Abstract
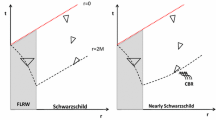
Usually, Hawking radiation is derived assuming (i) that a future eternal event horizon forms, and (ii) that the subsequent exterior geometry is static. However, one may be interested in either considering quasi-black holes (objects in an ever-lasting state of approach to horizon formation, but never quite forming one), where (i) fails, or, following the evolution of a black hole during evaporation, where (ii) fails. We shall verify that as long as one has an approximately exponential relation between the affine parameters on the null generators of past and future null infinity, then subject to a suitable adiabatic condition being satisfied, a Planck-distributed flux of Hawking-like radiation will occur. This happens both for the case of an evaporating black hole, as well as for the more dramatic case of a collapsing object for which no horizon has yet formed (or even will ever form). In this article we shall cast the previous statement in a more precise and quantitative form, and subsequently provide several explicit calculations to show how the time-dependent Bogoliubov coefficients can be calculated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.W. Hawking, Black hole explosions, Nature 248 (1974) 30 [SPIRES].
S.W. Hawking, Particle creation by black holes, Commun. Math. Phys. 43 (1975) 199 [Erratum ibid. 46 (1976) 206] [SPIRES].
W.G. Unruh, Notes on black hole evaporation, Phys. Rev. D 14 (1976) 870 [SPIRES].
F.J. Tipler, Do black holes really evaporate thermally?, Phys. Rev. Lett. 45 (1980) 949 [SPIRES].
P. Hajicek and W. Israel, What, no black hole evaporation?, Phys. Lett. A 80 (1980) 9.
J.M. Bardeen, Black holes do evaporate thermally, Phys. Rev. Lett. 46 (1981) 382 [SPIRES].
J.W. York Jr., Dynamical origin of black hole radiance, Phys. Rev. D 28 (1983) 2929 [SPIRES].
P. Hajicek, Origin of Hawking radiation, Phys. Rev. D 36 (1987) 1065 [SPIRES].
P.G. Grove, Observations on particle creation by static gravitational fields, Class. Quant. Grav. 7 (1990) 1353 [SPIRES].
M. Visser, Hawking radiation without black hole entropy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 (1998) 3436 [gr-qc/9712016] [SPIRES].
M. Visser, Acoustic black holes: horizons, ergospheres and Hawking radiation, Class. Quant. Grav. 15 (1998) 1767 [gr-qc/9712010] [SPIRES].
M. Visser, Essential and inessential features of Hawking radiation, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 12 (2003) 649 [hep-th/0106111] [SPIRES].
J. Lindesay and P. Sheldon, Penrose diagram for a transient black hole, Class. Quant. Grav. 27 (2010) 215015 [arXiv:1005.4449] [SPIRES].
G.E. Volovik, Simulation of Panlevé-Gullstrand black hole in thin 3 He-A film, Pisma ZhETF 69 (1999) 662 [JETP Lett. 69 (1999) 705] [gr-qc/9901077] [SPIRES].
M.K. Parikh and F. Wilczek, Hawking radiation as tunneling, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 (2000) 5042 [hep-th/9907001] [SPIRES].
M.K. Parikh, Energy conservation and Hawking radiation, hep-th/0402166 [SPIRES].
M.K. Parikh, A secret tunnel through the horizon, Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 13 (2004) 2351 [hep-th/0405160] [SPIRES].
S. Shankaranarayanan, T. Padmanabhan and K. Srinivasan, Hawking radiation in different coordinate settings: complex paths approach, Class. Quant. Grav. 19 (2002) 2671 [gr-qc/0010042] [SPIRES].
M. Angheben, M. Nadalini, L. Vanzo and S. Zerbini, Hawking radiation as tunneling for extremal and rotating black holes, JHEP 05 (2005) 014 [hep-th/0503081] [SPIRES].
A.J.M. Medved and E.C. Vagenas, On Hawking radiation as tunneling with back-reaction, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 20 (2005) 2449 [gr-qc/0504113] [SPIRES].
M. Arzano, A.J.M. Medved and E.C. Vagenas, Hawking radiation as tunneling through the quantum horizon, JHEP 09 (2005) 037 [hep-th/0505266] [SPIRES].
S.P. Robinson and F. Wilczek, A relationship between Hawking radiation and gravitational anomalies, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 (2005) 011303 [gr-qc/0502074] [SPIRES].
T. Clifton, Properties of black hole radiation from tunnelling, Class. Quant. Grav. 25 (2008) 175022 [arXiv:0804.2635] [SPIRES].
R. Banerjee and B.R. Majhi, Hawking black body spectrum from tunneling mechanism, Phys. Lett. B 675 (2009) 243 [arXiv:0903.0250] [SPIRES].
T. Padmanabhan, Gravity and the thermodynamics of horizons, Phys. Rept. 406 (2005) 49 [gr-qc/0311036] [SPIRES].
S. Hossenfelder, D.J. Schwarz and W. Greiner, Particle production in time-dependent gravitational fields: the expanding mass shell, Class. Quant. Grav. 20 (2003) 2337 [gr-qc/0210110] [SPIRES].
M. Visser, Dirty black holes: thermodynamics and horizon structure, Phys. Rev. D 46 (1992) 2445 [hep-th/9203057] [SPIRES].
T.A. Roman and P.G. Bergmann, Stellar collapse without singularities?, Phys. Rev. D 28 (1983) 1265 [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, S. Liberati, S. Sonego and M. Visser, Quasi-particle creation by analogue black holes, Class. Quant. Grav. 23 (2006) 5341 [gr-qc/0604058] [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, S. Liberati, S. Sonego and M. Visser, Hawking-like radiation does not require a trapped region, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 (2006) 171301 [gr-qc/0607008] [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, S. Liberati, S. Sonego and M. Visser, Fate of gravitational collapse in semiclassical gravity, Phys. Rev. D 77 (2008) 044032 [arXiv:0712.1130] [SPIRES].
M. Visser, C. Barceló, S. Liberati and S. Sonego, Small, dark and heavy: but is it a black hole?, PoS(BHs, GR and Strings)010 [arXiv:0902.0346] [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, S. Liberati, S. Sonego and M. Visser, Revisiting the semiclassical gravity scenario for gravitational collapse, AIP Conf. Proc. 1122 (2009) 99 [arXiv:0909.4157] [SPIRES].
S.W. Hawking, abstract of The information paradox for black holes: “The way the information gets out seems to be that a true event horizon never forms, just an apparent horizon.”, talk given at GR17, Dublin, Ireland (2004).
S.W. Hawking, Information loss in black holes, Phys. Rev. D 72 (2005) 084013 [hep-th/0507171] [SPIRES].
A. Ashtekar and M. Bojowald, Black hole evaporation: a paradigm, Class. Quant. Grav. 22 (2005) 3349 [gr-qc/0504029] [SPIRES].
S.A. Hayward, The disinformation problem for black holes, gr-qc/0504037, gr-qc/0504038 [SPIRES].
S.A. Hayward, Formation and evaporation of regular black holes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 (2006) 031103 [gr-qc/0506126] [SPIRES].
M. Visser, Acoustic propagation in fluids: an unexpected example of Lorentzian geometry, gr-qc/9311028 [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, S. Liberati and M. Visser, Analogue gravity, Living Rev. Rel. 8 (2005) 12 [gr-qc/0505065] [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, S. Liberati, S. Sonego and M. Visser, Minimal conditions for the existence of a Hawking-like flux, arXiv:1011.5593 [SPIRES].
B.L. Hu, Hawking-Unruh thermal radiance as relativistic exponential scaling of quantum noise, in Thermal field theory and applications, Y.X. Gui, F.C. Khanna and Z.B. Su eds., World Scientific, Singapore (1996), pg. 249–260 [gr-qc/9606073] [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, S. Liberati, S. Sonego and M. Visser, Causal structure of acoustic spacetimes, New J. Phys. 6 (2004) 186 [gr-qc/0408022] [SPIRES].
J. Macher and R. Parentani, Black-hole radiation in Bose-Einstein condensates, Phys. Rev. A 80 (2009) 043601 [arXiv:0905.3634] [SPIRES].
R. Brout, S. Massar, R. Parentani and P. Spindel, Hawking radiation without transplanckian frequencies, Phys. Rev. D 52 (1995) 4559 [hep-th/9506121] [SPIRES].
R. Brout, S. Massar, R. Parentani and P. Spindel, A primer for black hole quantum physics, Phys. Rept. 260 (1995) 329 [arXiv:0710.4345] [SPIRES].
J.D. Barrow, Sudden future singularities, Class. Quant. Grav. 21 (2004) L79 [gr-qc/0403084] [SPIRES].
J.D. Barrow, More general sudden singularities, Class. Quant. Grav. 21 (2004) 5619 [gr-qc/0409062] [SPIRES].
C. Cattoën and M. Visser, Necessary and sufficient conditions for big bangs, bounces, crunches, rips, sudden singularities and extremality events, Class. Quant. Grav. 22 (2005) 4913 [gr-qc/0508045] [SPIRES].
C.G. Callan Jr., S.B. Giddings, J.A. Harvey and A. Strominger, Evanescent black holes, Phys. Rev. D 45 (1992) 1005 [hep-th/9111056] [SPIRES].
S.W. Hawking and J.M. Stewart, Naked and thunderbolt singularities in black hole evaporation, Nucl. Phys. B 400 (1993) 393 [hep-th/9207105] [SPIRES].
N.D. Birrell and P.C.W. Davies, Quantum fields in curved space, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K. (1982) [SPIRES].
C. Barceló, L.J. Garay and G. Jannes, Sensitivity of Hawking radiation to superluminal dispersion relations, Phys. Rev. D 79 (2009) 024016 [arXiv:0807.4147] [SPIRES].
R. Schützhold and W.G. Unruh, On the origin of the particles in black hole evaporation, Phys. Rev. D 78 (2008) 041504 [arXiv:0804.1686] [SPIRES].
W.G. Unruh, Where are the particles created in black hole evaporation?, PoS(QG-Ph)039 [SPIRES].
A.B. Nielsen and M. Visser, Production and decay of evolving horizons, Class. Quant. Grav. 23 (2006) 4637 [gr-qc/0510083] [SPIRES].
G. Abreu and M. Visser, Kodama time: geometrically preferred foliations of spherically symmetric spacetimes, Phys. Rev. D 82 (2010) 044027 [arXiv:1004.1456] [SPIRES].
G. Abreu and M. Visser, Tolman mass, generalized surface gravity, and entropy bounds, Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 (2010) 041302 [arXiv:1005.1132] [SPIRES].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ArXiv ePrint: 1011.5911
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barceló, C., Liberati, S., Sonego, S. et al. Hawking-like radiation from evolving black holes and compact horizonless objects. J. High Energ. Phys. 2011, 3 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP02(2011)003
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP02(2011)003