Abstract
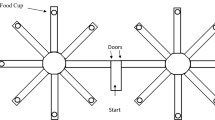
Pigeons were presented with a radial-arm-maze analog task involving five response keys in one of four spatial arrangements. Two of the arrangements involved two-dimensional key displays that differed in degree of spatial separation (large display, Group L, vs. small display, Group S). The other two arrangements involved one-dimensional key displays in either a vertical (Group V) or a horizontal (Group H) array. Acquisition was faster for Groups L and S than for Groups V and H, however, the spatial separation for Group L did not further facilitate performance relative to Group S. Groups H and V performed poorly on this task. When delays were interpolated at different points in the trial, Group L made fewer errors when interrupted early and late in the trial, than when interrupted in the middle of the trial. This result suggests that pigeons in Group L used retrospective coding for choices made early in the trial and prospective coding for choices yet to be made late in the trial. Groups H and V showed flat, point-of-delay-interpolation error functions, a finding consistent with their poor overall performance. Half the birds in Group S performed similarly to Group L birds; the other half performed similarly to birds in Groups H and V.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BEATTY, W. W., & SHAVALIA, D. A. (1980). Spatial memory in rats: Time course of working memory and effect of anesthetics. Behavioral and Neural Biology, 28, 454–462.
BROWN, M. F. (1990). The effects of maze-arm length on performance in the radial-arm maze. Animal Learning and Behavior, 18, 13–22.
BROWN, M. F., WHEELER, E. A., & RILEY, D. A. (1989). Evidence for a shift in the choice criterion of rats in a 12-arm radial maze. Animal Learning and Behavior, 17, 12–20.
COOK, R. G., BROWN, M. F., & RILEY, D. A. (1985). Flexible memory processing by rats: Use of prospective and retrospective information in the radial maze. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 11, 453–469.
CORBALLIS, M. C., & BEALE, I. L. (1976). The psychology of left and riqht. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
FARRELL, W. S., Jr. (1979). Coding left and right. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 5, 42–51.
HONIG, W. K., & THOMPSON, R. K. R. (1982). Retrospective and prospective processing in animal working memory. In G. H. Bower (Ed.), The psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 16, pp. 239–283). New York: Academie Press.
MAKI, R. H., GRANDY, C. A., & HAUGE, G. (1979). Why is telling right from left more difficult than telling above from below? Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 5, 52–67.
OLTON, D. S., & SAMUELSON, R. J. (1976). Remembrance of places passed: Spatial memory in rats. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 2, 97–116.
OLTON, D. S., & SCHLOSBERG, P. E. (1978). Food searching strategies in young rats: Win-shift predominates over win-stay. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 92, 609–618.
ROBERTS, W. A. (1972). Spatial separation and visual differentiation of cues as factors influencing short-term memory in the rat. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 78, 284–291.
ROBERTS, W. A., & VAN VELDHUIZEN, N. (1985). Spatial memory in pigeons on the radial arm maze. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 11, 241–260.
ROITBLAT, H. L., THAM, W., & GOLUB, L. (1982). Performance of Betta splendens in a radial arm maze. Animal Learning and Behavior, 10, 108–114.
SPETCH, M. L., & EDWARDS, C. A. (1986). Spatial memory in pigeons (Columba livia) in an open-field feeding environment. Journal of Comparative Psychology, 100, 266–278.
SPETCH, M. L., & HONIG, W. K. (1988). Characteristics of pigeons’ spatial working memory in an open field task. Animal Learning and Behavior, 16, 123–131.
WILKLE, D. M., & KENNEDY, D. (1985). Intrusion of stereotyped responding in pigeon spatial memory tasks. Behavioral Processes, 11, 159–169.
ZENTALL, T. R., STEIRN, J. N., & JACKSON-SMITH, P. (1990). Memory strategies in pigeons’ performance of a radial-arm-maze analog task. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 16, 358–371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by National Science Foundation Grant Rii-8902792 to Janice N. Steirn, by National Science Foundation Grant Bsn-8418275 to Thomas R. Zentall and Peter J. Urcuioli, and by a grant from the University of Kentucky Research Foundation to Thomas R. Zentall. We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Christopher Randall and Karen Roper in conducting this experiment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steirn, J.N., Zentall, T.R. & Sherburne, L.M. Pigeons’ Performances of a Radial-Arm-Maze Analog Task: Effect of Spatial Distinctiveness. Psychol Rec 42, 255–272 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03399600
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03399600