Abstract
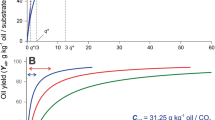
The solubility of soy lecithin lipids in supercritical CO2 was measured at pressures of 120, 200 and 280 bar and at temperatures of 40, 50 and 60 °C. The effects of temperature and pressure on the solubility of total lipids were studied by response surface methodology. The response surface equation to predict the solubility of total lipids in the above range of pressure and temperature is: Y=–3.237+0.0431* P–7.3×10–5 P 2–0.00011 P*T where Y is the total lipid solubility in g/kg CO2, P is the pressure in bar and T is the temperature in °C. The total lipids solubility increased with pressure at constant temperature, but decreased with increasing temperature. The total lipids consisted of a very small phospholipid content compared to neutral lipids and glycolipids at all the pressures and temperatures studied. Optimum search indicated a maximum solubility of total lipids of 1.829 g/kg CO2 at 263 bar and 40 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Began, G., Manohar, B., Udaya Sankar, K. et al. Response surfaces for solubility of crude soylecithin lipid in super critical carbon dioxide. Eur Food Res Technol 210, 209–212 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005513
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005513