PLoS Comput Biol 9(4):e1003012
Acknowledgements
The CBS is a member of the France-BioImaging (FBI) and the French Infrastructure for Integrated Structural Biology (FRISBI), two national infrastructures supported by the French National Research Agency (ANR-10-INBS-04-01 and ANR-10-INBS-05, respectively). We acknowledge the experimental assistance from the staff of the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF, Grenoble, France) during data collection. We would like to acknowledge the financial support from the Plan Cancer Inserm, project CONTERREC C16007FS (PB and WB) and the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche, under grants ANR-13-CESA-0012-04 (PB) and ANR-14-ACHN-0016 (AB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thouennon, E., Delfosse, V., Bailly, R. et al. Insights into the activation mechanism of human estrogen-related receptor γ by environmental endocrine disruptors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76, 4769–4781 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03129-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03129-x