Abstract
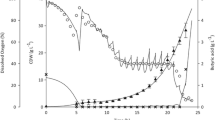
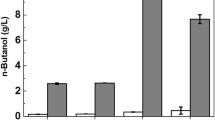
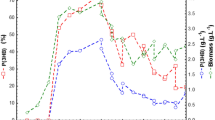
The effect of pH (between 4.4 and 6.6) on butyrate uptake by the mutant strain of Clostridium acetobutylicum was studied using the fermentation broth from fermentor-2 (solventogenic stage) of a two-fermentor continuous system. Low pH (< 4.6) adversely affected the overall metabolic activity as observed by low solvent production and carbohydrate consumption. Uptake of 4.0 ± 0.5 g l−1 butyrate, under batch incubation at 30 °C, was not inhibited at pH > 5.2, however, at pH < 5.2, a marked inhibition in butyrate uptake was noticed. A higher pH (e.g. pH 5.4) was required for the uptake of elevated concentration of externally added butyrate at 8.5 ± 1.0 g l−1. Batch incubation at relatively higher temperatures (35° and 37 °C) indicated a similar trend i.e., a pH of >5.5 was required for uptake of >8 g l−1 butyrate. Optimization studies for butyrate uptake by C. acetobutylicum suggested a direct correlation between minimum pH and butyrate concentration or temperature. The role of undissociated butyric acid appears to be critical in regulation of butyrate uptake.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 December 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soni, B., Jain, M. Influence of pH on butyrate uptake and solvent fermentation by a mutant strain of Clostridiumacetobutylicum . Bioprocess Engineering 17, 329–334 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008968
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008968