Abstract
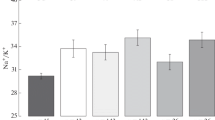
Transport rate constants (kij) describing the kinetics of Na exchanges in isolated rabbit aorta wall were determined by a previously established method involving the use of 22Na as a tracer and digital computer simulation without recourse to ancillary chemical measurements of extracellular space. A three compartment model consisting of (i) extracellular, (ii) intracellular and (iii) subcellular spaces (compartments) was found to describe adequately the kinetics of 22Na. Normative values for intercompartmental kij and extra to intracellular Na ratio were established. It appears that the Na extracellular space in rabbit arterial wall is larger than that in dog or rat arterial wall. Surprisingly, at variance with several tissues of different species (dog, rat, mouse and human tissues), aldosterone did not influence the extra to intracellular distribution of Na. The findings are interpreted in the light of results obtained previously by other workers using entirely unrelated methodologies and suggest that species difference is an important factor to consider when studying effects of aldosterone on tissue electrolyte distribution in the rabbit.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Llaurado J.G. Compartimentai approaches to water and electrolyte distribution. In: Brown J.H.U., Gann D.S. (Eds), Engineering Principles in Physiology. Academic Press, New York, 1973, vol. 2, p. 347.
Török J., Nedergaard O.A., Bevan J.A. Distribution of inulin space in the rabbit thoracic aorta. Experientia 27: 55, 1971.
Harrison R.G., Massaro T.A. Extracellular space of swine aorta measured with [14C] inulin and [14C] sucrose. Amer. J. Physiol. 231: 1806, 1976.
Llaurado J.G. Digital computer simulation as an aid to the study of arterial wall Na kinetics. J. Appl. Physiol. 27: 544, 1969.
Llaurado J.G. Some effects of aldosterone on sodium transport rate constants in isolated arterial wall: studies with computer simulation and analysis. Endocrinology 87: 517, 1970.
Smith G.A., Llaurado J.G. Computer modeling of nonsteady state sodium kinetics in liver. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 21: 433, 1974.
Llaurado J.G., Madden J.A. Sodium kinetics in aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 39: 868, 1975.
Genest J., Lemieux G., Davignon A., Loiw E., Nowaczynski W., Steyermark P. Human arterial hypertension: a state of mild chronic hyperaldosteronism? Science 123: 503, 1956.
Conn J.W., Cohen E.L., Rovner D.R., Nesbit R.M. Normokalemic primary aldosteronism: a detectable cause of curable “essential hypertension”. J.A.M.A. 193: 200, 1965.
Conn J.W., Rovner D.R., Cohen E.L, Nesbit R.M. Normokalemic primary aldosteronism: its masquerade as ‘essential hypertension’ J.A.M.A. 195: 21, 1966.
Kumar D., Hall A.E.D., Nakashima R., Gornall A.G. Studies on aldosterone: II. Hypertension as a cumulative effect of aldosterone administration. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 35: 113, 1957.
Masson G.M.C., Mikasa A., Yasuda H. Experimental vascular disease elicited by aldosterone and renin. Endocrinology 71: 505, 1962.
Hollander W., Kramsch D.M., Chobanian A.V., Melby J.C. Metabolism and distribution of intravenously administered d-aldosterone-1,2-H3 in the arteries, kidneys, and heart of dog. Circ. Res. 18–19: 1–35, 1966.
Bevan J.A., Bevan R.D., P.C., Pegram B.L, R.E., Su C. Analysis of changes in reactivity of rabbit arteries and veins two weeks after induction of hypertension by coarctation of the abdominal aorta. Circ. Res. 37: 183, 1975.
Berman M. Compartmental analysis in kinetics. In: Stacy R.W., Waxman B.D. (Eds.), Computers in Biomedical Research. Academic Press, New York, 1965, vol. 2, p. 173.
Llaurado J.G. Relationship between kinetics of inflow and outflow as the basis of a computer simulation for solving compartmental models: example of electrolyte transfers in cardiovascular tissues. In: Dynamic Studies with Radioisotopes in Medicine, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1971, pp. 13–26.
Gunn R.B., Patlak C.S. The uptake curve in tracer kinetics. Math. Biosci. 6: 19, 1970.
Villamil M.F., Rettori V., Barajas L., Kleeman C.R. Extracellular space and the ionic distribution in the isolated arterial wall. Amer. J. Physiol. 214: 1104, 1968.
Friedman S.M., Friedman C.L. Cell permeability, sodium transport, and the hypertensive process in rat. Circ. Res. 39: 433, 1976.
Altman J., Garay R., Papadimitriou A., Worcel M. Alterations in 22Na fluxes of arterial smooth muscles of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 59: 496P, 1977.
Llaurado J.G., Madden J.A, Meade R.C., Smith G.A. Distribution of thallium-201 injected into rats following stress: imaging, organ to plasma uptake ratios, and myocardial kinetics. J. Nucl. Med. 19: 172, 1978.
Gabella G. Caveolae intracellulars and sarcoplasmic reticulum in smooth muscle. J. Cell. Sci. 8: 601, 1971.
Woodbury D.M., Koch A. Effects of aldosterone and desoxycorticosterone on tissue electrolytes. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 94: 720, 1957.
French, I.W., Manery J.F. The effect of aldosterone on electrolytes in muscle, kidney cortex, and serum. Can. J. Biochem. 42: 1459, 1964.
Losert W., Senft C., Senft G. Extrarenale Wirkungen der Aldosterone und der Spirolactone. Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmak. 248: 450, 1964.
Richards P., Smith K., Metcalfe-Gibson A., Wrong O. Action of d-aldosterone on the electrolyte composition of human cells grown in vitro. Lancet 2: 1099, 1966.
Gross F., Schmidt H. Aldosterone overdosage in the rabbit. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh) 28: 467, 1958.
Dawborn J.K., Ross E.J. The effect of prolonged administration of aldosterone on sodium and potassium turnover in the rabbit. Clin. Sci. 32: 559, 1967.
Robb C.A., Davis J.O., Johnston C.I., Hartroft P.M. Effects of cortisone on renal sodium excretion in rabbits. Endocrinology 82: 1200, 1968.
Braverman B., Davis J.O. Adrenal steroid secretion in the rabbit: sodium depletion, angiotensin II, and ACTH. Amer. J. Physiol. 225: 1306, 1973.
Williams R.J.P., Wacker W.E.C. Cation balance in biological systems. J.A.M.A. 201: 18, 1967.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Llaurado, J.G., Smith, G.A. Kinetics of sodium in rabbit arterial wall: inability of aldosterone to alter extra to intracellular distribution. J Endocrinol Invest 1, 197–201 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350380
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350380