Abstract
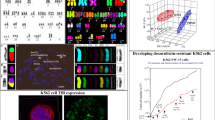
Hydroxyurea, a differentiation-inducing agent of human erythroleukemia K562 cells, is commonly used to treat some types of leukemia. However, the mechanism for its therapeutic effect is not clearly understood yet. In this study, we have observed an interesting effect of hydroxyurea on tumor cells: an induction of senescence-like changes. Human erythroleukemia K562 cells, when treated with hydroxyurea for 7 days or more, underwent a change into phenotypically senescent cells together with a reduction of hemoglobin generation, a differentiation marker. The hydroxyurea-treated cells showed positive senescence associated-β-galactosidase staining, a senescence index, and the accumulation of cdk (cyclin dependent kinase) inhibitors, such as p16INK4a, p21Waf1, and p27Kip1, implicated in cellular senescence. Nonetheless, these changes were not accompanied by DNA fragmentation. Taken together, we summarize that the long-term treatment of cancer cells with hydroxyurea can induce cellular senescence different from differentiation or programmed cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 February 2000 / Accepted: 6 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JI., Jeong, JS., Han, JY. et al. Hydroxyurea induces a senescence-like change of K562 human erythroleukemia cell. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126, 455–460 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00021281
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00021281