Abstract
Objective and Design: An unspecific human in vivo model of dermal pain and inflammation was developed by means of limited, localised and controlled cell damage.
Subjects: Twelve participants were recruited.
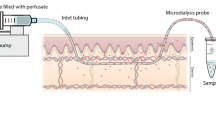
Treatment: Dermal microdialysis was used to deliver randomised and single blinded aqueous sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) at concentrations of 0.01%, 0.1% and 0.5% w/v to the volar forearm.
Methods: Nociceptive responses were recorded on a numerical scale, vasodilatation was assessed by laser Doppler scanning and sampled tissue fluid was analysed for PGE2 by ELISA.
Results: Saline control and 0.01% SDS did not differ in their ability to cause vasodilatation, flare reaction or pain. In contrast, SDS (0.1 and 0.5%) evoked a significant increase of blood flow (p<0.005), a widespread reddening (p<0.01), and stinging-burning pain (p<0.005). PGE2 concentration in the dialysate did not change during 0.01% SDS perfusion (p>0.9), but increased significantly following the stimulation with 0.1% and 0.5% SDS (20 to 30-fold). No significant differences of released PGE2 levels were determined between 0.1% and 0.5% SDS stimulation (p>0.05).
Conclusions: We demonstrated that localised intradermal administration of SDS induces a limited pain and inflammatory response in humans. Excitation of nociceptors was accompanied by a massive PGE2 release. Employing this experimental model, the relative contribution of endogenous mediators to induce, maintain or facilitate pain and vasodilatation can be investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 30 April 2003; returned for revision 11 November 2003; accepted by G. Geisslinger 2 December 2003.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fairweather, I., McGlone, F., Reilly, D. et al. Controlled dermal cell damage as human in vivo model for localised pain and inflammation. Inflamm. res. 53, 118–123 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-003-1234-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-003-1234-0