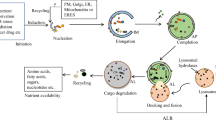
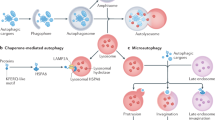
Abstract
Autophagy is a highly regulated process in eukaryotes to maintain homeostasis and manage stress responses. Understanding the regulatory mechanisms and key players involved in autophagy will provide critical insights into disease-related pathogenesis and potential clinical treatments. In this review, we describe the hallmark events involved in autophagy, from its initiation, to the final destruction of engulfed targets. Furthermore, based on structural and biochemical data, we evaluate the roles of key players in these processes and provide rationale as to how they control autophagic events in a highly ordered manner.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mizushima N (2011) Autophagy in protein and organelle turnover. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 76:397–402. doi:10.1101/sqb.2011.76.011023
Parzych KR, Klionsky DJ (2014) An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(3):460–473. doi:10.1089/ars.2013.5371
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ (2010) Eaten alive: a history of macroautophagy. Nat Cell Biol 12(9):814–822. doi:10.1038/ncb0910-814
Xie Z, Klionsky DJ (2007) Autophagosome formation: core machinery and adaptations. Nat Cell Biol 9(10):1102–1109
Zhong Y, Wang QJ, Li X, Yan Y, Backer JM, Chait BT, Heintz N, Yue Z (2009) Distinct regulation of autophagic activity by Atg14L and Rubicon associated with Beclin 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase complex. Nat Cell Biol 11(4):468–476. doi:10.1038/ncb1854
Levine B, Kroemer G (2008) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132(1):27–42. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ (2004) Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 306(5698):990–995
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y (2011) The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:107–132. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154005
Hurley JH, Schulman BA (2014) Atomistic autophagy: the structures of cellular self-digestion. Cell 157(2):300–311. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.070
Klionsky DJ, Codogno P, Cuervo AM, Deretic V, Elazar Z, Fueyo-Margareto J, Gewirtz DA, Kroemer G, Levine B, Mizushima N, Rubinsztein DC, Thumm M, Tooze SA (2010) A comprehensive glossary of autophagy-related molecules and processes. Autophagy 6(4):438–448. doi:10.4161/auto.6.4.12244
Chen Y, Klionsky DJ (2011) The regulation of autophagy—unanswered questions. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 2):161–170. doi:10.1242/jcs.064576
Hosokawa N, Sasaki T, Iemura S, Natsume T, Hara T, Mizushima N (2009) Atg101, a novel mammalian autophagy protein interacting with Atg13. Autophagy 5(7):973–979
Mercer CA, Kaliappan A, Dennis PB (2009) A novel, human Atg13 binding protein, Atg101, interacts with ULK1 and is essential for macroautophagy. Autophagy 5(5):649–662
Sancak Y, Bar-Peled L, Zoncu R, Markhard AL, Nada S, Sabatini DM (2010) Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids. Cell 141(2):290–303
Brugarolas J, Lei K, Hurley RL, Manning BD, Reiling JH, Hafen E, Witters LA, Ellisen LW, Kaelin WG Jr (2004) Regulation of mTOR function in response to hypoxia by REDD1 and the TSC1/TSC2 tumor suppressor complex. Genes Dev 18(23):2893–2904
DeYoung MP, Horak P, Sofer A, Sgroi D, Ellisen LW (2008) Hypoxia regulates TSC1/2-mTOR signaling and tumor suppression through REDD1-mediated 14-3-3 shuttling. Genes Dev 22(2):239–251
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF, Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS, Turk BE, Shaw RJ (2008) AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell 30(2):214–226
Budanov AV (2011) Stress-responsive sestrins link p53 with redox regulation and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 15(6):1679–1690. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3530
Fujioka Y, Suzuki SW, Yamamoto H, Kondo-Kakuta C, Kimura Y, Hirano H, Akada R, Inagaki F, Ohsumi Y, Noda NN (2014) Structural basis of starvation-induced assembly of the autophagy initiation complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2822
Stanley RE, Ragusa MJ, Hurley JH (2014) The beginning of the end: how scaffolds nucleate autophagosome biogenesis. Trends Cell Biol 24(1):73–81. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.07.008
Kamada Y, Funakoshi T, Shintani T, Nagano K, Ohsumi M, Ohsumi Y (2000) Tor-mediated induction of autophagy via an Apg1 protein kinase complex. J Cell Biol 150(6):1507–1513
Kabeya Y, Kamada Y, Baba M, Takikawa H, Sasaki M, Ohsumi Y (2005) Atg17 functions in cooperation with Atg1 and Atg13 in yeast autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 16(5):2544–2553
Dorsey FC, Rose KL, Coenen S, Prater SM, Cavett V, Cleveland JL, Caldwell-Busby J (2009) Mapping the phosphorylation sites of Ulk1. J Proteome Res 8(11):5253–5263. doi:10.1021/pr900583m
Kamada Y, Yoshino K, Kondo C, Kawamata T, Oshiro N, Yonezawa K, Ohsumi Y (2010) Tor directly controls the Atg1 kinase complex to regulate autophagy. Mol Cell Biol 30(4):1049–1058. doi:10.1128/MCB.01344-09
Cheong H, Nair U, Geng J, Klionsky DJ (2008) The Atg1 kinase complex is involved in the regulation of protein recruitment to initiate sequestering vesicle formation for nonspecific autophagy in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 19(2):668–681
Jao CC, Ragusa MJ, Stanley RE, Hurley JH (2013) A HORMA domain in Atg13 mediates PI 3-kinase recruitment in autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(14):5486–5491. doi:10.1073/pnas.1220306110
Suzuki H, Tabata K, Morita E, Kawasaki M, Kato R, Dobson RC, Yoshimori T, Wakatsuki S (2014) Structural basis of the autophagy-related LC3/Atg13 LIR complex: recognition and interaction mechanism. Structure 22(1):47–58. doi:10.1016/j.str.2013.09.023
Cheong H, Klionsky DJ (2008) Dual role of Atg1 in regulation of autophagy-specific PAS assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Autophagy 4(5):724–726
Chan EY, Longatti A, McKnight NC, Tooze SA (2009) Kinase-inactivated ULK proteins inhibit autophagy via their conserved C-terminal domains using an Atg13-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 29(1):157–171. doi:10.1128/MCB.01082-08
Ragusa MJ, Stanley RE, Hurley JH (2012) Architecture of the Atg17 complex as a scaffold for autophagosome biogenesis. Cell 151(7):1501–1512. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.028
Lazarus MB, Novotny CJ, Shokat KM (2015) Structure of the human autophagy initiating kinase ULK1 in complex with potent inhibitors. ACS Chem Biol 10(1):257–261. doi:10.1021/cb500835z
Di Bartolomeo S, Corazzari M, Nazio F, Oliverio S, Lisi G, Antonioli M, Pagliarini V, Matteoni S, Fuoco C, Giunta L, D’Amelio M, Nardacci R, Romagnoli A, Piacentini M, Cecconi F, Fimia GM (2010) The dynamic interaction of AMBRA1 with the dynein motor complex regulates mammalian autophagy. J Cell Biol 191(1):155–168. doi:10.1083/jcb.201002100
Russell RC, Tian Y, Yuan H, Park HW, Chang YY, Kim J, Kim H, Neufeld TP, Dillin A, Guan KL (2013) ULK1 induces autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase. Nat Cell Biol 15(7):741–750. doi:10.1038/ncb2757
Yamamoto H, Fujioka Y, Suzuki SW, Noshiro D, Suzuki H, Kondo-Kakuta C, Kimura Y, Hirano H, Ando T, Noda NN, Ohsumi Y (2016) The intrinsically disordered protein Atg13 mediates supramolecular assembly of autophagy initiation complexes. Dev Cell 38(1):86–99
He C, Klionsky DJ (2009) Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 43:67–93. doi:10.1146/annurev-genet-102808-114910
Kihara A, Noda T, Ishihara N, Ohsumi Y (2001) Two distinct Vps34 phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complexes function in autophagy and carboxypeptidase Y sorting in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol 152(3):519–530
Blommaart EF, Krause U, Schellens JP, Vreeling-Sindelarova H, Meijer AJ (1997) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors wortmannin and LY294002 inhibit autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem 243(1–2):240–246
Miller S, Tavshanjian B, Oleksy A, Perisic O, Houseman BT, Shokat KM, Williams RL (2010) Shaping development of autophagy inhibitors with the structure of the lipid kinase Vps34. Science 327(5973):1638–1642. doi:10.1126/science.1184429
Panaretou C, Domin J, Cockcroft S, Waterfield MD (1997) Characterization of p150, an adaptor protein for the human phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) 3-kinase. Substrate presentation by phosphatidylinositol transfer protein to the p150.Ptdins 3-kinase complex. J Biol Chem 272(4):2477–2485
McKnight NC, Zhenyu Y (2013) Beclin 1, an essential component and master regulator of PI3K-III in health and disease. Curr Pathobiol Rep 1(4):231–238. doi:10.1007/s40139-013-0028-5
Stack JH, Herman PK, Schu PV, Emr SD (1993) A membrane-associated complex containing the Vps15 protein kinase and the Vps34 PI 3-kinase is essential for protein sorting to the yeast lysosome-like vacuole. EMBO J 12(5):2195–2204
Yan Y, Flinn RJ, Wu H, Schnur RS, Backer JM (2009) hVps15, but not Ca2+/CaM, is required for the activity and regulation of hVps34 in mammalian cells. Biochem J 417(3):747–755. doi:10.1042/BJ20081865
Herman PK, Stack JH, DeModena JA, Emr SD (1991) A novel protein kinase homolog essential for protein sorting to the yeast lysosome-like vacuole. Cell 64(2):425–437
Fu LL, Cheng Y, Liu B (2013) Beclin-1: autophagic regulator and therapeutic target in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45(5):921–924. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.02.007
Rostislavleva K, Soler N, Ohashi Y, Zhang L, Pardon E, Burke JE, Masson GR, Johnson C, Steyaert J, Ktistakis NT, Williams RL (2015) Structure and flexibility of the endosomal Vps34 complex reveals the basis of its function on membranes. Science 350(6257):aac7365
Fan W, Nassiri A, Zhong Q (2011) Autophagosome targeting and membrane curvature sensing by Barkor/Atg14(L). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(19):7769–7774. doi:10.1073/pnas.1016472108
Fimia GM, Stoykova A, Romagnoli A, Giunta L, Di Bartolomeo S, Nardacci R, Corazzari M, Fuoco C, Ucar A, Schwartz P, Gruss P, Piacentini M, Chowdhury K, Cecconi F (2007) Ambra1 regulates autophagy and development of the nervous system. Nature 447(7148):1121–1125
Takahashi Y, Coppola D, Matsushita N, Cualing HD, Sun M, Sato Y, Liang C, Jung JU, Cheng JQ, Mule JJ, Pledger WJ, Wang HG (2007) Bif-1 interacts with Beclin 1 through UVRAG and regulates autophagy and tumorigenesis. Nat Cell Biol 9(10):1142–1151
Molejon MI, Ropolo A, Re AL, Boggio V, Vaccaro MI (2013) The VMP1–Beclin 1 interaction regulates autophagy induction. Sci Rep 3:1055. doi:10.1038/srep01055
Matsunaga K, Saitoh T, Tabata K, Omori H, Satoh T, Kurotori N, Maejima I, Shirahama-Noda K, Ichimura T, Isobe T, Akira S, Noda T, Yoshimori T (2009) Two Beclin 1-binding proteins, Atg14L and Rubicon, reciprocally regulate autophagy at different stages. Nat Cell Biol 11(4):385–396. doi:10.1038/ncb1846
Hayashi-Nishino M, Fujita N, Noda T, Yamaguchi A, Yoshimori T, Yamamoto A (2009) A subdomain of the endoplasmic reticulum forms a cradle for autophagosome formation. Nat Cell Biol 11(12):1433–1437. doi:10.1038/ncb1991
Yla-Anttila P, Vihinen H, Jokitalo E, Eskelinen EL (2009) 3D tomography reveals connections between the phagophore and endoplasmic reticulum. Autophagy 5(8):1180–1185
Walker S, Chandra P, Manifava M, Axe E, Ktistakis NT (2008) Making autophagosomes: localized synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate holds the clue. Autophagy 4(8):1093–1096
Axe EL, Walker SA, Manifava M, Chandra P, Roderick HL, Habermann A, Griffiths G, Ktistakis NT (2008) Autophagosome formation from membrane compartments enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and dynamically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol 182(4):685–701. doi:10.1083/jcb.200803137
Graef M, Friedman JR, Graham C, Babu M, Nunnari J (2013) ER exit sites are physical and functional core autophagosome biogenesis components. Mol Biol Cell 24(18):2918–2931
Tan D, Cai Y, Wang J, Zhang J, Menon S, Chou HT, Ferro-Novick S, Reinisch KM, Walz T (2013) The EM structure of the TRAPPIII complex leads to the identification of a requirement for COPII vesicles on the macroautophagy pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(48):19432–19437
Lemus L, Ribas JL, Sikorska N, Goder V (2016) An ER-localized SNARE protein is exported in specific COPII vesicles for autophagosome biogenesis. Cell Rep 14(7):1710–1722
Ge L, Zhang M, Schekman R (2014) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and COPII generate LC3 lipidation vesicles from the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment. Elife 3:e04135. doi:10.7554/eLife.04135
Kutateladze TG (2010) Translation of the phosphoinositide code by PI effectors. Nat Chem Biol 6(7):507–513. doi:10.1038/nchembio.390
Obara K, Sekito T, Niimi K, Ohsumi Y (2008) The Atg18-Atg2 complex is recruited to autophagic membranes via phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and exerts an essential function. J Biol Chem 283(35):23972–23980. doi:10.1074/jbc.M803180200
Polson HE, de Lartigue J, Rigden DJ, Reedijk M, Urbe S, Clague MJ, Tooze SA (2010) Mammalian Atg18 (WIPI2) localizes to omegasome-anchored phagophores and positively regulates LC3 lipidation. Autophagy 6(4):506–522. doi:10.4161/auto.6.4.11863
Itakura E, Mizushima N (2010) Characterization of autophagosome formation site by a hierarchical analysis of mammalian Atg proteins. Autophagy 6(6):764–776
Ichimura Y, Kirisako T, Takao T, Satomi Y, Shimonishi Y, Ishihara N, Mizushima N, Tanida I, Kominami E, Ohsumi M, Noda T, Ohsumi Y (2000) A ubiquitin-like system mediates protein lipidation. Nature 408(6811):488–492. doi:10.1038/35044114
Longatti A, Tooze SA (2012) Recycling endosomes contribute to autophagosome formation. Autophagy 8(11):1682–1683. doi:10.4161/auto.21486
Reggiori F, Tucker KA, Stromhaug PE, Klionsky DJ (2004) The Atg1–Atg13 complex regulates Atg9 and Atg23 retrieval transport from the pre-autophagosomal structure. Dev Cell 6(1):79–90
Young AR, Chan EY, Hu XW, Kochl R, Crawshaw SG, High S, Hailey DW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Tooze SA (2006) Starvation and ULK1-dependent cycling of mammalian Atg9 between the TGN and endosomes. J Cell Sci 119(Pt 18):3888–3900
Nair U, Cao Y, Xie Z, Klionsky DJ (2010) Roles of the lipid-binding motifs of Atg18 and Atg21 in the cytoplasm to vacuole targeting pathway and autophagy. J Biol Chem 285(15):11476–11488. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.080374
Ropolo A, Grasso D, Pardo R, Sacchetti ML, Archange C, Lo Re A, Seux M, Nowak J, Gonzalez CD, Iovanna JL, Vaccaro MI (2007) The pancreatitis-induced vacuole membrane protein 1 triggers autophagy in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 282(51):37124–37133
Moreau K, Renna M, Rubinsztein DC (2013) Connections between SNAREs and autophagy. Trends Biochem Sci 38(2):57–63. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2012.11.004
Reggiori F, Shintani T, Nair U, Klionsky DJ (2005) Atg9 cycles between mitochondria and the pre-autophagosomal structure in yeasts. Autophagy 1(2):101–109
Mari M, Griffith J, Rieter E, Krishnappa L, Klionsky DJ, Reggiori F (2010) An Atg9-containing compartment that functions in the early steps of autophagosome biogenesis. J Cell Biol 190(6):1005–1022. doi:10.1083/jcb.200912089
Kovacs AL, Palfia Z, Rez G, Vellai T, Kovacs J (2007) Sequestration revisited: integrating traditional electron microscopy, de novo assembly and new results. Autophagy 3(6):655–662
Hailey DW, Rambold AS, Satpute-Krishnan P, Mitra K, Sougrat R, Kim PK, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2010) Mitochondria supply membranes for autophagosome biogenesis during starvation. Cell 141(4):656–667. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.009
Ravikumar B, Moreau K, Jahreiss L, Puri C, Rubinsztein DC (2010) Plasma membrane contributes to the formation of pre-autophagosomal structures. Nat Cell Biol 12(8):747–757. doi:10.1038/ncb2078
Noda T, Kim J, Huang WP, Baba M, Tokunaga C, Ohsumi Y, Klionsky DJ (2000) Apg9p/Cvt7p is an integral membrane protein required for transport vesicle formation in the Cvt and autophagy pathways. J Cell Biol 148(3):465–480
Sekito T, Kawamata T, Ichikawa R, Suzuki K, Ohsumi Y (2009) Atg17 recruits Atg9 to organize the pre-autophagosomal structure. Genes Cells 14(5):525–538. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2443.2009.01299.x
Legakis JE, Yen WL, Klionsky DJ (2007) A cycling protein complex required for selective autophagy. Autophagy 3(5):422–432
He C, Baba M, Klionsky DJ (2009) Double duty of Atg9 self-association in autophagosome biogenesis. Autophagy 5(3):385–387
He C, Baba M, Cao Y, Klionsky DJ (2008) Self-interaction is critical for Atg9 transport and function at the phagophore assembly site during autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 19(12):5506–5516. doi:10.1091/mbc.E08-05-0544
Nair U, Jotwani A, Geng J, Gammoh N, Richerson D, Yen WL, Griffith J, Nag S, Wang K, Moss T, Baba M, McNew JA, Jiang X, Reggiori F, Melia TJ, Klionsky DJ (2011) SNARE proteins are required for macroautophagy. Cell 146(2):290–302. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.022
Satoo K, Noda NN, Kumeta H, Fujioka Y, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Inagaki F (2009) The structure of Atg4B–LC3 complex reveals the mechanism of LC3 processing and delipidation during autophagy. EMBO J 28(9):1341–1350. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.80
Yu ZQ, Ni T, Hong B, Wang HY, Jiang FJ, Zou S, Chen Y, Zheng XL, Klionsky DJ, Liang Y, Xie Z (2012) Dual roles of Atg8–PE deconjugation by Atg4 in autophagy. Autophagy 8(6):883–892. doi:10.4161/auto.19652
Hong SB, Kim BW, Lee KE, Kim SW, Jeon H, Kim J, Song HK (2011) Insights into noncanonical E1 enzyme activation from the structure of autophagic E1 Atg7 with Atg8. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18(12):1323–1330. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2165
Fujioka Y, Noda NN, Nakatogawa H, Ohsumi Y, Inagaki F (2010) Dimeric coiled-coil structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Atg16 and its functional significance in autophagy. J Biol Chem 285(2):1508–1515. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.053520
Fujita N, Itoh T, Omori H, Fukuda M, Noda T, Yoshimori T (2008) The Atg16L complex specifies the site of LC3 lipidation for membrane biogenesis in autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 19(5):2092–2100. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-12-1257
Johansen T, Lamark T (2011) Selective autophagy mediated by autophagic adapter proteins. Autophagy 7(3):279–296
Birgisdottir AB, Lamark T, Johansen T (2013) The LIR motif—crucial for selective autophagy. J Cell Sci 126(Pt 15):3237–3247. doi:10.1242/jcs.126128
Johansen T, Lamark T (2014) Selective autophagy goes exclusive. Nat Cell Biol 16(5):395–397. doi:10.1038/ncb2961
Xie Z, Nair U, Klionsky DJ (2008) Atg8 controls phagophore expansion during autophagosome formation. Mol Biol Cell 19(8):3290–3298. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-12-1292
Nair U, Yen WL, Mari M, Cao Y, Xie Z, Baba M, Reggiori F, Klionsky DJ (2012) A role for Atg8–PE deconjugation in autophagosome biogenesis. Autophagy 8(5):780–793. doi:10.4161/auto.19385
Itakura E, Kishi-Itakura C, Mizushima N (2012) The hairpin-type tail-anchored SNARE syntaxin 17 targets to autophagosomes for fusion with endosomes/lysosomes. Cell 151(6):1256–1269. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.001
Diao J, Liu R, Rong Y, Zhao M, Zhang J, Lai Y, Zhou Q, Wilz LM, Li J, Vivona S, Pfuetzner RA, Brunger AT, Zhong Q (2015) ATG14 promotes membrane tethering and fusion of autophagosomes to endolysosomes. Nature 520(7548):563–566
Hamasaki M, Furuta N, Matsuda A, Nezu A, Yamamoto A, Fujita N, Oomori H, Noda T, Haraguchi T, Hiraoka Y, Amano A, Yoshimori T (2013) Autophagosomes form at ER-mitochondria contact sites. Nature 495(7441):389–393
Guo B, Liang Q, Li L, Hu Z, Wu F, Zhang P, Ma Y, Zhao B, Kovacs AL, Zhang Z, Feng D, Chen S, Zhang H (2014) O-GlcNAc-modification of SNAP-29 regulates autophagosome maturation. Nat Cell Biol 16(12):1215–1226
Wang Z, Miao G, Xue X, Guo X, Yuan C, Zhang G, Chen Y, Feng D, Hu J, Zhang H (2016) The Vici syndrome protein EPG5 is a Rab7 effector that determines the fusion specificity of autophagosomes with late endosomes/lysosomes. Mol Cell 63(5):781–795
McEwan DG, Popovic D, Gubas A, Terawaki S, Suzuki H, Stadel D, Coxon FP, Miranda de Stegmann D, Bhogaraju S, Maddi K, Kirchof A, Gatti E, Helfrich MH, Wakatsuki S, Behrends C, Pierre P, Dikic I (2015) PLEKHM1 regulates autophagosome-lysosome fusion through HOPS complex and LC3/GABARAP proteins. Mol Cell 57(1):39–54
Wijdeven RH, Janssen H, Nahidiazar L, Janssen L, Jalink K, Berlin I, Neefjes J (2016) Cholesterol and ORP1L-mediated ER contact sites control autophagosome transport and fusion with the endocytic pathway. Nat Commun 7:11808
Chen D, Fan W, Lu Y, Ding X, Chen S, Zhong Q (2012) A mammalian autophagosome maturation mechanism mediated by TECPR1 and the Atg12–Atg5 conjugate. Mol Cell 45(5):629–641. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.12.036
Hasegawa J, Iwamoto R, Otomo T, Nezu A, Hamasaki M, Yoshimori T (2016) Autophagosome-lysosome fusion in neurons requires INPP5E, a protein associated with Joubert syndrome. EMBO J 35(17):1853–1867
Bonten EJ, Annunziata I, d’Azzo A (2014) Lysosomal multienzyme complex: pros and cons of working together. Cell Mol Life Sci 71(11):2017–2032. doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1538-3
Appelqvist H, Waster P, Kagedal K, Ollinger K (2013) The lysosome: from waste bag to potential therapeutic target. J Mol Cell Biol 5(4):214–226. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjt022
Teter SA, Eggerton KP, Scott SV, Kim J, Fischer AM, Klionsky DJ (2001) Degradation of lipid vesicles in the yeast vacuole requires function of Cvt17, a putative lipase. J Biol Chem 276(3):2083–2087. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000739200
Epple UD, Suriapranata I, Eskelinen EL, Thumm M (2001) Aut5/Cvt17p, a putative lipase essential for disintegration of autophagic bodies inside the vacuole. J Bacteriol 183(20):5942–5955. doi:10.1128/JB.183.20.5942-5955.2001
Epple UD, Eskelinen EL, Thumm M (2003) Intravacuolar membrane lysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Does vacuolar targeting of Cvt17/Aut5p affect its function? J Biol Chem 278(10):7810–7821. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209309200
van Zutphen T, Todde V, de Boer R, Kreim M, Hofbauer HF, Wolinski H, Veenhuis M, van der Klei IJ, Kohlwein SD (2014) Lipid droplet autophagy in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell 25(2):290–301. doi:10.1091/mbc.E13-08-0448
Mizushima N, Klionsky DJ (2007) Protein turnover via autophagy: implications for metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 27:19–40. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.27.061406.093749
Suriapranata I, Epple UD, Bernreuther D, Bredschneider M, Sovarasteanu K, Thumm M (2000) The breakdown of autophagic vesicles inside the vacuole depends on Aut4p. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 22):4025–4033
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ (2007) Permeases recycle amino acids resulting from autophagy. Autophagy 3(2):149–150
Yang Z, Huang J, Geng J, Nair U, Klionsky DJ (2006) Atg22 recycles amino acids to link the degradative and recycling functions of autophagy. Mol Biol Cell 17(12):5094–5104. doi:10.1091/mbc.E06-06-0479
Yu L, McPhee CK, Zheng L, Mardones GA, Rong Y, Peng J, Mi N, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Wan F, Hailey DW, Oorschot V, Klumperman J, Baehrecke EH, Lenardo MJ (2010) Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature 465(7300):942–946. doi:10.1038/nature09076
Rong Y, Liu M, Ma L, Du W, Zhang H, Tian Y, Cao Z, Li Y, Ren H, Zhang C, Li L, Chen S, Xi J, Yu L (2012) Clathrin and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate regulate autophagic lysosome reformation. Nat Cell Biol 14(9):924–934. doi:10.1038/ncb2557
Chen Y, Yu L (2013) Autophagic lysosome reformation. Exp Cell Res 319(2):142–146. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.09.004
Braulke T, Bonifacino JS (2009) Sorting of lysosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793(4):605–614. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.10.016
Rong Y, McPhee CK, Deng S, Huang L, Chen L, Liu M, Tracy K, Baehrecke EH, Yu L, Lenardo MJ (2011) Spinster is required for autophagic lysosome reformation and mTOR reactivation following starvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(19):7826–7831. doi:10.1073/pnas.1013800108
Acknowledgements
We thank Jiangsu collaborative innovation center of meat production and processing for technical assistance and J.D. Hulleman from UT Southwestern Medical Center for reading the manuscript. The work was supported by grants to R.L. from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31771532), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant no. 2017YFD0400200), the Jiangsu Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (Grant no. SBK2017010325), the Jiangsu Natural Science Funds (Grant no. SBK2016043530), the fundamental research funds for the central universities (Grant no. 0806j0498), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31771529) to R.Y.G. Funding was provided by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant no. BK20160729).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, X., Feng, W., Rong, Y. et al. Anatomy of autophagy: from the beginning to the end. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 75, 815–831 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2657-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2657-z