Abstract
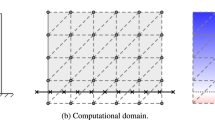
An efficient multigrid fictitious boundary method (MFBM) for the detailed simulation of solid-liquid flows with large number of moving particles is presented. The MFBM is based on a multigrid FEM background grid which covers the whole computational domain and can be chosen independently from the particles of arbitrary shape, size and number. An obvious advantage of the MFBM is that it is able to efficiently treat the interaction between the fluid and the moving rigid particles, especially a fixed multigrid mesh is allowed to be used and there is no need to remesh. Two examples of numerical simulations of three big disks plunging into 2000 small particles as well as sedimentation of 5,000 particles in a cavity are provided to show that the presented method is potentially powerful to simulate real particulate flows with large number of moving particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, H.H., Joseph, D.D. and Crochet, M.J.: Direct simulation of fluid particle motions, Theor. Comp. Fluid Dyn. 3, (1992), 285–306
Hu, H.H., Patankar, N.A. and Zhu, M.Y.: Direct numerical simulations of fluid-solid systems using the arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian techniques, J. Comput. Phys., 169, (2001), 427
Maury, B.: Characteristics ALE method for the unsteady 3D Navier-Stokes equations with a free surface, Int. J. of Comput. Fluid Dynamics, 6, (1996), 175–188
Glowinski, R., Pan, T.W., Hesla, T.I., Joseph, D.D. and Periaux, J.: A fictitious domain approach to the direct numerical simulation of incompressible viscous flow past moving rigid bodies: Application to particulate flow, J. Comput. Phy., 169, (2001), 363–426
Glowinski, R.: Numerical methods for fluids (Part 3), Handbook of numerical analysis, Volume IX, Ciarlet, P.G and Lions, J.L., Editors, North-Holland, (2003)
Wan, D.C. and Turek, S.: Direct Numerical Simulation of Particulate Flow via Multigrid FEM Techniques and the Fictitious Boundary Method, International Journal for Numerical Method in Fluids, in press. Currently available at http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/jissue/108061200 DOI: 10.1002/fld.1129
Wan, D.C., Turek, S. and Liudmila S. Rivkind: An Efficient Multigrid FEM Solution Technique for Incompressible Flow with Moving Rigid Bodies, Numerical Mathematics and Advanced Applications, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, (2004), 844–853.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, D., Turek, S. Modeling of liquid-solid flows with large number of moving particles by multigrid fictitious boundary method. J Hydrodyn 18 (Suppl 1), 93–100 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03400430
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03400430