Abstract
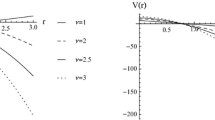
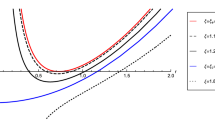
The collision of two particles in the background of a Sen black hole is studied. With the equations of motion of the particles, the center-of-mass energy is investigated when the collision takes place at the horizon of a Sen black hole. For an extremal Sen black hole, we find that the center-of-mass energy will be arbitrarily high with two conditions: (1) spin a ≠ 0 and (2) one of the colliding particles has the critical angular momentum l c = 2. For a nonextremal Sen black hole, we show that, in order to obtain an unlimited center-of-mass energy, one of the colliding particles should have the critical angular momentum l c ′ = 2r +/a (r + is the radius of the outer horizon for a nonextremal black hole). However, a particle with the angular momentum l = l c ′ could not approach the black hole from outside of the horizon through free fall, which implies that the collision with arbitrarily high center-of-mass energy could not take place. Thus, there is an upper bound of the center-of-mass energy for the nonextremal black hole. We also obtain the maximal center-of-mass energy for a near-extremal black hole and the result implies that the Planck-scale energy is hard to be approached. Furthermore, we also consider the back-reaction effects. The result shows that, neglecting the gravitational radiation, it has a weak effect on the center-of-mass energy. However, we argue that the maximum allowed center-of-mass energy will be greatly reduced to below the Planck-scale when the gravitational radiation is included.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bañados, J. Silk and S.M. West, Kerr Black Holes as Particle Accelerators to Arbitrarily High Energy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 (2009) 111102 [arXiv:0909.0169] [SPIRES].
E. Berti, V. Cardoso, L. Gualtieri, F. Pretorius and U. Sperhake, Comment on “Kerr Black Holes as Particle Accelerators to Arbitrarily High Energy”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 (2009) 239001 [arXiv:0911.2243] [SPIRES].
T. Jacobson and T.P. Sotiriou, Spinning Black Holes as Particle Accelerators, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 (2010) 021101 [arXiv:0911.3363] [SPIRES].
K.S. Thorne, Disk accretion onto a black hole. 2. Evolution of the hole, Astrophys. J. 191 (1974) 507 [SPIRES].
K. Lake, Particle Accelerators inside Spinning Black Holes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 (2010) 211102 [Erratum ibid. 104 (2010) 259903] [arXiv:1001.5463] [SPIRES].
A.A. Grib and Y.V. Pavlov, On Particle Collisions in the Gravitational Field of Black Hole, arXiv:1001.0756 [SPIRES].
A.A. Grib and Y.V. Pavlov, On the collisions between particles in the vicinity of rotating black holes, JETP Lett. 92 (2010) 125.
A.A. Grib and Y.V. Pavlov, On particle collisions near Kerr’s black holes, arXiv:1007.3222 [SPIRES].
O.B. Zaslavskii, Acceleration of particles as universal property of rotating black holes, Phys. Rev. D 82 (2010) 083004 [arXiv:1007.3678] [SPIRES].
S.-W. Wei, Y.-X. Liu, H. Guo and C.-E. Fu, Charged Spinning Black Holes as Particle Accelerators, Phys. Rev. D 82 (2010) 103005 [arXiv:1006.1056] [SPIRES].
A.A. Grib and Y.V. Pavlov, On particles collisions near rotating black holes, arXiv:1010.2052 [SPIRES].
A. Sen, Rotating charged black hole solution in heterotic string theory, Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 (1992) 1006 [hep-th/9204046] [SPIRES].
P.A. Blaga and C. Blaga, Bounded radial geodesics around a Kerr-Sen black hole, Class. Quant. Grav. 18 (2001) 3893 [SPIRES].
K. Hioki and U. Miyamoto, Hidden symmetries, null geodesics and photon capture in the Sen black hole, Phys. Rev. D 78 (2008) 044007 [arXiv:0805.3146] [SPIRES].
T. Houri, D. Kubiznak, C.M. Warnick and Y. Yasui, Generalized hidden symmetries and the Kerr-Sen black hole, JHEP 07 (2010) 055 [arXiv:1004.1032] [SPIRES].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ArXiv ePrint: 1007.4333
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, SW., Liu, YX., Li, HT. et al. Particle collisions on stringy black hole background. J. High Energ. Phys. 2010, 66 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP12(2010)066
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP12(2010)066