Abstract
Objective
In vitro but not in vivo evidence indicates that blockade of NF-κB is effective in reducing inflammation and production of IL-8. We hypothesized that the failure of in vitro experiments to predict in vivo outcome was due to the use of short time periods of observation and the use of single cytokines to stimulate NF-κB.
Methods
HEK cells with a NF-κB reporter gene or CaCo-2 cells were stimulated with CM (IL-1-β; TNF-α, and IFN-γ) or individual cytokines in the presence and absence of NF-κB inhibitors, a STAT1 inhibitor, and/or a p38 MAPK inhibitor for periods up to 24 h. NF-κB activation, IL-8 production, and nitric oxide production were measured.
Results
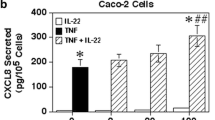
CM-induced IL-8 production in HEK cells was additive to synergistic. CM enhanced production of IL-8 at 24 h but not 4 h was independent of NF-κB. The p38 inhibitor SB203580 and the STAT1 inhibitor EGCG blocked CM-induced IL-8 production at both early and late time periods. The NF-κB inhibitors PDTC and BAY11-7082 were found to increase CM-stimulated IL-8 production in Caco-2 cells at 24 h.
Conclusions
Our data suggest an effective strategy to reduce IL-8 production is to block p38 or STAT1 rather than NF-κB.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jijon HB, Panenka WJ, Madsen KL, Parsons HG. MAP kinases contribute to IL-8 secretion by intestinal epithelial cells via a posttranscriptional mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;283:C31–41.
Parhar K, Ray A, Steinbrecher U, Nelson C, Salh B. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates interleukin-1beta-induced IL-8 expression via an effect on the IL-8 promoter in intestinal epithelial cells. Immunology. 2003;108:502–12.
Akhtar M, Watson JL, Nazli A, McKay DM. Bacterial DNA evokes epithelial IL-8 production by a MAPK-dependent NF-kappaB-independent pathway. FASEB J. 2003;17:1319–21.
Kim JM, Cho SJ, Oh YK, Jung HY, Kim YJ, Kim N. Nuclear factor-kappa B activation pathway in intestinal epithelial cells is a major regulator of chemokine gene expression and neutrophil migration induced by Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002;130:59–66.
Otte JM, Podolsky DK. Functional modulation of enterocytes by gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G613–26.
Harada A, Sekido N, Akahoshi T, Wada T, Mukaida N, Matsushima K. Essential involvement of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in acute inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 1994;56:559–64.
Bao Z, Ye Q, Gong W, Xiang Y, Wan H. Humanized monoclonal antibody against the chemokine CXCL-8 (IL-8) effectively prevents acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10:259–63.
Osman MO, Kristensen JU, Jacobsen NO, Lausten SB, Deleuran B, Deleuran M, Gesser B, Matsushima K, Larsen CG, Jensen SL. A monoclonal anti-interleukin 8 antibody (WS-4) inhibits cytokine response and acute lung injury in experimental severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis in rabbits. Gut. 1998;43:232–9.
Seydel KB, Li E, Zhang Z, Stanley SL Jr. Epithelial cell-initiated inflammation plays a crucial role in early tissue damage in amebic infection of human intestine. Gastoenterology. 1998;115:1446–53.
Sansonetti PJ, Arondel J, Huerre M, Harada A, Matsushima K. Interleukin-8 controls bacterial transepithelial translocation at the cost of epithelial destruction in experimental shigellosis. Infect Immun. 1999;67:1471–80.
Hoffmann E, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Holtmann H, Kracht M. Multiple control of interleukin-8 gene expression. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;72:847–55.
Garat C, Arend WP. Intracellular IL-1Ra type 1 inhibits IL-1-induced IL-6 and IL-8 production in Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells through inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Cytokine. 2003;23:31–40.
Jijon HB, Walker J, Hoentjen F, Diaz H, Ewaschuk J, Jobin C, Madsen KL. Adenosine is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling in human intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Immunol. 2005;237:86–95.
Gadjeva M, Tomczak MF, Zhang M, Wang YY, Dull K, Rogers AB, Erdman SE, Fox JG, Carroll M, Horwitz BH. A role for NF-kappa B subunits p50 and p65 in the inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced shock. J Immunol. 2004;173:5786–93.
Kawamura N, Kubota T, Kawano S, Monden Y, Feldman AM, Tsutsui H, Takeshita A, Sunagawa K. Blockade of NF-kappaB improves cardiac function and survival without affecting inflammation in TNF-alpha-induced cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;66:520–9.
Sousa LP, Lopes F, Silva DM, Tavares LP, Vieira AT, Rezende BM, Carmo AF, Russo RC, Garcia CC, Bonjardim CA, Alessandri AL, Rossi AG, Pinho V, Teixeira MM. PDE4 inhibition drives resolution of neutrophilic inflammation by inducing apoptosis in a PKA-PI3K/Akt-dependent and NF-kappaB-independent manner. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87:895–904.
Munoz C, Pascual-Salcedo D, Castellanos MC, Alfranca A, Aragones J, Vara A, Redondo JM, de Landazuri MO. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate inhibits the production of interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by human endothelial cells in response to inflammatory mediators: modulation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 transcription factors activity. Blood. 1996;88:3482–90.
Wang Q, Guo XL, Wells-Byrum D, Noel G, Pritts TA, Ogle CK. Cytokine-induced epithelial permeability changes are regulated by the activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in cultured Caco-2 cells. Shock. 2008;29:531–7.
Tedeschi E, Menegazzi M, Yao Y, Suzuki H, Forstermann U, Kleinert H. Green tea inhibits human inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression by down-regulating signal transducer and activator of transcription-1alpha activation. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;65:111–20.
Nemeth ZH, Deitch EA, Szabo C, Hasko G. Pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate inhibits NF-kappaB activation and IL-8 production in intestinal epithelial cells. Immunol Lett. 2003;85:41–6.
Ganster RW, Taylor BS, Shao L, Geller DA. Complex regulation of human inducible nitric oxide synthase gene transcription by Stat 1 and NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;8:8638–43.
Sunil Y, Ramadori G, Raddatzc D. Influence of NFkappaB inhibitors on IL-1beta-induced chemokine CXCL8 and -10 expression levels in intestinal epithelial cell lines: glucocorticoid ineffectiveness and paradoxical effect of PDTC. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2010;25:323–33.
Song GY, Chung CS, Chaudry IH, Ayala A. MAPK p38 antagonism as a novel method of inhibiting lymphoid immune suppression in polymicrobial sepsis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001;281:C662–9.
Liu SF, Ye X, Malik AB. In vivo inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B activation prevents inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and systemic hypotension in a rat model of septic shock. J Immunol. 1997;159:3976–83.
Greten FR, Arkan MC, Bollrath J, Hsu LC, Goode J, Miething C, Goktuna SI, Neuenhahn M, Fierer J, Paxian S, Van Rooijen N, Xu Y, O’Cain T, Jaffee BB, Busch DH, Duyster J, Schmid RM, Eckmann L, Karin M. NF-kappaB is a negative regulator of IL-1beta secretion as revealed by genetic and pharmacological inhibition of IKKbeta. Cell. 2007;130:918–31.
Lauzurica P, Martinez–Martinez S, Marazuela M, Gomez del Arco P, Martinez C, Sanchez-Madrid F, Redondo JM. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate protects mice from lethal shock induced by LPS or TNF-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:1890–900.
Chavez AM, Menconi MJ, Hodin RA, Fink MP. Cytokine-induced intestinal epithelial hyperpermeability: role of nitric oxide. Crit Care Med. 1999;27:2246–51.
Grandjean-Laquerriere A, Gangloff SC, Le Naour R, Trentesaux C, Hornebeck W, Guenounou M. Relative contribution of NF-kappaB and AP-1 in the modulation by curcumin and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate of the UVB-induced cytokine expression by keratinocytes. Cytokine. 2002;18:168–77.
Netsch MI, Gutmann H, Aydogan C, Drewe J. Green tea extract induces interleukin-8 (IL-8) mRNA and protein expression but specifically inhibits IL-8 secretion in caco-2 cells. Planta Med. 2006;72:697–702.
Porath D, Riegger C, Drewe J, Schwager J. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate impairs chemokine production in human colon epithelial cell lines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;315:1172–80.
Magro F, Fraga S, Ribeiro T, Soares-da-Silva P. Intestinal Na + -K + -ATPase activity and molecular events downstream of interferon-gamma receptor stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 2004;142:1281–92.
Intra J, Kuo SM. Physiological levels of tea catechins increase cellular lipid antioxidant activity of vitamin C and vitamin E in human intestinal caco-2 cells. Chem Biol Interact. 2007;169:91–9.
Navarro-Peran E, Cabezas-Herrera J, Sanchez-del-Campo L, Garcia-Canovas F, Rodriguez-Lopez JN. The anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties of epigallocatechin-3-gallate are mediated by folate cycle disruption, adenosine release and NF-kappaB suppression. Inflamm Res. 2008;57:472–8.
Kim SJ, Jeong HJ, Lee KM, Myung NY, An NH, Yang WM, Park SK, Lee HJ, Hong SH, Kim HM, Um JY. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses NF-kappaB activation and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and JNK in human astrocytoma U373MG cells. J Nutr Biochem. 2007;18:587–96.
Edelson MB, Bagwell CE, Rozycki HJ. Circulating pro- and counterinflammatory cytokine levels and severity in necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics. 1999;103:766–71.
Daig R, Andus T, Aschenbrenner E, Falk W, Scholmerich J, Gross V. Increased interleukin 8 expression in the colon mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1996;38:216–22.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shriners of North American Grant 8903.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Liwu Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Huber, N., Noel, G. et al. NF-κΒ inhibition is ineffective in blocking cytokine-induced IL-8 production but P38 and STAT1 inhibitors are effective. Inflamm. Res. 61, 977–985 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-012-0490-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-012-0490-2