Abstract
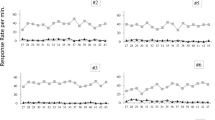
In two experiments, pigeons were given unsignaled food presentations (Group Unsignaled), tone-food pairings (Group Signaled), or no treatment (Group Control). All groups were subsequently given pairings of a white keylight with food. Although no group differences in autoshaping to white appeared, when birds were subsequently given autoshaping with a different colored light using partial reinforcement, either in a different set of chambers (Experiment 1) or in the same set of chambers (Experiment 2), an effect of prior treatment did appear. Birds in Group Unsignaled responded at a lower rate than those in Groups Signaled and Control, which did not differ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAKER, A., & BAKER, P. A. (1985). Does inhibition differ from excitation: Proactive interference, contextual conditioning, and extinction. In R. R. Miller & N. E. Spear (Eds.), Information processing in animals: Conditioned inhibition (pp. 151–183). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
BAKER, A. G., & MERCIER, P. (1989). Attention, retrospective processing, and cognitive representations. In S. B. Klein & R. R. Mowrer (Eds.), Contemporary learning theories: Pavlovian conditioning and the status of traditional learning theory (pp. 85–116). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
BAKER, A. G., MERCIER, P., GABLE, J., & BAKER, P. A. (1981). Contextual conditioning and the Us preexposure effect in conditioned fear. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 7, 109–128.
BALSAM, P. D., & GIBBON, J. (1988). Formation of tone-Us associations does not interfere with the formation of context-US associations in pigeons. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 14, 401–412.
BALSAM, P. D., & SCHWARTZ, A. L. (1981). Rapid contextual conditioning in autoshaping. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 7, 382–393.
DURLACH, P. J. (1983). Effect of signaling intertrial unconditioned stimuli in autoshaping. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 9, 374–389.
GIBBON, J., & BALSAM, P. D. (1981). Spreading association in time. In C. M. Locurto, H. S. Terrace, & J. Gibbon (Eds.), Autoshaping and conditioning theory (pp. 219–253). New York: Academic Press.
GODDARD, M. J., & JENKINS, H. M. (1988). Blocking of a CS-US association by a US-US association. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 14, 177–186.
HINSON, R. E. (1982). Effects of Ucs preexposure on excitatory and inhibitory rabbit eyelid conditioning: An associative effect of conditioned contextual stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 8, 49–61.
JENKINS, H. M., BARNES, R. A., & BARRERA, F. J. (1981). Why autoshaping depends on trial spacing. In C. M. Locurto, H. S. Terrace, & J. Gibbon (Eds.), Autoshaping and conditioning theory (pp. 255–284). New York: Academic Press.
JENKINS, H. M., & SHATTUCK, D. (1981). Contingency in fear conditioning: A reexamination. Bulletin of the Psychonomie Society, 17, 159–162.
RANDICH, A. (1981). The Us preexposzure phenomenon in the conditioned suppression paradigm: A role for conditioned situational stimuli. Learning and Motivation, 12, 321–341.
RANDICH, A., & LOLORDO, V. M. (1979). Associative and nonassociative theories of the US pre-exposure phenomenon: Implications for Pavlovian conditioning. Psychological Bulletin, 86, 523–548.
RESCORLA, R. A. (1984). Signaling intertrial shocks attenuates their negative effect on conditioned suppression. Bulletin of the Psychonomie Society, 22, 225–228.
RESCORLA, R. A., DURLACH, P. J., & GRAU, J. W. (1985). Contextual learning in Pavlovian conditioning. In P. D. Balsam & A. Tomie (Eds.), Context and learning (pp. 23–56). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
RESCORLA, R. A., & WAGNER, A. R. (1972). A theory of Pavlovian conditioning: Variations in the effectiveness of reinforcement and nonreinforcement. In A. H. Black & W. K. Prokasy (Eds.), Classical conditioning II: Current theory and research (pp. 64–99). New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
SCHWARTZ, B., REISBERG, D., & VOLLMECKE, T. (1974). Effects of treadle training on autoshaped keypecking: Learned laziness and learned industriousness or response competition? Bulletin of the Psychonomie Society, 3, 369–372.
TOMIE, A. (1976). Interference with autoshaping by prior context conditioning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 2, 323–334.
TOMIE, A. (1981). The effects of unpredictable food upon the subsequent acquisition of autoshaping: Analysis of the context blocking hypothesis. In C. M. Locurto, H. S. Terrace, & J. Gibbon (Eds.), Autoshaping and conditioning theory (pp. 181–215). New York: Academic Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada grant to Paula J. Durlach. We thank Suzanne Whatmore and Nancy Chiasson for their assistance in conducting this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durlach, P.J., McQuoid, L.M. & Regehr, G. A Latent Effect of Us Preexposure in Autoshaping. Psychol Rec 40, 347–358 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03399545
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03399545